Teradata Tutorial for Beginners
Introduction to Teradata
Teradata Corporation is an IT firm in America which provides vendor of analytic data platforms, application and other services. This firm develops products with strong data from the various sources and it also makes the data available for analysis.
"Teradata is a type of Relational Database Management System RDBMS. Teradata is a parallel open processing system used for developing large scale data warehouse application."
It can handle large volumes of data which are highly scalable. It is an open system which can be run on any operating system like Linux/Unix/Windows etc. Teradata provides many tools which support multiple data warehouse operations at the same time to different clients.
Teradata provides strategic intelligence and operational intelligence for active data warehouse. Strategic intelligence provides intelligent tools and utilities and queries that support strategic decision making. For example it can provide complex reports of the day which indicates business trends and predict it will continue to occur or not. Whereas operational intelligence provides intelligent tools and utilities and query that support operational or front line decision making.
In Teradata, active load is used to load data actively and inn one tending manner and also process other workloads at the same time. It also provides active load delivery for continuous data loading, which include streaming a queue, frequent batch update and moving changed data from other database platform to Teradata.
In Teradata Active Access is used for quick analytical intelligence which support operational business processes. The main benefit of Active Access is that it speeds up user and customer requests.
History of Teradata
| 1979 | Association of Teradata |
| 1984 | Release of Teradata first database computer DBC/1012 |
| 1986 | Teradata was declared as ‘Product of the Year’ by Fortune magazine. |
| 1999 | Built largest database using Teradata with 130 Terabytes |
| 2002 | V2R5 version release with Partition Primary and compression |
| 2006 | Launch of Master Data Management solution |
| 2008 | 13.0 released with Active Data Warehousing |
| 2011 | Acquires Teradata plunges and Aster into the Advanced Analytics Space |
| 2012 | Teradata 14.0 introduced |
| 2014 | Teradata 15.0 introduced |
| 2015 | Buys Apps Marketing Platform Appoxee |
| 2016 | join hands with Big data |
| 2017 | Acquires San Diego's StackIQ |
Features of Teradata
- Linear Scalability: It offers linear scalability when it deals with large data. It adds nodes to increase the performance of system.
- Unlimited Parallelism: It is based on MPP (Massively Parallel Architecture). So it is designed to be parallel since the beginning. A large task can be divided into smaller tasks and can be run parallel.
- Mature Optimizer: Teradata Optimizer can handle at least 64 joins in a query.
- Low TCO: Its ownership total cost is very low which is easy to setup, maintain, and administrate.
- Load & Unload utilities: It provides load & unload facility to move data into or from Teradata System.
- Connectivity: Main frame or network-attached systems can be connected to channel-attached systems of MPP system.
- SQL: It supports SQL which interact with the data stored in tables.
- Robust Utilities: It provides robust utilities to import and export data from or to Teradata systems like TPT, MultiLoad, FastLoad and FastExport.
- Automatic Distribution: It can distribute data to the disks with no manual intervention.
Architecture of Teradata
Teradata architecture is a MPP Architecture.
There are 3 important components of Teradata:
- Parsing Engine
- BYNET
- Access Module Processors (AMPs).
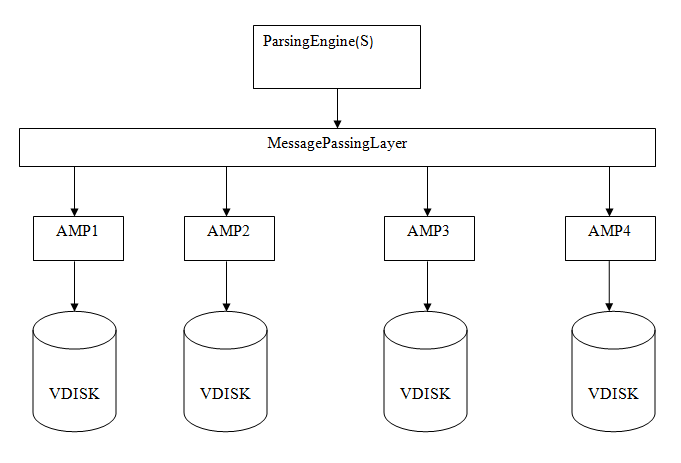
Storage Architecture
1. Parsing Engine
It parses the queries and also prepares the execution plan. It also manages the session for the user. It sends and optimizes the request to the users. When a client executes queries for inserting records, the parsing engine sends the records to the Message Passing layer. Message passing layer is also known as BYNET. Message passing layer is a software and hardware component. It offers networking and also retrieves the records and sends it to the target AMP.
2. AMP
It stands for Access Module Processor. It is used to check records on disks. AMP is used for the following activities:
- It is used to manage the database portion.
- It can manage the portion of each and every table.
- It can perform all task associated with generating a result set like a join, aggregation and sort.
- It also Performs Space management.
3. Retrieval Architecture
When the query for retrieving records is sent by the client, the parsing engine sends a request to BYNET. BYNET sends the request to the AMPs.
AMPs search in there disk parallel and recognize the required record and send it to BYNET.
AMPs search their disks in parallel and recognize the required records and send to BYNET. BYNET sends the records to Parsing Engine which is sent to the client.
Difference Between MPP and SMP
| MPP | SMP |
| MPP stands for Massively Parallel Processing. | SMP stands for Symmetric Multi-Processing. |
| In this computer system, many independent arithmetic units or entire microprocessors that run in parallel are attached. | The CPU's share the memory so code running in one system can affect the memory used by any another. |
| Databases are expanded by adding new CPUs. | It uses only one CPU to perform database searches. |
| No resources are shared among physical computers, so performance is improved. | The workload is distributed across the processors in the system for parallel jobs. |
| Performance of a MPP system is linear which will increase the number of nodes. | SMP databases run on multiple servers. It can share another resource. |
Advantages of Teradata
1) Teradata database is linearly scalable: It can expand the database capacity by adding more nodes to the existing database.
2) Extensive parallel processing: It has parallel processing capacity. It can also handle request from multiple ad-hoc and from many concurrent users.
3) Shared nothing architecture: The architecture of the Teradata database is also not shareable. It can tolerate faults and data protection.
Disadvantages
1. It is not suitable for small transaction OLTP databases.
2. Development of Teradata and DBA resources are harder to come by and therefore more expensive.
Applications of Teradata
- Customer Data Management: Helps to create and maintain long-lasting relationships with customers.
- Master Data Management: It develops an environment where master data can be used and synchronized and can be stored.
- Finance and Performance Management: It helps to improve speed and quality of financial report of an organization. It reduces finance infrastructure costs.
- Supply Chain Management: It improves operational chain which helps to improve customer services and reduces the time cycle.
- Demand Chain Management: It increases customer service sales and levels. It also predicts the demand for store item accurately.