Monitors in Operating System
Monitors in Operating System
Monitors are used for process synchronization. With the help of programming languages, we can use a monitor to achieve mutual exclusion among the processes. Example of monitors: Java Synchronized methods such as Java offers notify() and wait() constructs.
In other words, monitors are defined as the construct of programming language, which helps in controlling shared data access.
The Monitor is a module or package which encapsulates shared data structure, procedures, and the synchronization between the concurrent procedure invocations.
Characteristics of Monitors.
- Inside the monitors, we can only execute one process at a time.
- Monitors are the group of procedures, and condition variables that are merged together in a special type of module.
3. If the process is running outside the monitor, then it cannot access the monitor’s internal variable. But a process can call the procedures of the monitor.
4. Monitors offer high-level of synchronization
5. Monitors were derived to simplify the complexity of synchronization problems.
6. There is only one process that can be active at a time inside the monitor.
Components of Monitor
There are four main components of the monitor:
- Initialization
- Private data
- Monitor procedure
- Monitor entry queue
Initialization: - Initialization comprises the code, and when the monitors are created, we use this code exactly once.
Private Data: - Private data is another component of the monitor. It comprises all the private data, and the private data contains private procedures that can only be used within the monitor. So, outside the monitor, private data is not visible.
Monitor Procedure: - Monitors Procedures are those procedures that can be called from outside the monitor.
Monitor Entry Queue: - Monitor entry queue is another essential component of the monitor that includes all the threads, which are called procedures.
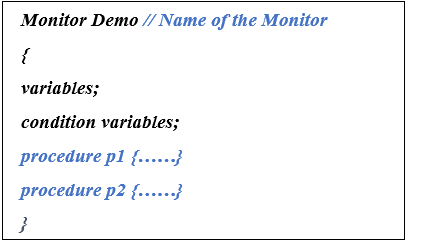
Syntax of monitor
Condition Variables
There are two types of operations that we can perform on the condition variables of the monitor:
- Wait
- Signal
Suppose there are two condition variables condition a, b // Declaring variable
Wait Operation
a.wait(): - The process that performs wait operation on the condition variables are suspended and locate the suspended process in a block queue of that condition variable.
Signal Operation
a.signal() : - If a signal operation is performed by the process on the condition variable, then a chance is provided to one of the blocked processes.
Advantages of Monitor
It makes the parallel programming easy, and if monitors are used, then there is less error-prone as compared to the semaphore.
Difference between Monitors and Semaphore
| Monitors | Semaphore |
| We can use condition variables only in the monitors. | In semaphore, we can use condition variables anywhere in the program, but we cannot use conditions variables in a semaphore. |
| In monitors, wait always block the caller. | In semaphore, wait does not always block the caller. |
| The monitors are comprised of the shared variables and the procedures which operate the shared variable. | The semaphore S value means the number of shared resources that are present in the system. |
| Condition variables are present in the monitor. | Condition variables are not present in the semaphore. |