Cryptarithmetic Problem in AI
Cryptarithmetic Problem
Cryptarithmetic Problem is a type of constraint satisfaction problem where the game is about digits and its unique replacement either with alphabets or other symbols. In cryptarithmetic problem, the digits (0-9) get substituted by some possible alphabets or symbols. The task in cryptarithmetic problem is to substitute each digit with an alphabet to get the result arithmetically correct.
We can perform all the arithmetic operations on a given cryptarithmetic problem.
The rules or constraints on a cryptarithmetic problem are as follows:
- There should be a unique digit to be replaced with a unique alphabet.
- The result should satisfy the predefined arithmetic rules, i.e., 2+2 =4, nothing else.
- Digits should be from 0-9 only.
- There should be only one carry forward, while performing the addition operation on a problem.
- The problem can be solved from both sides, i.e., lefthand side (L.H.S), or righthand side (R.H.S)
Let’s understand the cryptarithmetic problem as well its constraints better with the help of an example:
- Given a cryptarithmetic problem, i.e., S E N D + M O R E = M O N E Y

In this example, add both terms S E N D and M O R E to bring M O N E Y as a result.
Follow the below steps to understand the given problem by breaking it into its subparts:
- Starting from the left hand side (L.H.S) , the terms are S and M. Assign a digit which could give a satisfactory result. Let’s assign S->9 and M->1.
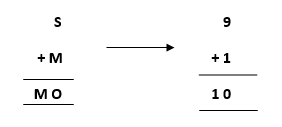
Hence, we get a satisfactory result by adding up the terms and got an assignment for O as O->0 as well.
- Now, move ahead to the next terms E and O to get N as its output.
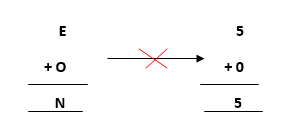
Adding E and O, which means 5+0=0, which is not possible because according to cryptarithmetic constraints, we cannot assign the same digit to two letters. So, we need to think more and assign some other value.
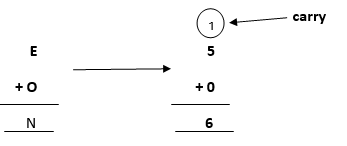
Note: When we will solve further, we will get one carry, so after applying it, the answer will be satisfied.
- Further, adding the next two terms N and R we get,
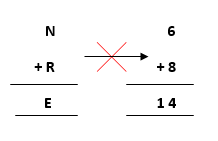
But, we have already assigned E->5. Thus, the above result does not satisfy the values
because we are getting a different value for E. So, we need to think more.
Again, after solving the whole problem, we will get a carryover on this term, so our answer will be satisfied.
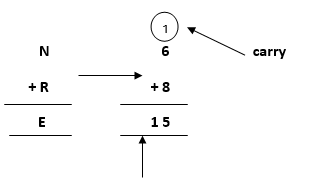
where 1 will be carry forward to the above term
Let’s move ahead.
- Again, on adding the last two terms, i.e., the rightmost terms D and E, we get Y as its result.

where 1 will be carry forward to the above term
- Keeping all the constraints in mind, the final resultant is as follows:

- Below is the representation of the assignment of the digits to the alphabets.
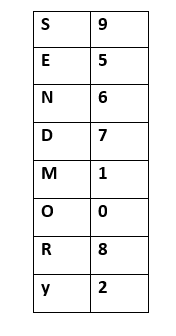
More examples of cryptarithmatic problems can be:
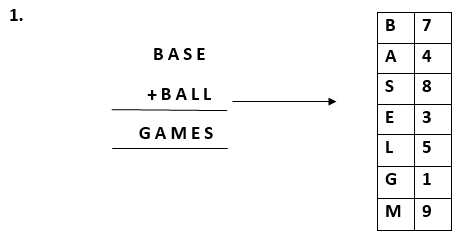
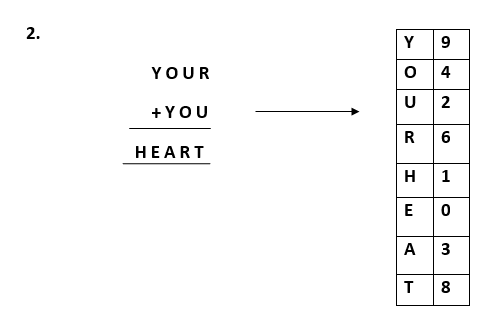
Similarly, we can also perform multiplication on the cryptarithmatic problems.
Related Posts:
- Constraint Satisfaction Problems in Artificial Intelligence
- Heuristic Functions in Artificial Intelligence
- Local Search Algorithms and Optimization Problem
- Problem-solving in Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence Tutorial | AI Tutorial
- Alpha-beta Pruning | Artificial Intelligence
- Adversarial Search in Artificial Intelligence
- Differences in Artificial Intelligence
- Uninformed Search Strategies – Artificial Intelligence
- Hill Climbing Algorithm