Specialization in DBMS
Specialization in DBMS
In the database management system, specialization breaks the higher-level entity into two or more than two lower entities. The main motive of this concept is to share the common attributes or properties between the entities in the same database.
This concept follows the top-down approach, which is just opposite to the generalization concept. The DBMS generalization concept combines the two or more lower-level entities in any database and form a new higher-level entity with the same properties of lower-entities.
Steps for Implementing the Specialization
If any user wants to implement the specialization concept for breaking the entity, then we have to follow the following steps one by one:
Step 1: The first step for each user is to identify the entity for breaking it into two or more entities.
Step 2: After that, the user has to examine the attributes of the identified higher-level entity.
Step 3: Now, the user has to define the subclasses or lower-level entities, which consist of the attributes of the higher-level entity. The lower-level entities are termed as specialized entities.
Step 4: This is the last step. In this step, the user has to define the relationship between the specialized entities and higher-level entity.
Example
Let us consider; there is a higher-level entity in the Company database, whose name is Employee. The Employee entity consists of five fields, whose names are ID, Name, Address, Age, and Salary.
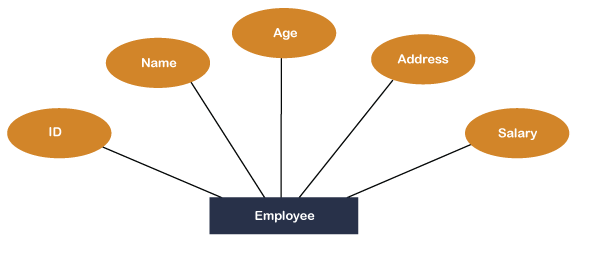
This Employee entity can be further broken into three entities in the same database, i.e., Tester, Accountant, and Coder. These three subclasses are the three types of employees who work in the same company, and all these three entities have common properties which are related to the parent Employee entity.
Difference Between Specialization and Generalization
| Specialization | Generalization |
| 1. This concept of a database system works in a top-down manner. | 1. This concept of a database system works in a bottom-up manner. |
| 2. In the generalization concept, schema size gets increased. | 2. In the generalization concept, schema size gets reduced. |
| 3. This technique is applied to the single higher-level entity. | 3. This technique is applied to the multiple lower-level entities. |
| 4. Inheritance process occurs in this mechanism because the properties of the superclass are shared with the subclasses. | 4. Inheritance process does not occur in this mechanism. |
| 5. In this technique, the higher-level entity of the ER diagram may not have the entities of the lower level. | 5. The higher-level entity in this technique must have lower-level entities. |
| 6. This mechanism splits the higher-level entity and form new entities with common properties. | 6. This mechanism takes the common features of multiple lower-level entities and forms a new higher entity. |