Salesforce Primitive Data Types in Apex
Primitive Data Types in Apex
There are 5 major data types available in Apex:
- Primitive (Integer, Double, Long, Date time, String, ID, or Boolean).
- Collections (Lists, sets, and maps).
- sObject.
- Enums.
- Classes, Objects, and Interfaces.
Primitive Data Types
| Datatype | Description |
| Integer | A 32-bit number that doesn`t include a decimal point. Integer num1=15; Integer num2=55; |
| Long | A 64-bit number that doesn`t include a decimal point. Long num3=547150L; |
| Decimal | A number that include decimal points is called decimal. Decimal decNum=20.87; |
| Double | A 64-bit number that include a decimal points is called double. Double d=8.14255; |
| Boolean | A Boolean value can only be assigned true, false, or null. Boolean is Active=False. |
| Date | Date value contain no information about time. A value that indicates a particular day is known as Date. E.g., 2019-11-13. |
| Time | The time data type stores hours, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds. |
| DateTime | Datetime data type stores both dates and times. |
Declaring Date Data Type
To declare a date variable, we have to define a date data type and the name of the variable.
The Date is a class in Salesforce. It is a predefined class.
Date Methods
The methods for the date are:
| Method Names | Usage |
| day( ) | day( ) returns the day of the month component. |
| daysInMonth(year, month) | daysInMonth(year, month) returns the number of days in a month of the specified year and a month. |
| format( ) | |
| isLeapYear(year) | isLeapYear(year) returns true if the defined year is a leap year. |
| month( ) | month( ) returns the month component. |
| newInstance(year, month, day) | newInstance(year, month, date) composes a date from Integer representations of the year, month, and day. |
| parse(stringDate) | parse(stringDate) builds a date from a String. The format of the string depends upon the local date format. |
| today( ) | today( ) returns the current date according to the current user`s time zone. |
| valueof(stringDate) | valueof(stringDate) returns a date that contains the value of the specified String. |
| valueof(fieldValue) | valueof(fieldValue) converts the defined object to a date. |
| year( ) | year( ) returns the year component. |
Example:
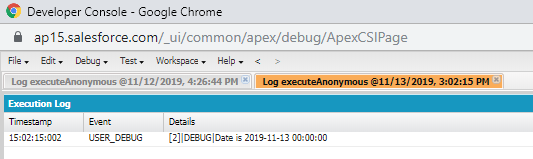
Date newDate=Date.newInstance(2019, 11, 13);
System.debug('Date is '+newDate);
Output:
Example:
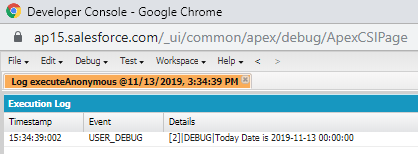
Printing today`s date.
Date today=Date.today();
System.debug('Today Date is '+today);
Output:
Example:
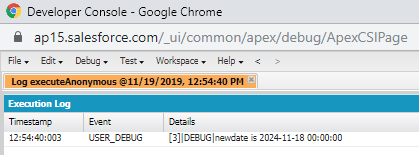
Adding years in today`s date.
Date todayDate=Date.today();
Date newDate1=todayDate.addYears(5); //The new date will be 19-11-2025
System.debug('newdate is ' +newDate1);
Output:
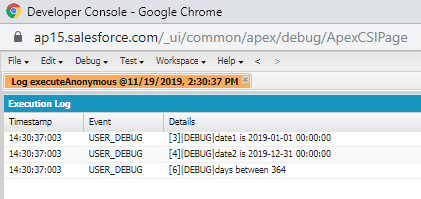
Example:
Adding months in today`s date
Date todayDate=Date.today();
Date newDate2=todayDate.addMonths(2); //The new date will be 19-01-2020
System.debug('new date is '+newDate2);
Output:
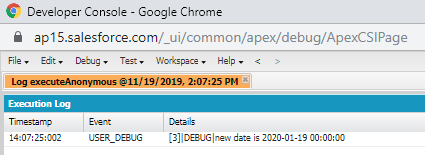
Example:
Adding days in today`s date.
Date todayDate=Date.today();
System.debug('today date is '+todayDate); //2019-11-19
Date newDate=todayDate.addDays(11);
System.debug('new date is '+newDate); //2019-11-30
Output:
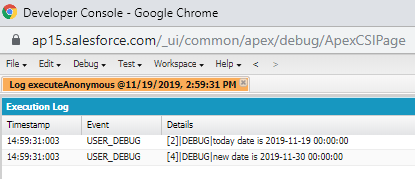
Example:
The below program is used to calculate no. of days between January 1 till December 31.
Date date1=Date.newInstance(2019, 1, 1); //The output will be 2019-1-1
Date date2=Date.newInstance(2019, 12, 31); //The output will be 2019-12-31
System.debug('date1 is '+date1);
System.debug('date2 is '+date2);
Integer daysdue=date1.daysBetween(date2);
System.debug('days between '+daysdue); //The output will be 364days
Output:
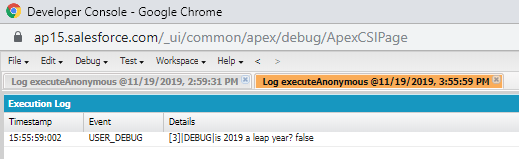
Example:
Date date1=Date.newInstance(2019, 11, 19);
Boolean isLeapYr=Date.isLeapYear(date1.year());
System.debug('is 2019 a leap year? '+isLeapYr); //False
Output:
Time:
Time is a primitive data type.
Time Methods:
The methods for Time are:
| Methods | Usage |
| addHours(additionalHours) | addHours(additionalHours) sum the defined number of hours to time. |
| addMilliseconds(additionalMilliseconds) | addMilliseconds(additionalMilliseconds) sum the defined number of milliseconds to a Time. |
| addMinutes(additionalMinutes) | addMinutes(additionalMinutes) sum the defined number of minutes to a Time. |
| addSeconds(additionalSeconds) | addSeconds(additionalSeconds) sum the defined number of seconds to a Time. |
| millisecond() | millisecond() returns the millisecond component of a Time. |
| minute() | minute() returns the minute component of a Time. |
| newInstance(hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) | newInstance(hour, minutes, seconds, milliseconds) build time from Integer representations of the defined hour, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds. |
| hour() | hour() returns the hour component of a Time. |
| second() | second() returns the second component of a Time. |
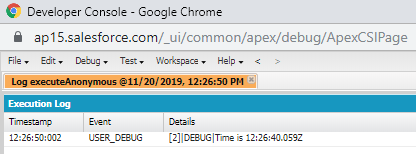
Example:
Time myTime=Time.newInstance(12, 26, 40, 59);
System.debug('Time is '+myTime);
Output:
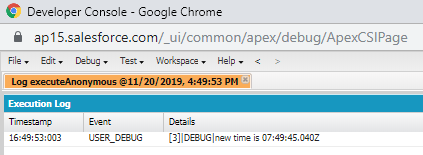
Example:
Time myTime=Time.newInstance(4, 49, 45, 40);
Time mytime2=myTime.addHours(3);
System.debug('new time after adding 3hrs is '+mytime2);
Output:
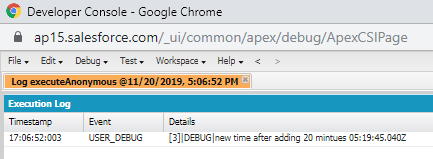
Example:
Time myTime=Time.newInstance(4, 49, 45, 40);
Time myTime3=myTime.addMinutes(30);
System.debug('new time after adding 20 mintues ' +myTime3);
Output:
Datetime:
Datetime constructs a Datetime from Integer representations of the defined year, month, day, hour, minute, and second in the local time zone. It will return datetime in GMT format.
Datetime Methods
| Methods | Usage |
| addDays(additionalDays) | This method adds the specified number of days to a given Datetime. |
| addHours(additionalHours) | This method adds the specified number of hours to a Datetime. |
| addMinutes(additionalMinutes) | This method adds the specified number of minutes to a Datetime. |
| addSeconds(additionalSeconds) | This method adds the specified number of seconds to a Datetime. |
| addYears(additionalYears) | This method adds the specified number of years to a Datetime. |
| date() | This method returns the Date component of a Datetime in the local time zone of the context user. |
| dateGMT() | This method returns Date component of the Datetime. |
| day() | This method returns the day-of-month component of a Datetime. |
| dayGmt() | This method returns the day-of-month component of a Datetime. |
| dayofYearGmt() | This method returns the day-of-year component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| format() | This method converts the date to the local time zone and returns the converted date as a formatted string by using the locale of the context user. And if the time zone cannot be determined, then GMT will be used. |
| format(dateFormatString) | This method converts to the local time zone and then returns the converted date as a string by using the Java simple date format. |
| formatLong() | This method converts the date to the local time zone, and it returns the converted data in a long date format. |
| getTime() | This method returns the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00. |
| hour() | This method returns the hour component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| hourGmt() | This method returns the hour component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| millisecond() | This method returns the millisecond component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| millisecondGmt() | This method returns the millisecond component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| minute() | This method returns the minute component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| minuteGmt() | This method returns the minute component of a Datetime in the GMT time. |
| month() | This method returns the month component of a Datetime in the time zone of the context user (1=Jan). |
| newInstance(milliseconds) | This method constructs Datetime and initializes it to represent the specified year, month, and day at midnight in the local time zone. |
| newInstance(date, time) | This method constructs a Datetime from the defined date and time in the local time zone. |
| newInstance(year, month, day) | This method constructs a Datetime from Integer representations of the defined year, month, and day at midnight in the local time zone. |
| newInstance(year, month, day, hour, minute, second) | This method constructs a Datetime from Integer representations of the defined year, month, day, hour, minute, and second. |
| newInstanceGmt(date, time) | This method constructs a Datetime from the specified date and time in the GMT time zone. |
| second() | This method returns the second component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| secondGmt() | This method returns the second component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| time() | This method returns the time component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| timeGmt() | This method returns the time component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| valueOf(dateTimeString) | This method returns the time component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
| valueOf(fieldValue) | This method converts the specified object to a Datetime. |
| valueOfGmt(dateTimeString) | This method returns a Datetime that contains the value of the specified String. |
| year() | This method returns the year component of a Datetime in the local time zone. |
| yearGmt() | This method returns the year component of a Datetime in the GMT time zone. |
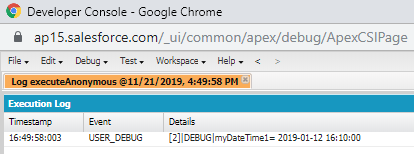
Example:
Datetime myDateTime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 1, 12, 8, 10, 00);
System.debug('myDateTime1= '+myDateTime1);
Output:
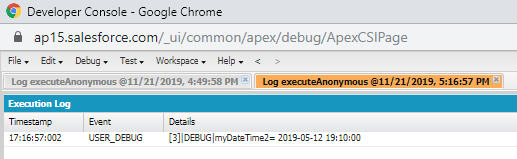
Example:
Datetime myDateTime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 5, 12, 8, 10, 00);
Datetime myDateTime2=myDateTime1.addHours(4);
System.debug('myDateTime2= '+myDateTime2);
Output:
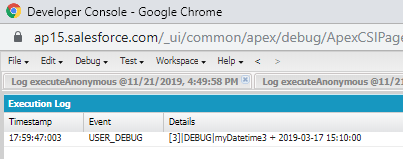
Example:
Datetime myDateTime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 3, 12, 8, 10, 00);
Datetime myDatetime3= myDatetime1.addDays(5);
System.debug('myDatetime3 + '+myDatetime3);
Output:
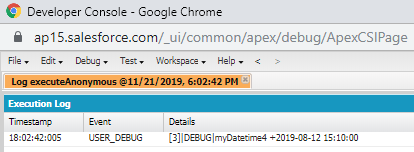
Example:
Datetime myDateTime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 3, 12, 8, 10, 00);
Datetime myDatetime4=myDatetime1.addmonths(5);
System.debug('myDatetime4 +'+myDatetime4);
Output:
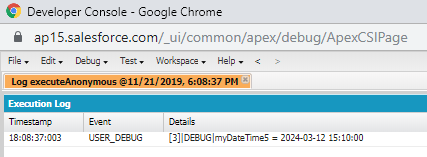
Example:
Datetime myDateTime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 3, 12, 8, 10, 00);
Datetime myDateTime5=myDateTime1.addYears(5);
System.debug('myDateTime5 = '+myDateTime5);
Output:
Example:
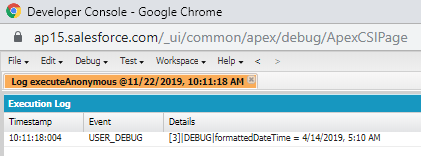
Datetime newDatetime1=Datetime.newInstance(2019, 4, 14, 5, 10, 15);
String formattedDateTime=newDatetime1.format();
System.debug('formattedDateTime = '+formattedDateTime);
Output: