CSS Units
CSS Units
In CSS, there are so many units available to show the length’s measurement. A single unit of CSS is applied to examine the size of the property, which the user set for content or element. The CSS unit is required to depict any measurement like margin: 30px; where the pixel or px is a unit of CSS. These units are applied to set the lengths, padding, margin, and many others.
Let’s understand some key points.
- We can’t apply the whitespace among the unit and the number.
- A unit may be neglected for 0.
- A few CSS properties permit the length’s negative values.
The CSS units can be of two types:
- Relative length
- Absolute length
Relative lengths
This type of length is suitable to design any responsive site for the reason it scales relative to a parent or any size of the window. It describes the length, i.e., relative to other length properties.
If the screen size varies a lot, then the units of relative length are better because these units scale among the distinct rendering mediums (depending over the device). We can apply any relative units similarly, like a default for a responsive unit. The relative length provides help to ignore update designs for distinct screen sizes.
A few relative lengths are discussed and explained in the following table:
| Unit | Name |
| em | This unit is relative to an element’s font-size. |
| ex | These units are relative to the component’s font’s x-height. It is used rarely. Any x-height can be examined by the lowercase letter ‘x’ height. |
| ch | This unit is quite similar to the ex unit, but rather than using the ‘x’ letter’s height, it measures an integer “0” (zero) width. |
| rem | It is considered as the font size of the root element. |
| vh | These units corresponds to the viewport’s height. 1vh= 1% or 1/100 of the height of viewport. |
| vw | These units are relative to the viewport’s width. 1vh= 1% or 1/100 of the width of viewport. |
| vmin | These units are relative to the viewport’s smaller dimension. 1vh= 1% or 1/100 of the lower dimension of a viewport. |
| vmax | These units are relative to the viewport’s smaller dimension. 1vh= 1% or 1/100 of the lower dimension of a viewport’s. |
| % | This unit is applied to represent a measurement like a percentage, i.e., relative to other values. |
Consider the below examples:
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
text-align: center;
}
p
{
line-height: 0.1cm;
color: navy;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Relative units </h1>
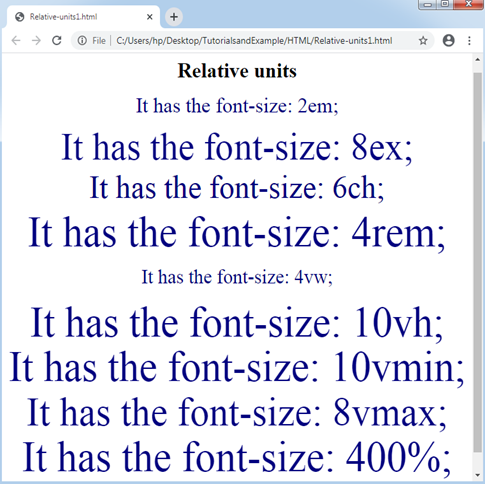
<p style = "font-size: 2em;" > It has the font-size: 2em; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 8ex;" > It has the font-size: 8ex; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 6ch;" > It has the font-size: 6ch; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 4rem;" > It has the font-size: 4rem; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 4vw;" > It has the font-size: 4vw; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 10vh;" > It has the font-size: 10vh; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 10vmin;" > It has the font-size: 10vmin; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 8vmax;" > It has the font-size: 8vmax; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 400%;" > It has the font-size: 400%; </p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Example: Time
A few animations attribute need values to show in time.
| Unit | Description |
| s | This value is the time duration in seconds. |
| ms | This value Is the time duration in milliseconds. 1ms= 1/100 of any second |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div
{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: lime;
border-radius: 50px;
transition-property: background, width, height;
transition-duration: 1s, 2s, 3s;
}
div:hover
{
width:300px;
background: orange;
height:300px;
border-radius: 80px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
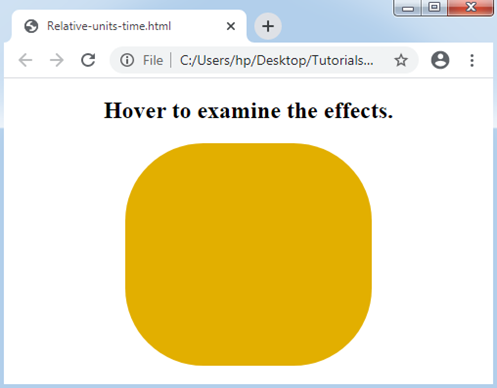
<h2> Hover to examine the effects. </h2>
<div></div>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Example: Angles
The transformation attributes of CSS need values to show in angles.
| Units | Description |
| deg | It shows the angles inside the degrees. |
| grad | It shows the angles inside the gradians, which is 1/400 of any turn. |
| turn | It shows the angles inside the turns, which is 360 degrees. |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
img
{
border: 9px ridge gray;
border-radius: 30px;
margin: 10px;
transition-duration: 2s;
}
#img1:hover
{
transform: rotate(30deg);
transform-origin: bottom left 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
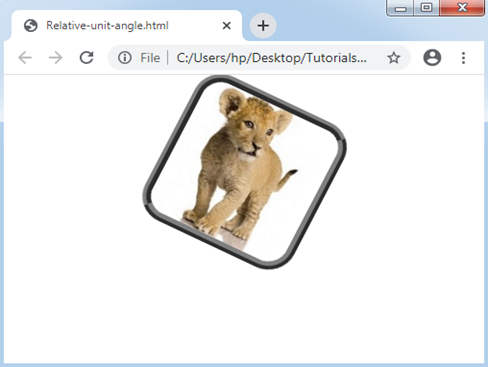
<img src="Lion1.png" id="img1"/>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Absolute lengths
The absolute length is the units of fixed-length type. The length, i.e., is displayed with the use of the absolute units can be represented absolutely of that size. As the screen size varies a lot, thus it is not suggested to use the on-screen. So, any absolute unit must be applied if the output’s medium is known, like the print layout.
These units will be helpful if the responsiveness will not be considered inside a project. It is not more favorable for some responsive sites due to it does not scale if any screen changes.
The absolute length will be considered to be of the same size all the time, generally. The units of absolute length are discussed below:
| Units | Name | Description |
| cm | Centimeters | This unit applied to depict the measurements within the centimeters. |
| mm | Millimeters | This unit asked to illustrate the measurements within the millimeters. |
| in | Inches | This unit referred to represent the measurements within the inches. 1in= 96px= 2.54cm |
| pt | Points | This unit applied to depict the measurements within the points. 1pt = 1/72 of 1 inch |
| pc | Picas | This unit referred to represent the measurements within the picas. 1pc = 12pt so, there 6 picas will equal to 1 inch. |
| px | Pixels | This unit applied to depict the measurements within the pixels. 1px = 1/96th of inch |
Example:
In the following illustration, we will apply the CSS property font-size for some paragraphs to represent the values with the use of the units as above-mentioned of absolute length.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body
{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Absolute units </h1>
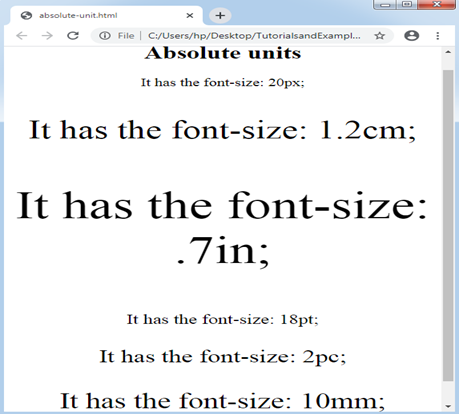
<p style = "font-size: 20px;" > It has the font-size: 20px; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 1.2cm;" > It has the font-size: 1.2cm; </p>
<p style = "font-size: .7in;" > It has the font-size: .7in; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 18pt;" > It has the font-size: 18pt; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 2pc;" > It has the font-size: 2pc; </p>
<p style = "font-size: 10mm;" > It has the font-size: 10mm; </p>
</body>
</html>
Output: