SQL Data Manipulation Language
Data Manipulation Language manipulates/make changes in data present in a table.
It only affects data/records of table, not on the schema/structure of table.
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE are the commands of DML.
- INSERT INTO table_name VALUES ( value1,value2,….);
- INSERT INTO table_name (column 1,column 2, column 3) VALUES (value1, value2,value3);
Example:
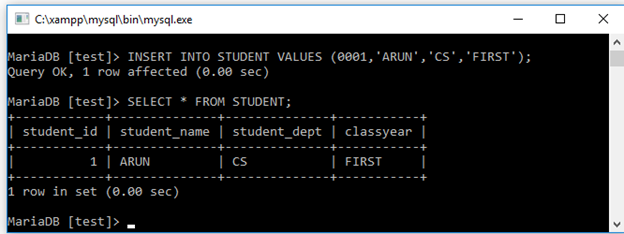
INSERT INTO STUDENT VALUES (0001,'ARUN','CS','FIRST');
INSERT INTO STUDENT (classyear, student_name,student_dept,student_id) VALUES ('FIRST','VRUN','CS',0002);
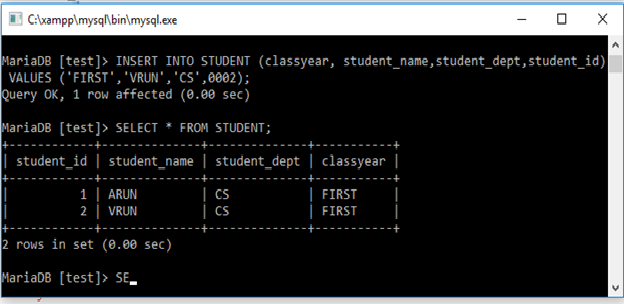
Here, user can change the sequence of columns while inserting values in table. We can increase or decrease number of columns.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM Table_name [WHERE Condition];
Example:
Delete From Student Where Student_id=06;
Here, Single row is deleted as per where condition.
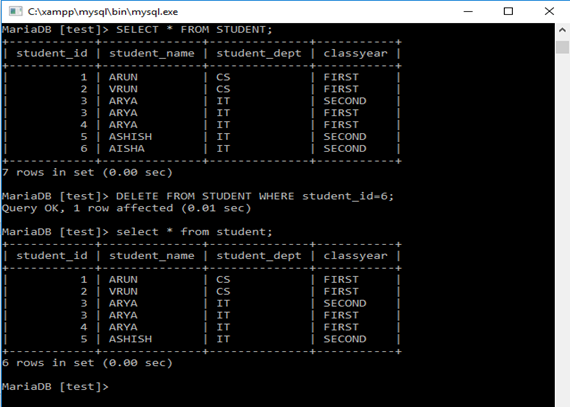
Delete From Student Where Student_name=’ARYA’;
Multiple rows deleted, as three rows were present with the same name ARYA. Here, where condition decides how many records to delete.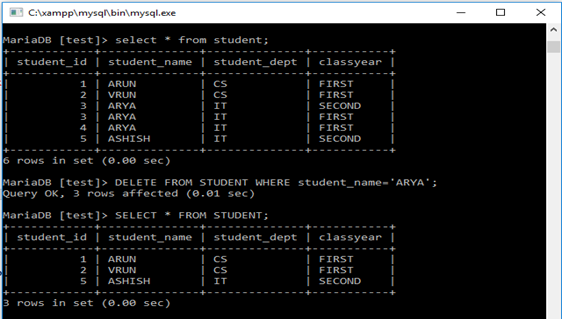
Delete From Student;
In the above query, where condition is not specified so, all records are deleted from STUDENT table. If user want to delete single or multiple records then where condition is required. Delete query without where condition deletes all records from table.
Syntax:
UPDATE Table_name set column_name = value [Where condition];
Example:
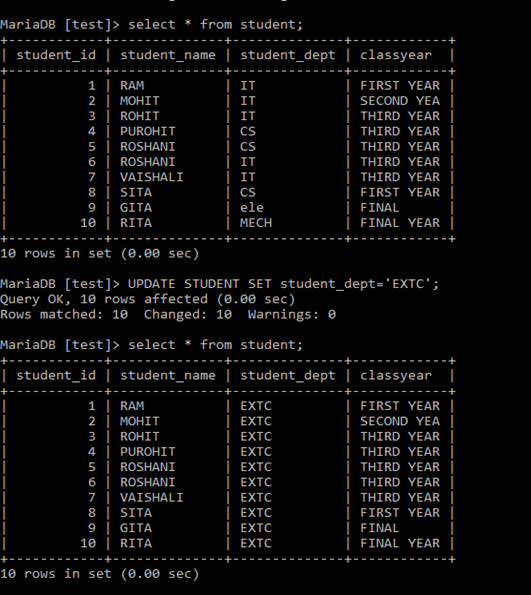
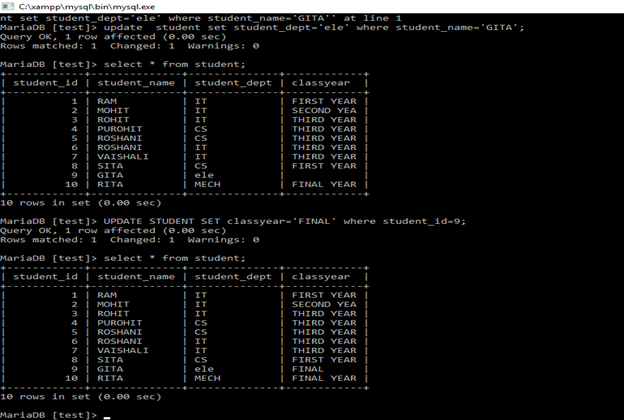
update student set student_dept='ele' where student_name='GITA';
UPDATE Student SET classyear='FINAL' Where student_id=9;
By using UPDATE command, user can update single value or multiple values in the table.
To change single value/to change specific value, ‘Where’ condition is required.
UPDATE without where condition changes complete column values in the table.
UPDATE STUDENT SET student_dept='EXTC';