Hibernate Inheritance - Single Table
Hibernate Inheritance
In this inheritance strategy, only one table is created for all the classes involved in the hierarchy with an additional column known as a discriminator column. The discriminator column helps indifferentiating between the two subclasses. A SINGLE_TABLE strategy is the default strategy.
Following are the annotations used in this strategy:
- @Inheritance- It defines the inheritance strategy used in the application. This annotation is specified on the entity class that is the root of all the entity classes.
- @DiscriminatorColumn- It specifies the discriminator column for SINGLE_TABLE and JOINED inheritance strategies.
- @DiscriminatorValue- Discriminator values are the values of the @DiscriminatorColumn. This annotation is used to specify the values of the discriminator column for the given type entity.
Syntax of SINGLE_TABLE Inheritance
@Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
If @Inheritance annotation is not specified or no strategy is specified, it will consider SINGLE_TABLE strategy by default.
Example of SINGLE_TABLE Inheritance
In this example, we are taking three classes; i.e., Payment.java, Card.java, and Cheque.java.
The class- hierarchy is given below:-
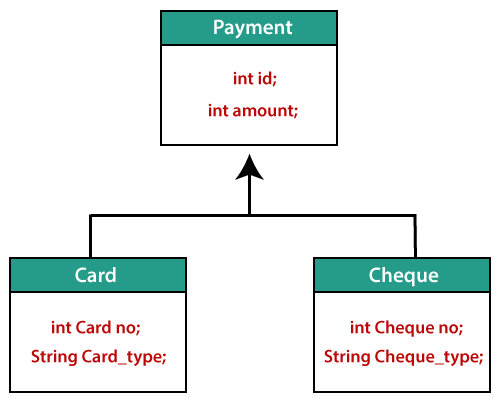
- Create all POJO classes.
In this step, we are going to create all the persistent classes, i.e., Payment.java, Card.java, and Cheque.java.
Payment.java
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorColumn;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="payment")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
@DiscriminatorColumn(name = "paymtmode", discriminatorType =
DiscriminatorType.STRING, length = 10)
public class Payment {
@Id
@Column(name="payid")
private int id;
@Column(name="amount")
private int amount;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
}
Card.java
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue(value="card")
public class Card extends Payment{
@Column(name="cardnum")
private int cardno;
@Column(name="crdtype")
private String card_type;
public int getCardno() {
return cardno;
}
public void setCardno(int cardno) {
this.cardno = cardno;
}
public String getCard_type() {
return card_type;
}
public void setCard_type(String card_type) {
this.card_type = card_type;
}
}
Cheque.java
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue(value="cheque")
public class Cheque extends Payment {
@Column(name="chqnum")
private int chequeno;
@Column(name="chqtype")
private String cheque_type;
public int getChequeno() {
return chequeno;
}
public void setChequeno(int chequeno) {
this.chequeno = chequeno;
}
public String getCheque_type() {
return cheque_type;
}
public void setCheque_type(String cheque_type) {
this.cheque_type = cheque_type;
}
}
- Create the Configuration file.
The configuration file contains the information of mapping classes and database. We will map all the persistent classes in the configuration file (hibernate.cfg.xml).
hibernate.cfg.xml
org.hibernate.dialect .MySQL5Dialect com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc:mysql:// localhost:3306/example root root update
- Create the main class that stores the object of Persistent object
In this step, we are going to create a main class (which contains the main method) that stores the object of the persistent class.
App.java
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
Configuration cfg= new Configuration();
cfg.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
SessionFactory s= cfg.buildSessionFactory();
Session session=s.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Pay p=new Pay();
p.setAmount(5100);
Card c= new Card();
c.setAmount(1000);
c.setCardno(33558882);
c.setCard_type("VISA");
Cheque chq=new Cheque();
chq.setAmount(11100);
chq.setChequeno(010036);
chq.setCheque_type("ORDER");
session.save(p);
session.save(c);
session.save(chq);
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println( "successfully added" );
}
}
- OUTPUT
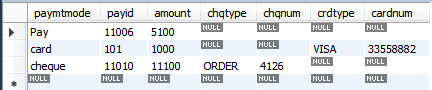
- DATABASE TABLE
DISADVANTAGES
The main disadvantages of this strategy are:
- Most of the values are null in the table; hence, we cannot apply not null constraint.
- In this strategy, the table cannot be normalized, which means we cannot expand this table into new tables or columns.
To overcome these disadvantages, we use TABLE_PER_CLASS strategy.