Ethernet Networks in Review
Ethernet Networks in Review
Today, Ethernet is the most used technology for the LANs. It is described as IEEE 802.3 standard. Ethernet is a connection-based media access method i.e., Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) that allows all the hosts on a network to share the same bandwidth of a link.
Ethernet uses coaxial, twisted pair and fiber optic cables.
CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD stands for – Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. It is a protocol that helps devices to share the same bandwidth. CSMA/CD was created to reduce the problem of collisions that occur when data are transmitted simultaneously from different nodes.
In CSMA/CD, when a node is transmitting data, all the other nodes on a network receive and examine that transmission.
How does the CSMA/CD work?
When a host wants to transmit data over the network, it first checks for the presence of a digital signal on the network. If no other host is transmitting, the host will then proceed with its transmission. The transmitting host continuously monitors the network to make sure no other hosts begin transmitting. If the host detects another signal on the network, it sends out an extended jam signal that causes all nodes to stop sending data.
We use Backoff algorithms to determine when the colliding stations can retransmit.
When a collision occurs on an Ethernet, the following things happen:
- A jam signal informs all devices that a collision occurred.
- Collision invokes a backoff algorithm.
- Each device on the Ethernet stops transmitting for a short time until their backoff timers expire.
- All hosts have equal priority to transmit after the timers are expired.
Collision Domain
- It is a network segment in which two or more devices are sharing the same bandwidth.
- Collision domain can slow down network performance along with it security threat.
- Hub has a single collision domain.
- The switch has per-port collision domain.
- The router has per-port collision domain.
Broadcast Domain
- It is a set of devices in which one device sends a broadcast frame, and all other devices will receive that frame in the same broadcast domain.
- A broadcast domain can improve network performance.
- A broadcast message goes to every PC and network device.
- Hub has a single broadcast domain.
- Switch has a single broadcast domain by default.
- The router has a per-port broadcast domain.
Problem Statement
Find the number of collision domains and broadcast domains.
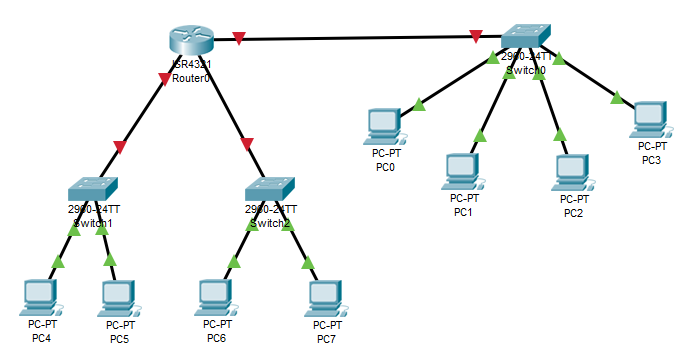
Solution:
The number of the collision domain is 11
The number of the broadcast domain is 3