Decomposition Reaction: Definition, Example, Types, Applications
In this tutorial, we will cover the definition, applications, uses, examples including various chemical reactions, types, and various other details information regarding Decomposition Reaction.
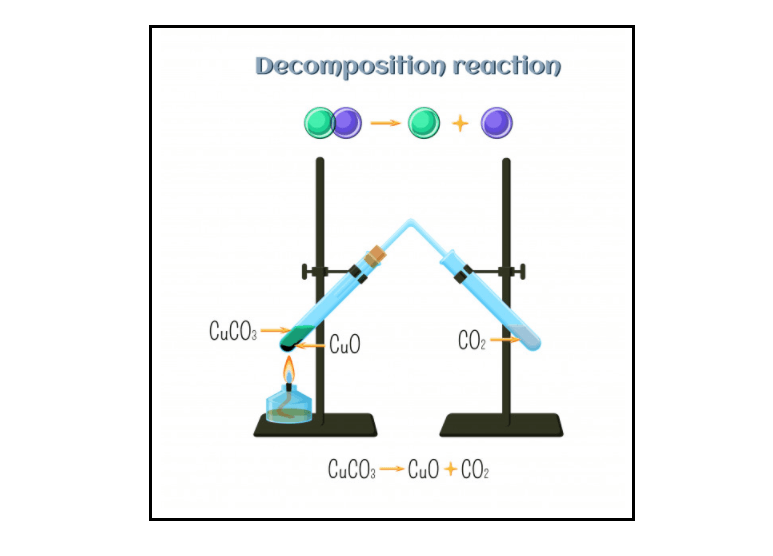
What is a Decomposition Reaction?
A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a compound splits into two or more simple substances under certain conditions. Decomposition Reaction is also referred to as the opposite of the combination reaction.
The generic equation format of a Decomposition Reaction is as follows:
XY -> X + Y
Where XY represents the parent molecule (reactant) of any compound and X & Y represents the product molecules.
Decomposition reactions occur all around us, but we never bother to notice it.
Let’s see some real time examples of Decomposition reaction. The various examples of decomposition equations are covered below.
- Decomposition of Water, can be represented by given below chemical reaction. The electrolysis of water (H2O) gives two components i.e., hydrogen and oxygen.
2H2O ? 2H2 + O2
- Decomposition of soft drinks (carbonic acid), which can be illustrated by the given below chemical equation:
H2CO3 ? H2O + CO2
- Decomposition of sodium carbonate, , which is further represented with the help of the below given chemical equation:
Na2CO3 ? Na2O + CO2
- Decomposition of sugar, which is further represented with the help of the below given chemical equation:
C12H22O11 ? 12C + 11H2O
Why Decomposition occurs?
In this universe, every single compound has its limitations under specific conditions. Any substance undergoes decomposition because of an undesired reaction that happens whenever the specific substance is exposed to intense conditions that exceed its atomic threshold.
Though there could be other reasons that could incur the decomposition reaction, which are as follows:
- Mass Spectrometry
- Gravimetric Analysis
- Thermogravimetric Analysis
Types of Decomposition Reaction
Primarily, the three types of decomposition reactions are as follows:
1. Thermal decomposition reaction
Thermal decomposition reaction is initiated by thermal energy. Or we can say thermal decomposition reaction requires heat to be supplied to its reactants for activation. These reactions are usually endothermic as thermal energy is needed to separate constituent elements and break chemical bonds. An example of a thermal decomposition reaction is as follows:
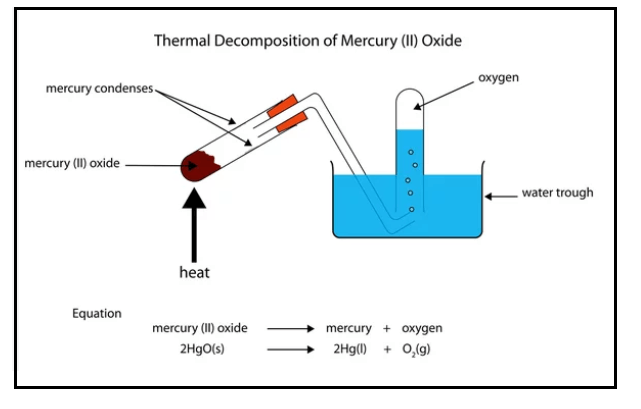
The chemical equation of Thermal decomposition reaction is given below:
2HgO(s) ? 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
When heated, mercury (II) oxide (HgO) decomposes into mercury (Hg) and oxygen (O2). This process is used to extract the mercury element, which is further used in many industrial and medical appliances.
- Electrolytic decomposition reaction
An electrolytic decomposition reaction is defined as the kind of decomposition reaction where electrical energy is supplied as the activation energy to carry out the decomposition. A simple example of an electrolytic decomposition reaction is electrolysis of water, which is shown in the below reaction:
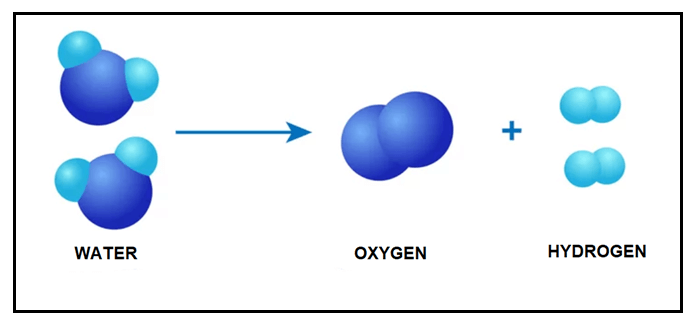
The chemical equation of Electrolytic decomposition reaction is given below:
2H2O? 2H2 + O2
- Photo or Photochemical or Photolytic reaction
Photo decomposition is a chemical reaction in which energy from photons is absorbed to break down the reactant into its constituents. For instance, in the below illustration you can see the decomposition of ozone into dioxygen and an oxygen radical.
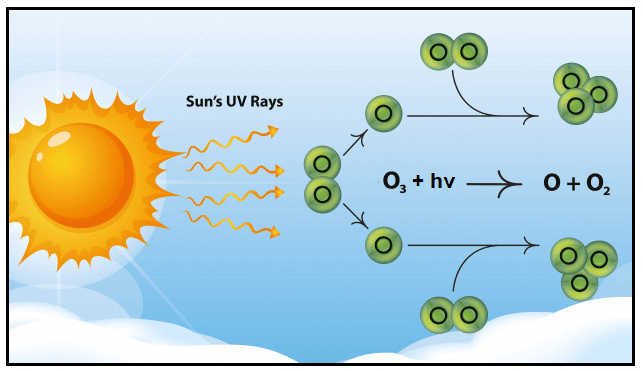
The chemical equation of photochemical decomposition is given below:
O3 + h? ? O2 + O.
Uses of Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition is all around all. It happens under our nose, and we are not aware of it. Following are the day to day uses of a decomposition reaction:
- The decomposition reaction is widely used globally for the Manufacturing of cement (calcium oxide) that is further used in the construction of buildings.
- One of the common uses of a decomposition reaction is the extraction of metallurgical processes. For instance: the extraction of valuable metals from their oxides, chlorides, etc.
- It helps to provide quick relief from stomach acidity or indigestion.
- It is used in Thermite welding.
Double Decomposition Reaction
Double Decomposition Reaction is a chemical reaction where the constituent reactants mutually exchange their cations and anions and produce two new compounds.
The chemical equation for Double Decomposition reaction is as follows:
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ? NaCl(aq) + HOH(l)
In the above example, you can see that the Hydrochloric acid (HCL) and Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) are reacting to form two new reactants i.e, Sodium Chloride(salt or NaCl) and hydrogen hydroxide (HOH).
Catalytic Decomposition
As the name suggests, this type of chemical reaction involves a catalyst to break down the component into two or more substances. Though, the catalyst only acts as a supporting element and does take part in the reaction. It is used often used to speed up the chemical process by lowering down the activation energy. For instance, at a natural speed, hydrogen peroxide decomposes at a slow speed. The chemical equation for Catalytic Decomposition is as follows:
2H2O2 + catalyst ? 2H2O + O2
Where, the catalyst could be Manganese (IV) Oxide, Potassium Iodide, Sodium Iodide, Lead Dioxide, Catalase.
Decomposition Reaction Frequently Asked Questions/ FAQ’s
Question 1: What is the vice versa of ‘Decomposition Reaction’?
Answer: Combination reaction is the vice versa of Decomposition reaction. In these reactions, a single product is formed by combining two or more products.
Question 2: Are all Decomposition Reactions Endothermic?
Answer: All Decomposition reactions are not compulsorily Endothermic. It can be exothermic or endothermic. Though, the latter is rare. For instance
Example 1: Decomposition of Nitric oxide
2NO ? N2 + O2
The above chemical equation of NO to N2 and O2 is exothermic.
Example 2: Decomposition of Ozone
O3 + h? ? O2 + O.
The Decomposition of Ozone (O3) to Oxygen (O) is exothermic.
Question 3: Mention any one application of Decomposition Reactions.
Answer: One of the major practices of Decomposition reaction is to extract metals from their ores. For instance, calamine produces zinc after going through a decomposition reaction.