Alpha-beta Pruning | Artificial Intelligence
Alpha-beta pruning is an advance version of MINIMAX algorithm. The drawback of minimax strategy is that it explores each node in the tree deeply to provide the best path among all the paths. This increases its time complexity. But as we know, the performance measure is the first consideration for any optimal algorithm. Therefore, alpha-beta pruning reduces this drawback of minimax strategy by less exploring the nodes of the search tree.
The method used in alpha-beta pruning is that it cutoff the search by exploring less number of nodes. It makes the same moves as a minimax algorithm does, but it prunes the unwanted branches using the pruning technique (discussed in adversarial search). Alpha-beta pruning works on two threshold values, i.e., ? (alpha) and ? (beta).
- ?: It is the best highest value, a MAX player can have. It is the lower bound, which represents negative infinity value.
- ?: It is the best lowest value, a MIN player can have. It is the upper bound which represents positive infinity.
So, each MAX node has ?-value, which never decreases, and each MIN node has ?-value, which never increases.
Note: Alpha-beta pruning technique can be applied to trees of any depth, and it is possible to prune the entire subtrees easily.
Working of Alpha-beta Pruning
Consider the below example of a game tree where P and Q are two players. The game will be played alternatively, i.e., chance by chance. Let, P be the player who will try to win the game by maximizing its winning chances. Q is the player who will try to minimize P’s winning chances. Here, ? will represent the maximum value of the nodes, which will be the value for P as well. ? will represent the minimum value of the nodes, which will be the value of Q.
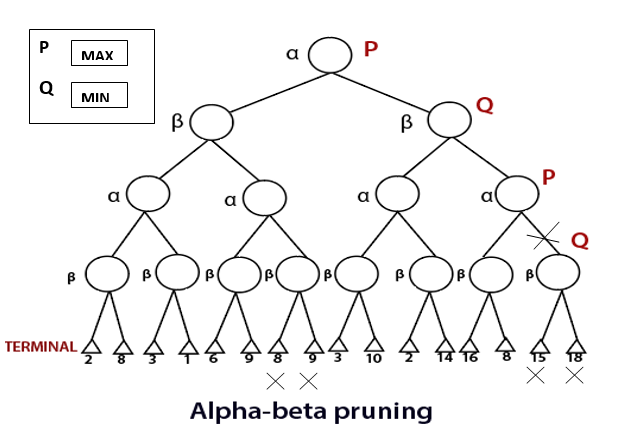
- Any one player will start the game. Following the DFS order, the player will choose one path and will reach to its depth, i.e., where he will find the TERMINAL value.
- If the game is started by player P, he will choose the maximum value in order to increase its winning chances with maximum utility value.
- If the game is started by player Q, he will choose the minimum value in order to decrease the winning chances of A with the best possible minimum utility value.
- Both will play the game alternatively.
- The game will be started from the last level of the game tree, and the value will be chosen accordingly.
- Like in the below figure, the game is started by player Q. He will pick the leftmost value of the TERMINAL and fix it for beta (?). Now, the next TERMINAL value will be compared with the ?-value. If the value will be smaller than or equal to the ?-value, replace it with the current ?-value otherwise no need to replace the value.
- After completing one part, move the achieved ?-value to its upper node and fix it for the other threshold value, i.e., ?.
- Now, its P turn, he will pick the best maximum value. P will move to explore the next part only after comparing the values with the current ?-value. If the value is equal or greater than the current ?-value, then only it will be replaced otherwise we will prune the values.
- The steps will be repeated unless the result is not obtained.
- So, number of pruned nodes in the above example are four and MAX wins the game with the maximum UTILITY value, i.e.,3
The rule which will be followed is: “Explore nodes if necessary otherwise prune the unnecessary nodes.”
Note: It is obvious that the result will have the same UTILITY value that we may get from the MINIMAX strategy.