Virtual Memory in Operating System
What is Virtual Memory
Virtual Memory is a storage scheme in which the users have an illusion that users have a significant amount of Main Memory. We can perform this by taking a section of Secondary storage as the Main Memory.
With the help of virtual memory, we can load or store the large size processes than the available memory.
In other words, Virtual Memory is defined as an area in which the programs of large size are able to store themselves in the form of pages.
Virtual Memory is helpful in the scenario where the users have a small amount of physical memory. With the help of demand paging and demand segmentation, virtual memory is implemented.
How Virtual Memory Works
In today’s scenario, the concept of Virtual Memory is quite common. Virtual Memory is used when pages need to be loaded in the Main memory, but there is no availability of memory for the pages.
So, in this situation, instead of avoiding pages to enter into the Main Memory, the operating system finds the space for RAM (Random Access Memory) which are slightest used in the current time or, which are not referenced into the secondary storage for the purpose of creating the space for the new pages into the Main memory.
Because all this mechanism is done automatically, so this makes the computer with a more amount of RAM (Random Access Memory).
Benefits of Virtual Memory
The benefits of virtual memory are:
- With the help of Virtual Memory, we can execute the number of processes at once.
- It is helpful to fit the various programs into a smaller program.
- With the help of Virtual Memory, we can run multiple applications at a time.
- In this, a similar code or data can be shared with the memory.
- Code or data must be read from the disk when needed.
- Virtual Memory is useful in the implementation of a multiprogramming environment.
- The processes are kept in the main memory. Due to this, the CPU is used effectively.
- In Virtual Memory, the user is able to run a large-size application in the less RAM.
- In Virtual Memory, no requirement to purchase or buy more RAMs memory.
- We can place the code anywhere in the physical memory without any need for relocation.
Drawbacks of Virtual Memory
The drawbacks of virtual memory are:
- Virtual Memory can reduce system stability.
- Virtual memory does not provide the same performance as RAM.
- When the system use virtual memory, then the application may run slower.
- To switch between the applications, Virtual Memory requires more time.
- If we use Virtual Memory, then we don’t have more hard disk space for its use.
Snapshot of a Virtual Memory Management System
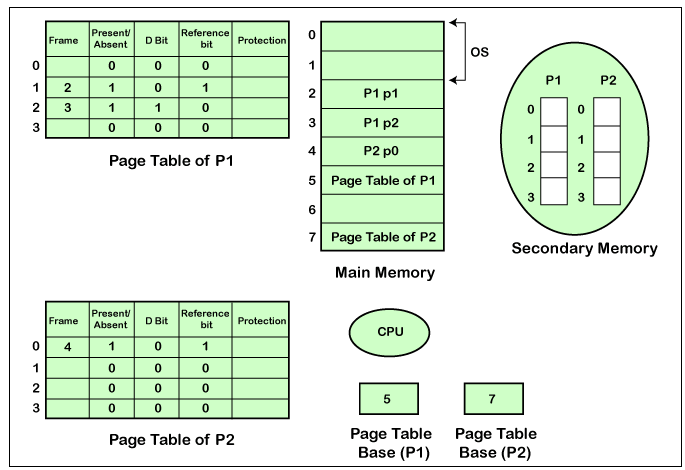
Suppose we have two processes, which are process P1 and the process P2. Process P1 and P2 comprises of four pages. Each page size is 1 KB. There are eight frames that are present in the Main Memory, and the size of each frame is 1 KB. The operating system is residing in the first 2 partitions. The first page of the process P1 is stored in the third partition. In the memory, the other frames are also occupied with the different process pages.
The size of each page table is 1KB. So, we can fit each of these in one frame. We can see in the above diagram; the page table consists of several types of information.
There is a register contained in the CPU that includes the base address of the page table. The base address of the process P1 is 5, and the base address of the process P2 is 7. To access the actual corresponding entry, the base address of the page table is added to the page number of the logical address.