Configure DHCP
DHCP
- DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
- It is a client server-based architecture which involves DHCP client and DHCP server.
- It is a messaging system for the communication between the DHCP server and DHCP client.
- It allows the clients to acquire their IP address dynamically.
- DHCP uses UDP port numbers 67 for destination server and port number 68 for the client.
The DHCP messaging system’s message and their types are given below:
- Discover
- Offer
- Request
- Acknowledgment
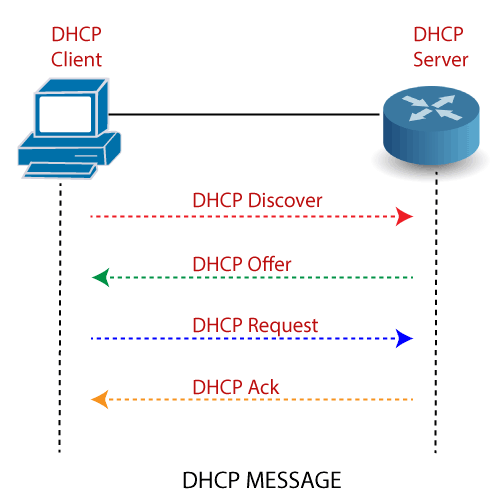
Every DHCP server that receives the message, responds with a DHCP offer containing:
- The IP Address being offered to the DHCP client.
- The network mask offered to the DHCP client.
- The amount of time the client can keep and use this address.
- The IP address of the DHCP server makes this offer.
Components of DHCP
Before start configuring DHCP, it is important to understand all of its components.
A list of DHCP components are given below:
DHCP Server: DHCP Server is a networked device that is used to run the DHCP service and hold the information about the IP address or related configuration.
DHCP Client: DHCP client receives configuration information from a DHCP Server. It can be a computer, mobile phone, or any other device that requires connectivity to the network.
IP address pool: IP address pool is the range of IP addresses that are available to DHCP clients. These addresses are generally handed out sequentially from lowest to highest.
Subnet: Subnet helps us to keep networks manageable.
DHCP relay: DHCP relay is responsible for forwarding the requests and responses between the DHCP clients and the DHCP servers.
Configure DHCP
There are following steps involve configuring DHCP on a Router –
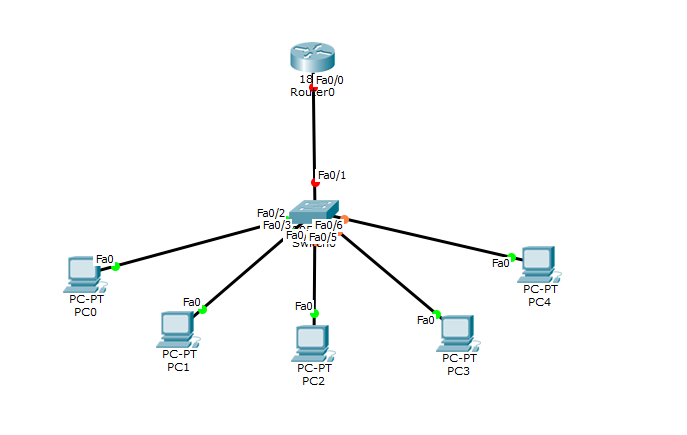
Step1: Create the Network topology:
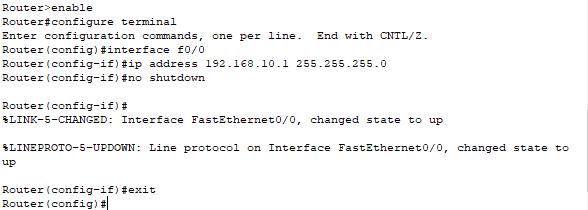
Step2: On the router0, configure an IP address to the router’s interface that is connected to the switch and act as the default gateway.
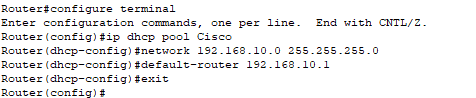
Step3: Now, create an ip dhcp pool and named it as Cisco. In this Pool, provide a Network address that has given to the DHCP clients.
After creating the DHCP pool, assign the router's interface ip address as a default-router address for clients.
Step4: In this step, we will exclude ip address range by typing “ipdhcp excluded address” command.
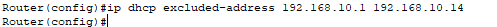
After completing all the above steps, click on any PC then go to Desktop -> IP Configuration ->DHCP.
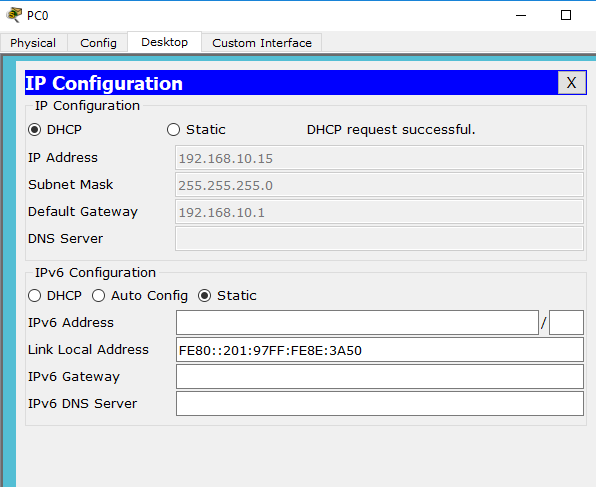
You see that the ip address 192.168.10.15 is configured automatically, as it is shown in the above screenshot.
Advantages of DHCP
DHCP offers the following advantages:
- IP address management –DHCP provides easier IP address management scheme. In a network, without DHCP, you must assign IP addresses manually. But When the DHCP is enabled, the DHCP server provides IP address automatically.
- Centralized network client configuration – In the DHCP, all configuration information is stored in one place that is“DHCP data store." It does not need a client to change the configuration. It can make changes for multiple clients just by changing the information stored in the data store.
- Support of local clients and remote client – DHCP supports both local clients and remote client by providing the IP addresses automatically to each client that work on a network.
- Large network support –There are millions of clients that can use DHCP. The DHCP uses multithreading to process the clients request simultaneously.
- Remove Delicacy – DHCP removes duplicate or invalid assignment of IP addresses. Therefore, no chance of conflicts in IP addresses.
Disadvantages of DHCP
- Makes router busy – When we configure DHCP on a router, it will make the router busier and consume some additional memory.
- Security Issues – In DHCP, there is a high-security risk. Because the information is sent over the network, that's why there may be a chance of information getting lost or hacked by someone.
- The client is not able to access the network in the absence of a DHCP server.