CCNA Tutorial
What is CCNA?
CCNA stands for Cisco Certified Network Associate. It is a certification course offered by Cisco.
CCNA improves your understanding of the internet working and how different network topologies work together to form a network.
What is Cisco?
Cisco is the American multinational technology company in the centre of California. It is the king of routing, switching, and security. Most of the companies use Cisco devices in their daily routine.
Cisco developers manufacture and sell networking hardware, telecommunication equipment, and other high-technology services and products.
Why CCNA?
- CCNA validates the ability to understand, operate, configure, and troubleshoot routed and switched network.
- It helps to resolve a customer's problem more efficiently.
- Once you are CCNA certified, you can get a higher salary.
- It teaches the candidate how to create a point-point connection.
- It explains how to construct network addresses.
Types of CCNA Certification
There are different types of CCNA Certification given below:
- CCNA Routing & Switching (R&S)
- CCNA Wireless
- CCNA Data Center
- CCNA Security
- CCNA Service Provider
- CCNA Voice
Note: This tutorial covers everything about CCNA routing and switching.
Network Connecting Devices
Network connecting devices are used to connect two or more devices to share data or resources from one network to another network.
Some important network connecting devices are given below:
HUB
- The general meaning of the word hub is any connecting device.
- It works on the physical layer of OSI Model.
- A hub is designed to connect computers in a private network.
- It is used to connect peer to peer small networks.
- Hub is slow and insecure.
Switch
- A switch also connects computers like a hub.
- It works on the Data link layer of OSI Model.
- It determines what computer or device the packet is intended for and sends it to that computer only.
- A switch is fast and secure.
Router
It is designed to receive, analyze, and move incoming packets to another network.
A router has more capabilities than other devices, such as a hub or a switch.

End Devices
The network devices that people are most familiar with are called end devices. It is a source to a destination device in a networked system.
Example
PC, Server, Laptop, etc.
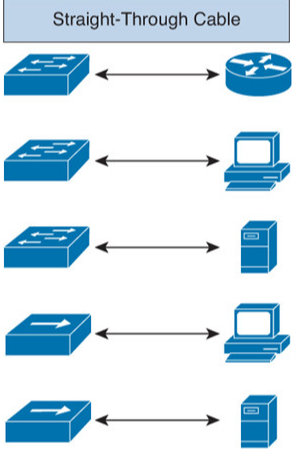
Straight-through Cable
It is used when we want to
- Connect Switch to Router
- Connect Switch to PC
- Connect Switch to Server
- Connect Hub to PC
- Connect Hub to Server
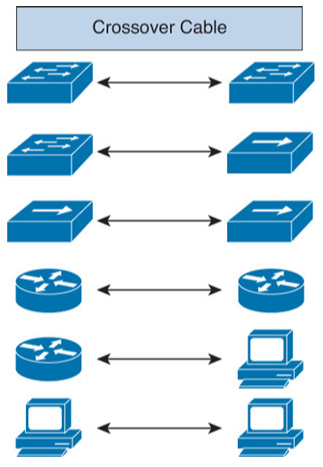
Crossover Cable
It used when we want to
- Connect Switch to Switch
- Connect Switch to Hub
- Connect Hub to Hub
- Connect Router to Router
- Connect Router to PC
- Connect PC to PC
What is next after CCNA?
If you learn CCNA, then you get the job opportunity in the following designation:
- Technical Support Representative
- Network Support Engineer
- Network Administrator
- IT Manager
- System Administrator
After getting sufficient experience in the job, you can also move for professional and expert level certification i.e., Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) and Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert (CCIE).
CCNA Tutorial Topics
Internetworking:
Ethernet Networking and Data Encapsulation:
Introduction to TCP/IP:
IP Addressing
Cisco’s Internetworking Operating System(IOS):
- Download and install Cisco packet tracer
- Cisco IOS Overview
- Power on a Cisco Device
- Getting familiar with the IOS modes
Administrative Configurations
- Configure Hostname
- Configure Banners
- Configure Password
- Configure IP on a router
- Saving, Erasing, and Verifying Configuration
Managing a Cisco Internetwork:
- The Internal Components of a Cisco Router and Switch
- Configuring DHCP
- Check Networking Connectivity and Troubleshooting
IP Routing:
- Routing Basics
- Configuring IP Routing
- Configuring IP Routing in Our Network
- Static Routing
- Dynamic Routing
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF):
Enhanced IGRP
Switching
- Switching Services
- Configuring Catalyst Switches
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Types of Spanning Tree Protocol
- PortFast and BPDU Guard
- Etherchannel
VLAN’s
- VLAN Basics
- Configuring VLAN’s
Access Lists
- Introduction to Access Lists
- Standard Access Lists
- Extended Access Lists
Network Address Translations (NAT)
- What is NAT?
- Types of NAT
- Port Address Translation (PAT) configuration
Internet Protocol Version 6(IPv6)
- What is IPv6
- IPv6 routing protocols
- How to configure IPv6
IP Services
- Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP)
- Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
- Syslog
- SNMP
Wide Area Networks
- Introduction to Wide Area Network
- High Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
- Virtual Private Networks