Difference Between Orbits and Orbitals Atom
Difference Between Orbits and Orbitals
Atom:
Everything around you is made up by atoms. Atom is the smallest unit of element. It is a Greek word which means Indivisible. Atom can’t be divided furthermore. By the joining of two or more atoms, molecules form.
Atom is made up by mainly Nucleus and Electrons. Nucleus is the centre of atom where two more charge; Protons and Neutrons exist. Protons are positively charged ions and neutrons have no charge. It means the neutrons are neutral in nature.
So there is no doubt to say that Nucleus charge with positive ion due to protons.
Electrons have negatively charged. Because we all know that opposite charges or ions attract each other. So there is a force applied between nucleus and electrons, this force are known as ElectroMagneticForce. It occurs between the charged particles or ions. Electromagnetic force can be attractive as well as repulsive in nature.
The magnitude of held charge on the electrons is equal to the charge held by photos; because of this there is a cancellation of charge and atom or molecules are neutral.
What is Orbit?
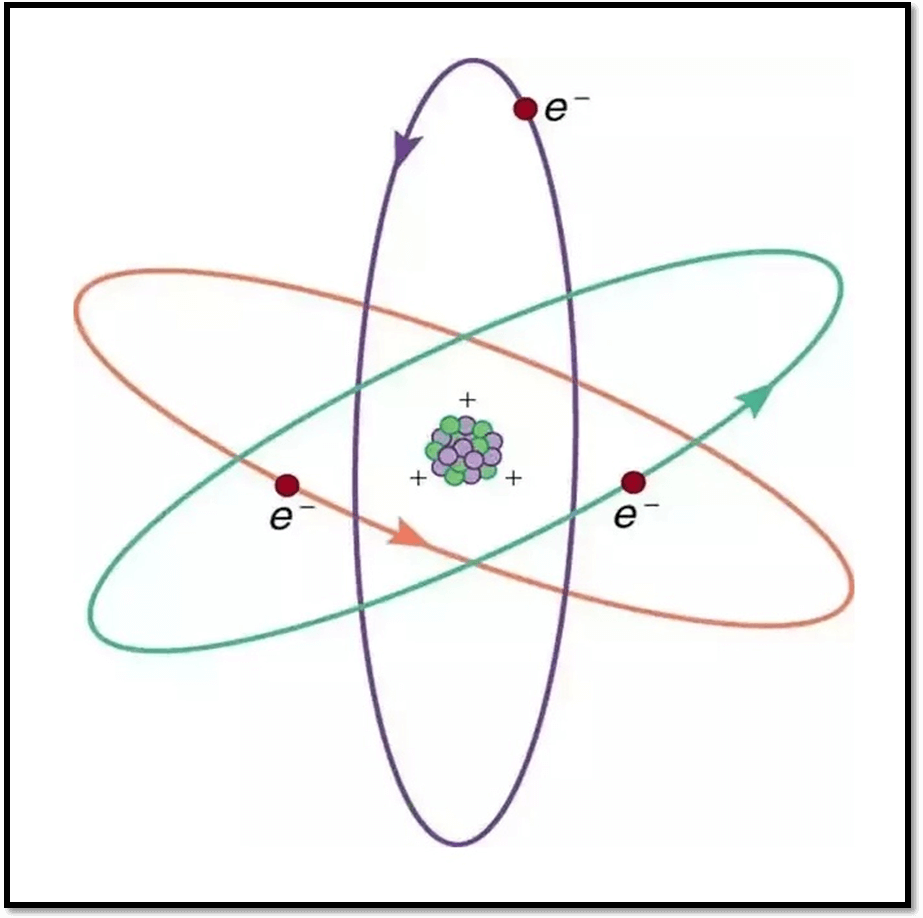
At a macro level, every planet revolves around the sun and also following a fixed circular path. It means there is no other path for revolution. Due to this continuously circular motion; we call that path Orbit.

Similarly, applying this example at a micro level and consider electron as Earth. Electrons continuously revolve around the nucleus on a fixed circular paths, this path is known as Orbits.
Characteristics of Orbits
There are some properties or characteristics of Orbits which are describing below:
- Orbit is a fixed circular path around the nucleus.
- These are stable or fixed, so also known as Stationary Orbits.
- It is the simple representation of electron’s motion.
- There no such real circular path. Basically due to the repeated revolution of electrons, we call it fixed circular path.
- In the orbits, electron repeats its motion.
- Orbits are spherical or circular. Orbits have simpler and planner representation.
- There are so many orbits around the nucleus and every orbit has its own name. Every orbit has different energy level.
Types of Orbits
There are so many orbits around the nucleus. All the orbits have different radius from the centre (nucleus) and due to this distance, energy level also vary with the distance.
| n = 1 | K Orbit |
| n = 2 | L Orbit |
| n = 3 | M Orbit |
| n = 4 | N Orbit |
Where, n =1,2,3,4...so on represent the Principal Quantum Numbers. It shows the main or principal energy level. By the increasing value of n, the energy of electron and radius of shell also increase.
Drawbacks of Orbit Theory
Why we need to study about orbital? Why orbit theory was not enough to locating position of electrons. This is a very common question. These following points can help to bring more clarity about why orbits are not enough to determine the position of electron?
- An orbit could not describe the shape of molecules on the basis of circular path. This is because of the non-directional nature of molecules.
- Orbit theory could not explain the bonding among same or different molecules.
- Furthermore, Orbits were against to the Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle.
“It is impossible to exact determination ofthe position and momentum (or velocity) of a particle or electron at the same time.
- Orbit theory is not enough to explain the Bohr Theory of Atomic Structure. It complies that the nearest orbit from nucleusor the base orbit in the atom have lowest energy, the inner orbit have more energy than the base orbit and the outer orbit have highest energy.
What are Orbitals?
On the basis of orbits we can’t define the location or position of electrons where the probability is high. Because electron can be revolve in either X Direction or Y Direction or in Z Direction.
Electrons have particle nature as well as wave nature. On the basis of Wave Theory of Electrons; there is no such fixed circular path (circular orbits) around the nucleus rather ElectronClouds exist. There is three dimensional space around the nucleus. In this three dimensional region electrons continuously revolve around the nucleus. Sometimes these electrons come too close to nucleus and sometimes it far away.
There are three dimensional spaces around the nucleus where the probability of finding electrons is highest and this space is known as Orbital.
In other words, Orbital is a three dimensional space where approximately more electrons find.
Characteristics of Orbitals
There are some specific characteristics that atomic orbital contains. Let’s discuss in detail:
- Nucleus is the centre of every atomic orbital.
- Orbital indicates the wave properties of an electron.
- Furthermore, concept of atomic orbital helps in explaining Structure and Bonding of Molecules.
- The maximum number of electron in one orbital is Two where one electron is spinning clockwise and another one is spinning in opposite direction; that is anti clockwise.
- The Eigen Functions of an electron represent its atomic orbital. Byputting all the different values of energies in Schrodinger Wave Equation, the obtain function is known as Eigen Function.
- According to the Electron Cloud Model of Hydrogen Atom,“The region where density of Electron Cloud is most known as Atomic Orbital.”
- Orbitals have 95 per cent probability to locating electrons.
- Atomic orbital with the same energy are known as Degenerated Orbitals.
Types of Orbitals
Orbital is a three dimensional region where the probability of finding electrons is utmost. In Hydrogen Atom, there is only one electron so the Electronic Configuration of Hydrogen is 1s¹. That’s whythe probability of locating electron is highest in 1s orbital.
In every element the outermost electrons of molecules take part in making bonding with other molecules.
The orbital names s, p, d, and f stand for names given to groups of lines originally noted in the spectra of the alkali metals. These line groups are called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. There are certain combinations of each orbital and principal energy level number or shells.
- Fern=1 orbit, known as K shell, there is only s orbital exist.
- Furthermore, in n=2 orbit, called L shell, there is two orbitals present. That is s and p orbital.
- For n=3 orbit, known as M shell, there are total three orbitals found; these are s, p and d orbital.
- When it comes n=4 orbit or N shell, there are total four orbitals s, p, d and f.
S Orbital
SOrbital is spherical shaped region or space where the probability of locating electron is utmost. S orbitals are symmetric and it appears like a two dimensional circle around the nucleus.
- The order for size of radius is 1s< 2s< 3s<4s.
- The probability of finding electron is supreme in the s orbital. This orbital is very close to the nucleus. All orbitals have l = m = 0, but the value or principal quantum number can vary.
- There is only one subshell in s orbital. These orbitals can hold maximum 2 electrons.Even these two electrons can never have same value of quantum numbers for the atom.
- These two electrons in s orbital have different spin quantum number.
Node or Nodal Point:
A node is a region where no electrons are present. Nodal point are such points where the possibility of electron is almost zero. There are no nodes or nodal plane exist in s orbitals.
P Orbital
The shape of p orbital is dumbbell. There are 3 orbitals in p orbital. So the p orbital can occupy maximum six electrons in three orbitals.
The energy of all three orbitals is same. These orbitals are arranged on CartesianAxis X,Y and Z. And represent by Px, Py and Pz respectively.
The nodal plane exist in p orbital is at the centre. In p orbital there are two lobes which separate from each other. The point where both lobes intersect each other is called node.At the node the electron density is zero.
- Therefore P orbital have one nodal plane which is passes through the nucleus. For calculating the number of nodes is n – 2.
- The size of p orbital absolutely depends on the principal quantum number. It means by the increasing value of n, the size of orbital also increase. The order on the basis of size in p orbital is 2p< 3p < 4p.
- The all three orbitals have identical shape, size and energy level. So these orbitals are called degenerated orbitals.
- For p orbital, the value of l (azimuthal quantum number) is 1.
There are three orbitals in p orbital. The value for (magnetic quantum number) m = +1, 0, -1 respectively for the three orbitals.
The three blocks of p are given below:
| Px m = -1 | Py m = 0 | Pz m = +1 |
D orbital
The shape of D orbital is double dumbbell in a plane. It is like a two dumbbells, with an right angle (90° angle). For d orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number l = 2.
- There are five orbitals in D orbitals. These Orbitals begin with the third principal energy level. It means n = 3is minimum energy level for D subshells.
- In these five orbital, the total number of electrons is 10.
- D orbital has two nodes. D orbital have nodal plane between the two axes, where electron density is maximum.
- These five orbitals are dxy, dyz, dzx, dx²-y², dz².
- In the other hand, there are 5 orbital in D orbital so value of m for d orbital are ( -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 ) respectively.
The table can help to understand better the d orbitals:
| dxy m = -2 | dyz m = -1 | dzx m = 0 | dx²-y² m = +1 | dz² m = +2 |
- dx²-y² orbital have the highest energy in d orbital,
The reason is the electron in this orbital can easily make bonds with other molecules in all four directions.
- dz² have different shape from other four orbitals. But all other orbitals have similar shape.
F Orbitals
The shape of F orbital is very complex. So we can’t describe any fixed shape of f orbital.
- There are total seven orbitals, so that the total number of electrons for f orbital is fourteen.
- Minimum principal quantum number for f orbital is 4 (n = 4).
- The value of l = 3 for f orbital.
- Magnetic quantum number for f orbital is –3, –2, –1, 0, +1, +2, +3 corresponding the all seven orbitals.
- There is a lot energy differences between the all seven orbital, the reason behind is the diffuse shape of f orbital.
Difference between Orbits and Orbitals
Most of the students often get confused to differentiate between orbit and orbitals. They understand both of them are equal. But this is not true; both of these are far different from each other. The table given below will be helpful to bring clarity and distinguish between orbit and orbital:
| S.No. | Orbits | Orbitals |
| 1 | Orbits are fixed circular path around the nucleus. | Orbitals are three dimensional region around the nucleus. |
| 2 | They have fixed spherical or circular shape. | Orbitals have no fixed shape. They have different shapes from each other; like circular, dumbbell etc. |
| 3 | They represent the planner motion of the electron. | They represent the three dimensional motion. |
| 4 | Orbits are non directional. | Except s orbital, all other orbitals are directional. |
| 5 | The number of electrons in orbits varies with the number of orbit. | In orbitals, the total number of electrons is certain or fixed. |
| 6 | Orbits can not justify the wave nature of electron. It only covers the particle nature of electron. | Orbitals justify the particle nature as well as wave nature of electron. |
| 7 | There is no explanation regarding the molecular bonding. | Orbitals define properly about the molecular structure and bonding. |
| 8 | Orbits theory unable to satisfy the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. | Orbital theory justifies the Heisenberg Principle because it also compiles the wave nature. |
| 9 | It does not satisfy the Bohr Theory of Atomic Structure. | Orbitalsabsolutely favour the Bohr Theory. |
| 10 | The planner motion of electrons represent by the principal energy level; that is K, L, M, N. | The three dimensional motion of electron represent by s, p, d, f orbitals. |
| 11 | The maximum number of electrons in one orbit are 2n², where n is the number of orbit. | The maximum electrons in one orbital two. |
Conclusion:
It is clear that both orbit and orbital are represent a certain path on which electron is revolving around the nucleus yet far different from each other.
On the one hand orbit theory is a very simple whereas orbital theory has more complicated concept but it describe more clearly about the exact position of electrons. Orbit and orbital both theories exist due to the revolution of electrons.
.