Unix Operating System
Unix Operating System
Unix Operating System is a multiuser, portable, time-sharing, and multitasking operating system that was developed in 1969. Unix operating system was developed by a group of AT & T Laboratory employees Dennis Ritchie, Joe Ossanna, Douglas Mcllroy, and Ken Thompson at Bell Labs. The first language that was used to developed a Unix operating system was Assembly Language and then the Unix operating system was developed by using the C language in 1973.
There are several types of Unix operating system which are present in the market such as AIX, BSD, Solaris, and HP Unix. Unix operating system is known as multiuser system because multiple users can use it simultaneously.
Unix operating system is a multitasking environment because in this, we can run number of programs simultaneously.
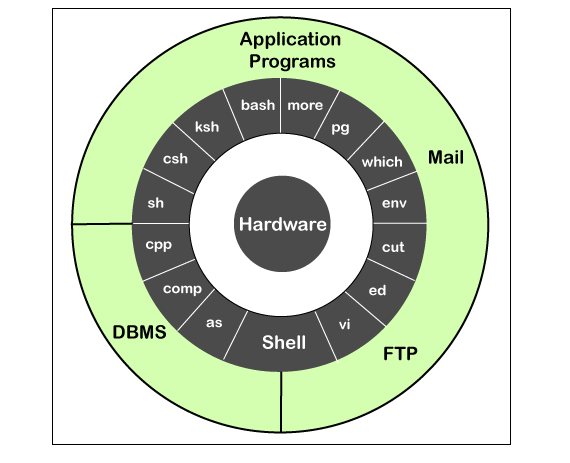
Unix operating system is mainly made up of three parts such as Kernel, Shell, and File.
Features of Unix Operating System
There are various features of Unix operating System:
- Open Source
- Multitasking capability
- Multi user capability
- Security
- Portability
- Communication
- Open Source: - The Unix operating system is an open source code. So anyone can modify the code of the Unix operating system as per the requirements.
- Multitasking Capability: - The Unix operating system is a multitasking operating system because in Unix operating system, multiple programs can be run simultaneously. And this feature increases the utilization of the CPU resources. In Unix operating system, we can type a program in a program editor and concurrently we can also run some other commands.
- Multiuser Capability: - The Unix operating system is a multiuser operating system because it allows multiple users to use a system simultaneously.
- Security: - The Unix operating system is a highly secured operating system because Unix use different provisions to protect the data. Every Unix user is happy to work with the Unix operating system because it provides a virus-free environment to the user.
There are two security levels provided by the Unix operating system:
- File Level Security: - File level security is managed or, controlled by the owner of the file.
- System Level Security: - System level security is managed or controlled by the system administrator.
- Portability: - Portability is the wonderful feature of the Unix operating system. In the Unix operating system, the term portability means that Unix is able to port to every type of operating system. Unix operating system is portable because it is written in C language and the C language is also a portable language.
- Communication: - The Unix operating system provides a tremendous communication among the users. The communication can be of any kind means the communication can be within network of the one main computer or in between the network of two or more computer.
In the Unix operating system, we can easily exchange data, programs and mail via networks.
Architecture of Unix Operating System
The operating system is mainly made up of four components:
- Kernel
- Shell
- Files and Directories
- Commands and Utilities
- Kernel: - Kernel is the main component of the operating system. It is like the heart of the operating system. The main task of the kernel is to interact with the hardware and various types of task such as File management, Memory management, and Task management.
- Shell: - Another component used to implement a Unix operating system is Shell. Shell is the essential component of the Unix operating system. The shell is a command line interpreter. When the user types the command, the shell interprets it and then shell call that program which need a user. There are various types of standard syntax shell used for the commands such as Korn Shell, C Shell, and Bourne Shell.
- Commands and Utilities: - Another component of the Unix operating system is commands and utilities. There are different types of command and utilities which is used to develop the Unix operating system such as grep, mv, cp, and cat.
- Files and Directories: - In Unix operating system, files are used to organize the data. Then we organize the files into the directories. Again, organize the directories into a Tree-structure.