PHP Date and Time
DATE:
The PHP date() function formats a date or time.
The timestamp is used to format a more readable date and time into a PHP date () function.
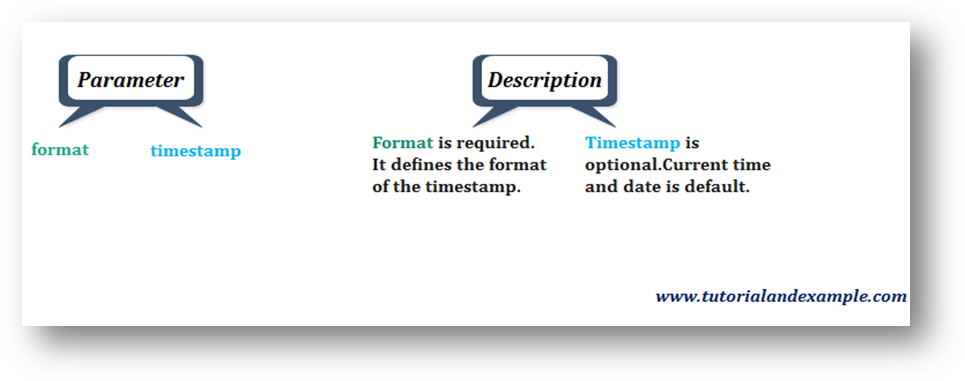
Syntax:
date(format,timestamp)
Simple Date:
Characters that are mainly used for dates:
d: The “d” is used to get the day of the month (from 1 to 31).
m: The “m” is used to get the month (From (1) to (12)).
y: The “y” is used to get the year ( in four digits).
l: The lowercase (l) is used to represent the day of the week.
Other special characters, like “/”, “.”, or “-“ can also be used between the characters to add additional formatting.
Example1:
";
echo "Today is” . date("m/d/Y") . "
";
echo "Today is” . date("Y/m/d") . "
";
?>
Output:
Today is 22/06/2019 Today is 06/22/2019 Today is 2019/06/22
-> In the above example, we get to know that we can write a date into a different format with the help of characters.
Example2:
"; ?>
Output:
Today`s Date Is 2019.06.22
Example3:
";
echo "Today " . date("d") . "
";
echo date("M") . "
";
echo " Year " . date("Y") . "
";
?>
Output:
Hello Saturday Today 22 Jun Year 2019
- In the above example, “M” is used to define the month name.
With the help of the date() function, we can update copyright year on our website.
Example4:
© 2018-|All Rights Reserved|www.tutorialandexample.com|
Output:
© 2018-2019|All Rights Reserved|www.tutorialandexample.com|
Example5:
Output:
Date is valid
Example6:
";
print_r($sun);
echo date("H:i:s",$sun);
?>
Output:
Array ( [sunrise] => 1561247655 [sunset] => 1561297943 [transit] => 1561272799 [civil_twilight_begin] => 1561246042 [civil_twilight_end] => 1561299557 [nautical_twilight_begin] => 1561244083 [nautical_twilight_end] => 1561301515 [astronomical_twilight_begin] => 1561241999 [astronomical_twilight_end] => 1561303599 ) 01:54:15
- In the above example, with the help of our current location longitude and latitude, we can easily find the sunrise, sunset, current time, etc.
TIME:
Characters that are mainly used for time:
H: The H character is used for 24hour format (00 to 23).
h: The lowercase “h” is used for 12hour format of an hour(01 to 12).
i: The lowercase “i” is used for minutes with leading zero(00 to 59).
s: The lowercase “s” is used for seconds with leading zero (00 to 59).
a: The “a” is used for ANTE MERIDIEM (a.m.) or POST MERIDIEM (p.m.).
Time Zone:
We can set a timezone to use; we need the time correct according to a specific location.
If the time we get from the code is not the right time, it is because our server is in another country or it set up on a different timezone.
Example:
Output:
The time is 04:20:19.pm.
PHP mktime() Function:
The timestamp parameter in the date() function defines a timestamp.
The mktime() function returns the Unix timestamp for a date. It contains the number of seconds between the Unix Epoch (June 23, 2019, 00:00:00 GMT).
Syntax:
mktime(hour, minute, second, month, day, year)
Example
Output:
Current Date and Time is 2019-06-23 12:30:10pm
- In the above example, the mktime() function creates a date and time from several of parameters.
PHP strtotime():
The PHP strtotime() function is used to convert a human-readable string into Unix Time.
Syntax:
strtotime(time,now)
Example1:
" . "
"; $d=strtotime("next Saturday"); echo date("d-m-Y h:i:sa", $d) . "
" . "
"; $d=strtotime("+3 Months"); echo date("d-m-Y h:i:sa", $d) . "
" . "
"; $d=strtotime("+6 Years"); echo date("d-m-Y h:i:sa", $d) . "
" . "
"; ?>
Output:
24-06-2019 12:00:00am 29-06-2019 12:00:00am 23-09-2019 10:37:14am 23-06-2025 10:37:14am
Example2:
";
$startdate = strtotime("+2 days", $startdate);
}
?>
Output:
Jun 28 Jun 30 Jul 02 Jul 04 Jul 06 Jul 08 Jul 10 Jul 12 Jul 14 Jul 16 Jul 18 Jul 20 Jul 22 Jul 24 Jul 26 Jul 28 Jul 30 Aug 01 Aug 03 Aug 05 Aug 07
- The second and third line of the above code is telling us about the starting date or day(here we have selected the Friday) which means the execution will start from Friday, and it lasts to 6weeks, and it will return Month and date to the user and it will also return weekdays with the difference of 2.
Example3:
Output:
There are 53 days remain left for Independence Day.
- In the above example, the ceil function is used by which we calculate the time from the current date to the given date.