Session Layer and Presentation Layer
Session Layer and Presentation Layer
Session Layer
The fifth layer is the Session layer in the OSI model, which controls connections between many computers. It manages, establishes, and terminates the session connection between two communication hosts. The figure shows below.
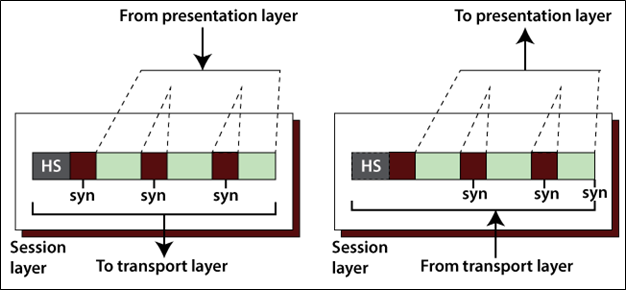
Major functions of the Session Layer
- Dialog control: In the session layer, it permits two systems to enter a dialog that permits the communication between two processes in either half-duplex mode and full-duplex mode.
- Synchronization: It allows us to incorporate checkpoints into the data stream. For example, suppose the system is sending a message of 1000 bits, it inserts the checkpoints after every 50 bits and to ensure that each 50 bits unit is received and acknowledged individually. In this case, if a crash happens during the transmission of 453 bit, that only needs to be a retransmission of 401 to 453. Previous of 401 bits are not required to re-sent.
- Token Management: The session layer stops two hosts from attempting the same operation at the same time.
Necessary protocols of the session layer
- Remote procedure call protocol (RPC)
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
- Session Control Protocol (SCP)
- Session Description Protocol (SDP)
Presentation Layer
The sixth layer is the Presentation Layer in the OSI model. In the Presentation layer, it deals with the syntax and semantics information which exchanges between two systems. The figure shows below.
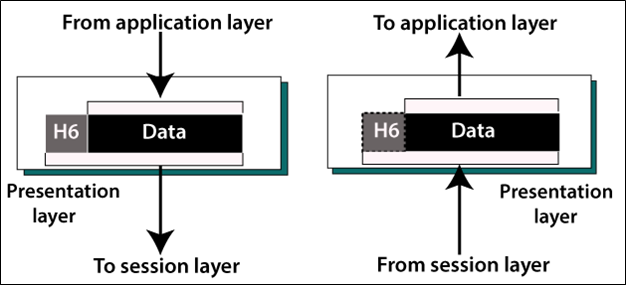
Major functions of the Session Layer
- Translation: It converts a message to compatible bit-streams before being transmitted. Because various computers use various encoding methods, it is responsible for interoperability between these various encoding methods, which is changing the message into a standard format.
- Encryption: Encryption means to transform the original message into another form, that will not be readable by others.
- Compression: In Compression, Reduces the number of bits to be transmitted over the network.