RPA Tutorial
What is RPA (Robotic Process Automation)?
The RPA stands for "Robotic Process Automation." It supports several manual and repetitive tasks to automate like human beings. We can say that “RPA is a process of creation and training of software bot (automated programs) to automate the business process.”
“The RPA is the technology which allows anyone to configure the computer software or robot for emulating and integrating the actions of humans to interact within the digital systems to implement or execute the business process."
RPA is the digital workforce. It interacts with the computer system in the same as the human does. It automates repetitive and tedious tasks.
Robotic Process Automation is the sequence of commands which are executed by the automated programs under some defined sets of business rules.
The primary purpose of RPA is to replace repetitive and boring clerical tasks into the virtual workforce by robots or machines. We train the bots (automated programs) what to do and let them do the work.
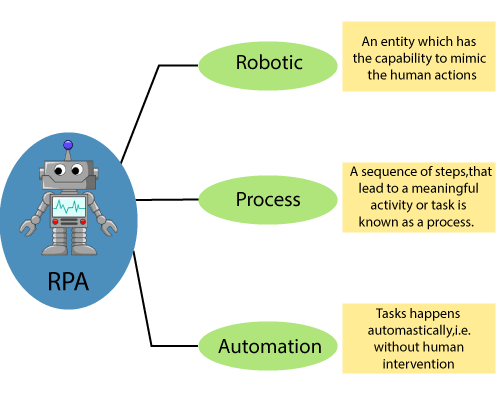
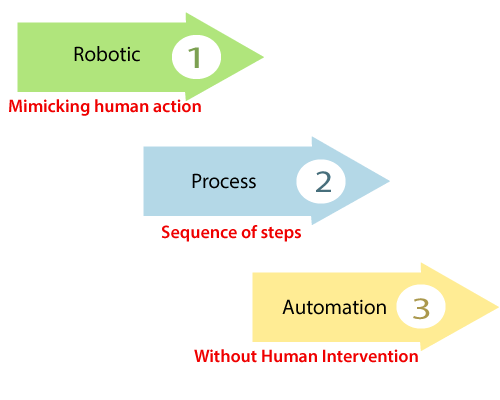
The RPA is an acronym for Robotic Process Automation. These three terms are given below:
Robotic: The Robotic means "an entity which can be a program to mimic human actions." The unit or entity which is capable of being programmed by the computer for doing the complex tasks is called a robot.
Process: Process is the sequence of steps that leads to meaningful activity or task.
Automation: when any task happens automatically without human intervention, it is known as automation.
RPA History
The Robotic Process automation is used in both IT and Non-IT industries. Nowadays, every organization have a repetitive, boring, tedious task so, RPA is necessary to eliminate these types of task by making the automation of tasks. It creates a fast growth of the business processes.
The machine learning was the first step towards the creation of Robotic Process Automation. In 1959, it was developed by the "Arthur Samuel." He was working in IBM in the field of artificial intelligence.
In the 1960s, Natural Language Processing was developed, which is combined artificial intelligence with the interactions between computers and human beings.
In the early 1990s, Artificial Intelligence was taken over by many industries, especially for manufacturing companies. But its implementation within the financial sector has suddenly decreased because of its costs and implementation problems. This was when Natural Language Processing came in the IT industries.
The primary purpose of NLP (Natural Language Process) was to help the computer to understand and process the human language more accurately. The Machine Learning and Natural Language processing both can be seen in the Robotic Process Automation.
RPA Component
The components of RPA have together build a platform, which can automate any repetitive task. Robotic Process automation is beneficial for the reusability within the systems, simplify changes, etc.
It has focused on the business rules without any need to create the links. The RPA is also beneficial to the target application integration, which can be changed without the risk of changing business rules.
In the field of Robotic Process Automation, the development does not require the understanding of business rules.
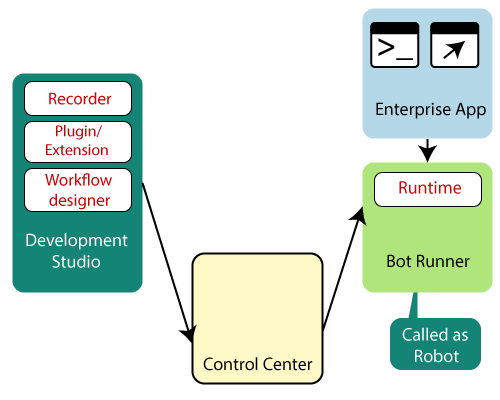
Figure: Component of RPA
There are some basic components of RPA which are given below:
- Recorder
The UiPath’s recorder is used to record the UI mouse movements and keyboard activities to generate automation scripts.
These recorded activities are generated as per sequence or well maintained in increasing order. The recorder can also be used to playback the recorded actions.
- Development Studio
The Development Studio or UiPath studio is used to create or develop the automation workflows by which we can automate the task easily.
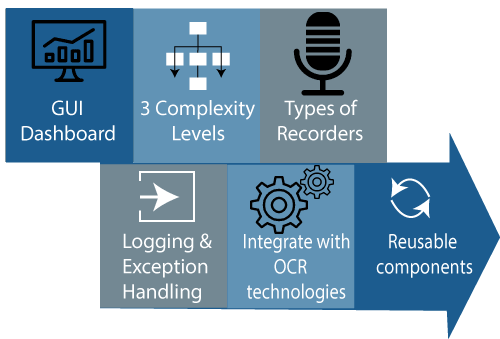
Figure: Features of Development Studio.
There are some features of UiPath studio which are given below:
- GUI Dashboard
- Three Complexity Levels
- Types of Recorders
- Logging and Exception Handling
- Integrate with the OCR technologies
- Reusable components
- Plug-in/Extension
The Reusable RPA plugins are the programs that can be added in the RPA tool to take care of specific tasks such as data extraction from invoices, manipulate the dates in different databases, and transcribing speech. This plugin/Extension is very useful due to fewer development efforts, error rates, and implementation time.
- Bot (automated program)Runner
Bot Runner is the machine where the user can run the bot (automated program). The user could have multiple bots running in parallel. The user only needs the run license to run the bots.
- Control Center
The Control Center is the centralized dashboard where the user can easily schedule, manage, control, and scale the activity of a vast digital workforce.
RPA Features
Artificial intelligence and cognitive intelligence are two common features of RPA. Both features are involved in machine learning, computer vision, and cognitive automation to help the bots for improving the decision making over the period.
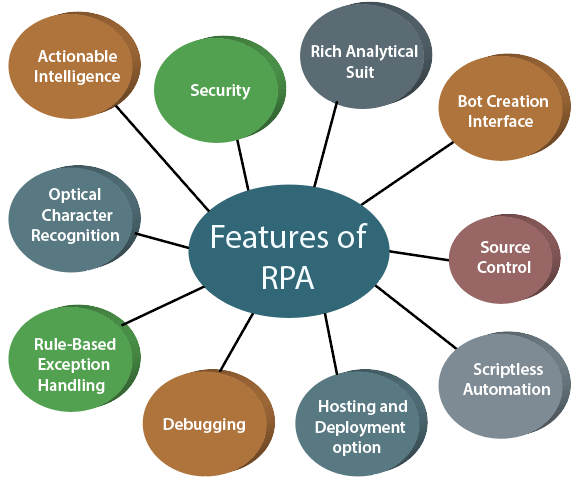
There are some unique features of RPA which are given below:
1. Rich Analytical suit
The Rich Analytical suit is used to discover the performance of the robot workforce. It manages and monitors the automated functions from the central console in RPA.
2. Security
The RPA tools include role-based security, which ensures the action-specific permissions. Some Robotic Process Automation tools enable the configuration as well as customization of encryption capability to secure a specific data type against the interruption of network communication.
3. Bot Creation Interface
Robotic Process Automation tools support the creation of bots quickly and effortlessly. RPA product includes the option to create and edit bots manually by using the Task Editor.
4. Source Control
The Source Control method allows developers to examine the difference between versions of a particular process to discover what has changed.
5. Hosting and Deployment Option
RPA supports customer deployment across virtual machines, terminal services, and cloud. As compared to other deployment options, cloud deployment attracts most of the customers for its scalability and flexibility. The RPA system is very powerful in deploying the robots in a group of hundreds automatically.
6. Rule-Based Exception Handling
The Robotic Process Automation allows deployment with the rule-based exception handling. This feature of RPA proactively handles the exception.
7. Debugging
Few RPA tools should stop running to make the change and replicate the process. Other RPA tools allowed dynamic interaction at the time of debugging. Debugging is a very important feature of RPA.
8. Scriptless automation
The RPA tools are code-free and may automate the application of any department. The employee or user with less programming skills can also create the bots.
9. Seamless Integration
This feature of RPA is mainly used for the optimization of the user's software infrastructure to fit into the purpose of achieving data management and enterprise decision making.
10. Optical Character Recognition
The optical character recognition in the RPA is a new trend nowadays. Screen Scraping is the most standard feature of the RPA tool, which deals with the capturing of bitmap data from the system screen and cross-check it against cross details. This process is integrating with OCR engines like Microsoft and Google.
11. Actionable Intelligence
This Actionable feature of RPA refers to the ability to gain and apply the knowledge as the skills. The Robot obtains both structured and unstructured data, and they can convert it into the information, and that information transforms into the actionable intelligence for the end-user or customers.
RPA Key Challenges
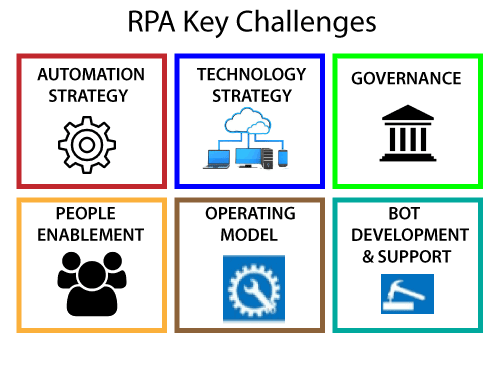
There are some important key challenges in implementing the robotic process automation, which is given below:
- Automation Strategy
- Technology Strategy
- Governance
- People Enablement
- Operating Model
- Bot Development &Support
RPA Life Cycle
The RPA life cycle has six phases. This RPA life cycle doesn't have a defined structure. All these stages of the RPA life cycle are used to execute the build bot (automated program). The brief explanations of all stages of RPA life cycle are given below:
- Discovery Phase
The process architect in this phase analyzes the client's requirements. According to the client’s requirement, it is decided that the process can be automated or not. If the process is automated, then the complexity of the process is analyzed. After this Discovery phase, the next phase is the Solution Design Phase.
- Solution Design Phase
The solution or steps to automate the task is designed in this phase. The Technical architect makes the Process Definition Document (PDD) collaborate with the Process Architect. This document contains the information of every process or steps in depth.
Once the client's requirement is analyzed, and the Process Definition Document is created, then the next process is to decide some requirements for the project, such as Budget, time to be spent, number of people working on the project, etc.
Then, the project architects need to create the Object Model Diagram of Flow Chart to understand the flow of the process.
The architects will be able to understand with the help of the flow chart, which step has to be automated, and what are the requirements for that step.
After the creation of Flow Chart, the project architect need to choose an RPA tool to automate the task, and then, they are ready to start with developing the bot.
So, the next phase is the Development Phase, which is given below.
- Development Phase
In the Development Phase, the automation developer creates an automation script with the help of the chosen RPA tool. These automation Scripts are created by referring to the previously created process definition document (PDD).
There are various RPA tools present in the market, but the top three RPA tools are UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere.
The required automation depends on the task; they may or may not require the coding. There are several Scenarios in RPA, where the user does not need coding at all.
- UAT (User Acceptance Testing)
The User Acceptance Phase comes after the development Phase in the RPA lifecycle. In this phase, the Developed bot is tested either by the testing team or the development team itself.
The bot (automated program) is tested in the pre-production environment. In this environment, the testing team tests how the users can use this bot to automate the specific task.
If the testing is successful, then we will move forward to the next stage. But if testing fails, then the bot (automated program) goes back to the previous development phase.
In the previous phase, the errors are found in the testing phase, which is rectified and needed to be tested again.
Once the bot is successfully tested, and then we move forward to the next stage in the RPA life cycle.
- Deployment and maintenance phase
After developing and testing the bot, we need to deploy the bot (automated program) into the production environment. Once the bot is deployed, the user can easily use it.
But, if there is an issue with the bot, then we need to go back to the development phase again, and the testing team resolves the issue.
- Execute bots
In this phase of the RPA life cycle, the bots are executed, and after that, we need to check the generated meaningful result.
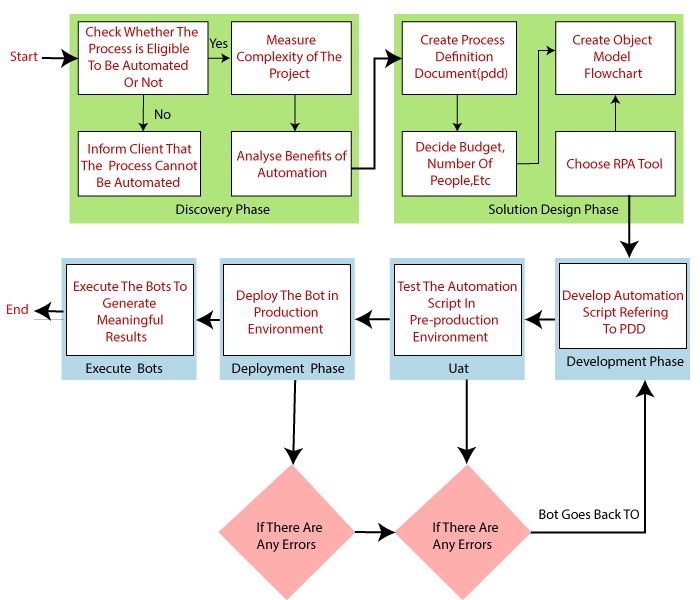
Figure: The Process of building the bot
Example of RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Most of individuals demand automation. Robotic Process Automation allowed the organizations to make the use of their robotic software to finish all the repetitive, time-consuming work for improved customer satisfaction.
After the development of RPA, employees can now look into many other matters instead of doing the same old boring task. There are some fields where we can use the Robotic Process Automation, are given below:
1. Website Scrapping
The website scraping, web harvesting, screen scraping, or web data extraction is the data scraping which is used for extracting the data from websites.
The web scraping software may access the World Wide Web directly by using the hypertext protocol or web browser. It is related to downloaded structured data from the web.
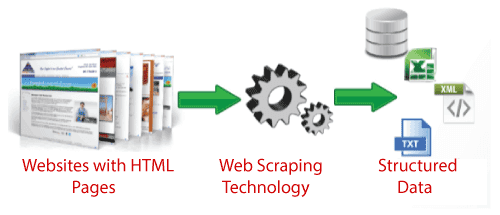
There are various advantages of web scrapping which are given below:
- Fewer errors and cost
- Faster Setup
- Maintenance of the Scrapping team is not required.
- Automate the batch to download the task.
- Gather social media data.
2. Transferring the data from one system to another
Organizations are wasting their time to manage their data for the backups and restorations so, the transformation of data from one system to another is the example of RPA.
3. Call Center Operations
The call centers of any organization have all the information about the customer on a single screen instead of looking into different applications to gain access to different kinds of details.

There are some advantages of RPA implementation in the area of the call center that are given below:
- Shorter average of call duration.
- Improvement in communication.
- Optimized use of resources.
- Automated responses and triggers.