Blockchain Terminologies
Blockchain Terminologies: In this section, we will learn about a few terminologies used in Blockchain technology. Understanding these terms will help you to learn the blockchain technology in an efficient way.

1. Transaction
A transaction in Blockchain is defined as the unit of a task that is stored in the records. Blockchain represents a ledger. A blockchain transaction is a peer-to-peer transfer of cryptocurrencies in a trustless environment, without the need of an intermediate. Collectively these transactions are known as blocks. These blocks are stored in Blockchain after validation by all the users who participate in the network.
2. Ledger
A ledger can be explained as the continuously growing file that keeps the record of the stored transaction. Blockchain technology also works like a digital ledger that records transactions in sequential manner, where every participant of the network holds a copy.
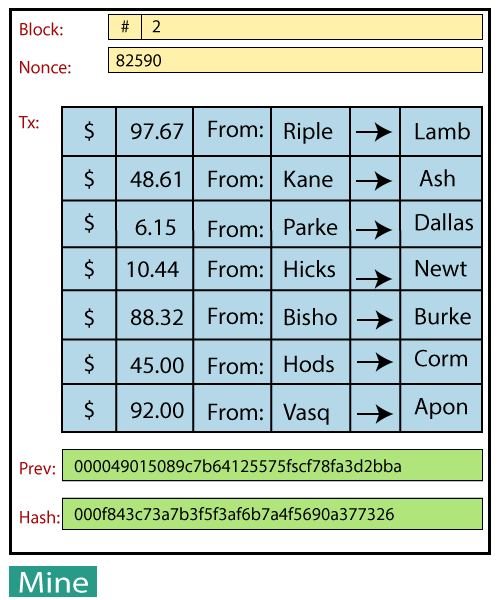
3. Block
A block is a part of the Blockchain that records the recent information. Once a block is executed, it goes into the Blockchain as a permanent database creating a new block. All Blocks are linked with each other like a chain in chronological order. In Blockchain, every block contains a previous hash value of the previous block.
Items inside a block
- Block number or index
- Data(one or more transactions)
- Timestamp
- Hash (index+data+timestamp)
- Previous Hash
A simple block in Blockchain looks like:
4. Genesis Block
The first block of a Blockchain is called Genesis Block and contains 0 as the previous address. It is also known as block zero thatmeans no transaction or data was mined before the genesis block. It is the foundation of Blockchain on which additional blocks are added sequentially to form a chain.
5. Nonce: A random number associated with hash value and difficulty level to create a new hash to solve some puzzles in Proof of work consensus. It is a short form of “number only used once” that is a one-time code can be used only once in a Blockchain. A nonce is a 32-bit abbreviation whose value is adjusted by the miners. A hash value of a block can be less than or equal to the goal of the network.
6. Cryptographic Hash
A cryptographic hash can be defined as a set of random numbers and alphabets that works as an encrypted output of fixed length. A hash value is created based on data present for the particular transaction. Blockchain uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to generate the hash value. A simple hash looks like: 03ac674216f3e15c761ee1a5e255f067953623c8b388b4459e13f978d7c846f4
7. Proof of work (POW)
Proof of work is an algorithm in Blockchain technology which is used to validate transactions and generate a new block for the chain. It is also known as a consensus algorithm. POW (Proof of work) helps miners to compete against each other to mine the transaction for the reward. Currently, the block reward for the Bitcoin network is twenty-five bitcoins for each mined block.
8. Double spent
Double-spending refers to the spending the cryptocurrency multiple times by its owner. It is a state in Blockchain that occurs when the Bitcoin is stolen. The user will send a copy of the currency transaction to make it valid or can delete the transaction details from the block. It is not possible in real currency.
9. Decentralized Distributed Ledger Technology (DDLT)
A distributed ledger is a database that allows the sharing of data with multiple nodes across the Blockchain network. Decentralization of the Blockchain removes the need for a central authority in the network and eliminates the chances of a 'single point of failure.
10. Smart Contract:
A smart contract can be defined as a self-executing computer program. Nick Szabo introduced it in 1994, as a decentralized computation program that controls the transfer of digital assets between different users under certain conditions. Smart contracts are kept on a Blockchain and auto executed when pre-set conditions are satisfied.
11. Blockchain Explorer:
A blockchain explorer is an online browser similar to Mozilla and Google chrome, which allows users to browse and explore information about blockchain technology. All bitcoin and other users depend on blockchain explorer to manage their records and transactions. It allows users to explore the entire Blockchain platform that clients are using.