Blockchain Tutorial
The 21st century is all about digitalization and technology. With the rising need for modernization in our daily lives, people are exploring new technologies. Blockchain technology has created a stir in the past few years. we will be learning about every aspect of Blockchain technology. We will deal with the role and importance of Blockchain technology in the future.

Blockchain technology provides a method to one internet user to transfer digital assets to another internet user, such that the transfer is sure to be safe and secure because every user knows that the transaction has taken place, and no one can challenge the correctness of the transfer.
Blockchain is the pillar technology behind the digital cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Blockchain provided the answer to digital currency and its secure transaction because it records data and information in a public space in the form of transactions that cannot be changed or remove from the chain once completed.
Blockchain is a platform where transactions are performed in the form of cryptocurrency. It can be defined as a continuously growing chain of blocks. Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable database that records the derivation of digital assets. It allows users to reach consensus without trusting each other.
Everyone knows about cryptocurrency like bitcoin but hardly few people understand the role of the technology behind it. Blockchain technology made the cryptocurrency possible. The different features of Blockchain allow us to use it beyond the cryptocurrency. Most of the people often think that blockchain and bitcoin are the same, though they are not the same.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed and immutable database used to manage the transactions. It comprises a sequential collection of blocks or systems in which transactions made in cryptocurrency are maintained across different servers that are linked in a network. Furthermore, every Blockchain is a protocol that can automatically lookup and update the data on different nodes. So, it is certainly going to be a smart and productive invention.
Blockchain Definition
Blockchain can be defined as a continuously growing chain of blocks, which is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable database that records the derivations of digital assets. Every user of the network can reach consensus without trusting each other.
It is the world's most trusted compact cryptocurrency company. It connects the world with future products, including digital and crypto wallet, bitcoin explorer, and market information.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is undoubtedly a great invention. Let's take a quick look at the different kinds of Blockchain available and their functionality.
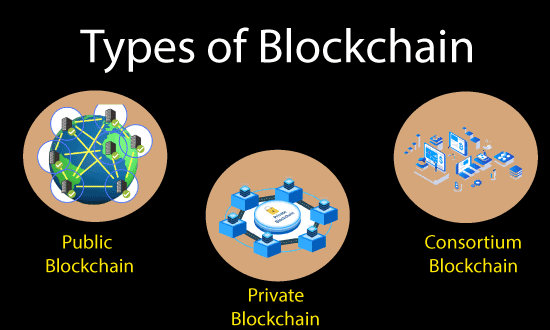
Blockchains comprises three different types that are as follows:
1. Public Blockchains
In public blockchains, any user can join the network, read and write, or send and receive data using the required software. It is a decentralized network that doesn’t have a single entity to control the flow as public blockchains are permissionless. Every transaction that takes place on public blockchains is completely transparent, which means anyone can access the transaction details. Example- Bitcoin, Dash, Ethereum, Litecoin, etc.
Below are some features of the public blockchain:
- These are designed to be fully decentralized, with no individual controlling the flow of the transaction.
- Public blockchains are open to anyone; regardless of nationality or location, which makes it harder for authorities to filter the users.
- Each participant has a token associated with them that is designed to provide them some incentive and reward in the network.
2. Private blockchains
In private blockchains, only authorized users are allowed to access the chain. It is also known as permissioned blockchain as it restricts the unauthorized users to participate in the network. There can be more than one person or organization that controls the system and this allows the need of third parties for transactions. In simple words, access permissions for reading and writing are kept centralized to an individual organization. Example- Hyperledger, R3 Corda, EWF (energy), etc.
Below are some features of the private blockchain:
- Users always need permission to participate in the network.
- A private blockchain is more centralized and secure than public blockchains.
- Transactions in private blockchain are available only for the allowed participants of the network.
3. Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are permissioned networks that allow certain entities or group of users to read and write data with certain restrictions. It can be best explained when compared to their counterpart, public blockchains. Though it is semi-decentralized, consortium blockchain is controlled by a group of approved individuals rather than a single entity. Example- Quorum, hyperledger, etc.
Below are some features of the blockchain:
- Consortium blockchain provides more efficiency by collaborating some aspects of their business.
- Anyone can be included in the network by its participants from the supply chain, to the central bank, and to the governments.
- It offers different use cases of blockchain, bringing together many businesses and organizations around the globe that work together and also compete against each other.
It can be differentiated based on permission less blockchains like Bitcoin and permissioned ones like DLT. In Bitcoin-based Blockchains, no one needs to trust any third-party entity to run it transparently. The main difference between the different types of blockchains is the range of availability.
Advantages of Blockchain
- Blockchain is a decentralized network that doesn’t have a single person controlling the network, which means there is no central authority that keeps the data of Blockchain.
- The data or information can be hashed, and the hash value can be incorporated into a transaction stored in the block, which acts as a proof of the exact time at which the data existed.
- Transparency is a key feature in building the trust and integrity with users. Blockchain networks offer supreme transparency in case of a valid ledger of transactions.
- It enhances trust across financial and business networks that mean clients don't need to trust each other when operating on any Blockchain network. It builds trust through its transparency and security.
- It eliminates the need of an intermediate or third party to verify the transactions. Only participant nodes can validate the legacy of the transactions.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger of permanent records of all transactions or digital events that have been stored and shared among all participating nodes. Based on the functionality, it is simply an advanced Distributed Ledger Technology. Since it was the first fully functional DTL, it is well known as BlockDAG and TDAG.
Below are the reasons that explain why the blockchain technology has gained so much attention:
- Anyone can track the record if they want to, as it is transparent.
- No single entity controls it, as it is decentralized.
- No one can modify the stored data as Blockchain is immutable.
- The data is cryptographically hashed before processing it to the chain.
Audience:
This tutorial has been prepared for the aspirants who are keen to learn new technology. It will cover the various aspects of cryptography, need of decentralized server, distributed network, Blockchain creation, Blockchain supply chain, and many other concepts related to Blockchain Technology.
Prerequisite skills:
Before going through this tutorial, you must have fundamental knowledge of Distributed networking, Cryptography, Basic data structures, Blockchain Wallet, HTML, and javaScript.
Blockchain Index
- Blockchain Tutorial
- History of Blockchain
- Blockchain Terminologies
- Working of Blockchain
- Difference between Blockchain and DLT
- Blockchain Versions
- Introduction to Smart Contracts
- Blockchain Applications
- Cryptography
- Role of Bitcoin Miners
- Blockchain Hash Function
- Bitcoin Basic Component
- Blockchain Block Hashing
- How to Block Hashes Work in Blockchain
- Blockchain Pow
- Coinbase Transaction
- Bitcoin Key Concepts
- Key Areas of Blockchain
- Blockchain Cryptocurrency
- Blockchain DAO
- Blockchain Double Spending
- Blockchain Bitcoin Cash
- Bitcoin Forks and SegWit
- Blockchain Merkle Tree
- Difference between Blockchain and Database
- Bitcoin Mitigating Attacks
- Who sets the Bitcoin Price
- Getting Started with Bitcoin
- How to choose Bitcoin Wallet
- Sending and Receiving Bitcoin
- Converting Bitcoins to Fiat Currency
- Ethereum 2.0
- Blockchain Data Management
- Steps to become a Blockchain developer
- Smart Contracts
- Advantages of Blockchain in healthcare
- Decentralized Voting System using Blockchain
- Demur-rage currencies in Blockchain
- How can Blockchain Technology help IoT to reach its full potential
- Project Ideas on Blockchain for Professionals
- Consensus Algorithms in Blockchain
- Top 10 Blockchain Project Concepts
- Uses of Blockchain
- Obtaining Free Test Ethers
- What does a Blockchain contain
- What does the IT industry mean by BaaS
- Top Blockchain Project Ideas for Beginners
Cryptography
- Introduction and Features of Cryptography
- DNA cryptography
- ECB Mode in Cryptography
- Elliptic curve in cryptography
- Format String Vulnerabilities in Cryptography and Network Security
- Kerberos in Cryptography and Network Security
- Blowfish Algorithm in Cryptography
- Data Encryption Standards
- Feistel Cipher in Cryptography
- HMAC Algorithm in Cryptography
- IP Security in Cryptography
- ElGamal Algorithm
- ElGamal Cryptosystem
- What is IDEA
- Advantages of Cryptography