Output Devices in Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics Output Devices
An output device is a component of hardware or the main physical part of a computer that can be touched and seen. An output device is an electromechanical device.
“The Computer gives instructions and data from input devices and processes it and returns the result called as output.”
For Example: Printer, Plotter, Monitor, Projector etc.
Printers:
A printer is a peripheral device which is used to represent the graphics or text on paper. The quality is measured by its resolution. The resolution of any printer is measured in dot per inch (dpi).
The printer usually works with the computer and connected via a cable. In present, many digital device support printer features so that we can use Bluetooth, Wi-fi, and cloud technology to print.
Types of Printers
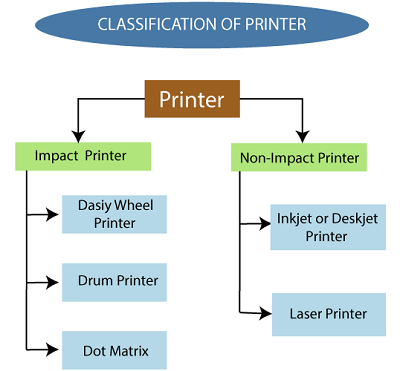
Some types of printers are:
- Impact Printers
- Non-impact Printers
Impact Printers
In impact printers, there is a physical contact established between the print head, ribbon, ink-cartridge, and paper.
The printers hit print head on an ink-filled ribbon than the letter prints on the paper. Impact printers are works like a typewriter.
These printers have three types:
- Daisy Wheel Printers
- Drum Printers
- Dot Matrix Printer
Daisy Wheel Printers:
By these, we can print only one character at a time. The head of this printer looks like a daisy flower, with the printing arms that appear like petals of a flower; that’s why it is called “Daisy printer.”
It can print approx. 90 characters per second.
Daisy wheel printers are used to print the professional quality document. It is also called “Letter Quality Printer.”
Advantages:
- More reliable
- Better printing Quality
Disadvantages:
- Slow than Dot Matrix
- More Expensive
- Noisy in operation
Drum Printers:
It has a shape like a drum, so it is called “Drum Printer.” This type of printer contains many characters that are printed on the drum.
The surface of the drum is break down into the number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to character132. A drum will have 132 tracks. The number of tracks is divided according to the width of the paper.
It can print approx. 150-2500 lines per minute.

Advantages:
- High Speed
- Low Cost
Disadvantages:
- Poor Printing Quality
- Noisy in Operation
Dot Matrix Printer:
It is also known as the “Impact Matrix Printer.” Dot Matrix Printer can print only one character at a time. The dot matrix printer uses print heads consisting of 9 to 24 pins. These pins are used to produce a pattern of dots on the paper to create a separate character.
Dot-matrix printer can print any shapes of character, special character, graphs, and charts.

Advantages:
- Low Printing Cost
- Large print size
- Long Life
Disadvantages:
- Slow speed
- Low Resolution
Non-impact Printers
In Non-impact printers, there is no physical contact between the print head or paper head. A non-impact printer prints a complete page at a time. The Non-impact printers spray ink on the paper through nozzles to form the letters and patterns.
The printers that print the letters without the ribbon and on papers are called Non-impact printer. Non-impact printers are also known as “Page Printer.”
These printers have two types:
- Inkjet Printer:
- Laser Printer:
1. Inkjet Printer: It is also called “Deskjet Printer.” It is a Non-impact printer in which the letters and graphics are printed by spraying a drop of ink on the paper with nozzle head.
A Color inkjet printer has four ink nozzles, sapphire, red, yellow, and black, so it is also called CMYK printer. We can produce any color by using these four colors.
The prints and graphics of this printer are very clear. These printers are generally used for home purposes.

Advantages:
- High-Quality Printout
- Low noise
- High Resolution
Disadvantages:
- Less Durability of the print head
- Not suitable for high volume printing
- Cartridges replacement is expensive
2. Laser Printer: It is also called “Page Printer” because a laser printer process and store the whole page before printing it. The laser printer is used to produce high-quality images and text. Mostly it is used with personal computers. The laser printers are mostly preferred to print a large amount of content on paper.

Advantages:
- High Resolution
- High printing Speed
- Low printing Cost
Disadvantages:
Costly than an inkjet printer
Larger and heavier than an inkjet printer
Plotters:
A plotter is a special type of output device. It is used to print large graphs, large designs on a large paper. For Example: Construction maps, engineering drawings, architectural plans, and business charts, etc.
It was invented by “Remington rand” in 1953.
It is similar to a printer, but it is used to print vector graphics.
Types of Plotter
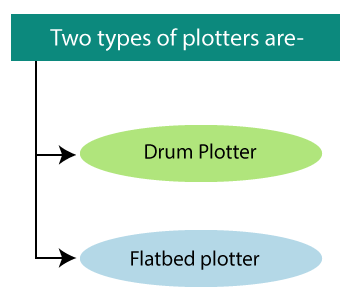
- Flatbed Plotter: In a flatbed plotter, the paper is kept in a stationary position on a table or a tray. A flatbed plotter has more than one pen and a holder. The pen rotates on the paper upside-down and right-left by the using of a motor.
Every
pen has a different color ink, which is used to draw the multicolor design.
We can quickly draw the following designs by
using a flatbed printer.
For Example: Cars, Ships, Airplanes, Dress design, road and highway blueprints, etc.

Advantages of Flatbed Plotter
- Larger size paper can be used
- Drawing Quality is similar to an expert
Disadvantages of Flatbed Plotter
- Slower than printers
- More Expensive than printers
- Do not produce high-Quality text printouts
2. Drum Plotter: It is also called “Roller plotter.” There is a drum in this plotter. We can apply the paper on the drum. When the plotter works, these drums moves back and forth, and the image is drawn.
Drum plotter has more than one pen and penholders. The pens easily moves right to left and left to right.
The movement of pens and drums are controlled by graph plotting program.
It is used in industry to produce large drawings (up to A0).

Advantages of Drum Plotter
- Draw Larger Size image
- We can print unlimited length of the image
Disadvantages of Drum Plotter
- Very costly
Related Posts:
- Input Devices in Computer Graphics
- Display Devices in Computer Graphics
- Image Representation in Computer Graphics
- Output Devices in Computer Graphics
- Color Models in Computer Graphics
- Animation in Computer Graphics
- Applications of Computer Graphics
- History of Computer Graphics
- Homogenous Coordinates in Computer Graphics
- Scan Conversion of an Ellipse Computer Graphics
- Filled Area Primitives Computer Graphics