Blockchains vs Distributed ledger Technology
Blockchains VS Distributed ledger Technology
Blockchain is explored by a wide range of audiences daily. There are lots of terms used for the Blockchain technology; one of them is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). Blockchain and DLT are often used interchangeably but they are not same. Blockchain and DTL share the same objective of the decentralized database.
Blockchain is comparable to a distributed ledger, whereas distributed ledger cannot be seen as Blockchain. We can better understand the differences between both the terms using below descriptions:
What is Distributed ledger technology?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is an online system that records the transactions and their details on multiple nodes at the same time. It can be described as an online software technology that collects information as a record of the ledger. The circulation of the transaction to other nodes occurs automatically on a peer-to-peer server on a regular basis. DLT information and records can be shared either publicly or on a private basis among the participants. It sounds like Blockchain, but these two terms are not the same.
The implementer controls the whole implementation process in DLT. DLT was the main reason behind the first step towards a decentralized blockchain, but it would not necessarily form a chain of blocks.
What is Blockchain?
On the other hand, there is blockchain technology, which is a form of a distributed ledger with a particular technological backend. As we all know, it forms an immutable ledger of records comprising transactions that are controlled by a decentralized server. In blockchain, records are permitted by participant nodes consensus. With blockchain technology, anyone can store entries into a record of a transaction, and a group of users and individual can control how the record of information and transaction is edited and updated.
Though blockchains are possibly more significant than distributed ledgers, still DLT can be useful for the global economy's technological store, especially in cases where it would be unwise to hitch a genuinely decentralized blockchain.
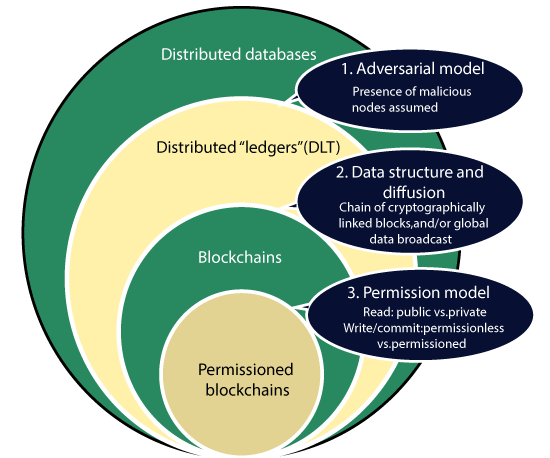
One of the main differences between both the technologies is Blockchain is permissionless, whereas DTL is permissioned. In the case of Blockchain, anyone can participate in the network, but in DTL, only selected participants can access to the network. This decides the size and type of the server as in permissioned type blockchain, the number of participant nodes is smaller.
Blockchain VS DLT
| Blockchain Technology | Distributed Ledger Technology |
| Blockchain is a specific type of the Distributed Ledger Technology, which is open and permissionless. | DLT is a permissioned decentralized database that is shared and managed by various users of the network. |
| Blockchain consists of a series of time-stamped "blocks" that record the concurrent state of the overall Blockchain. It needs to be cryptographically validated in order to allow and form the next block to enter in the chain. | On the other hand, some distributed ledgers do not cryptographically validate the chains of blocks, and it's worth stressing that they still feature cryptographic consensus. |
| There is no provision for KYC (know your customers). | Each client need to have KYC to ensure their identity. |
| There are miners to mine the transaction. It is less secure as every user has a copy of the transaction. | There are no miners and it is more secure as the transaction copy is shared with relevant stakeholders only. |