Working of Blockchain
How Blockchain Works
A Blockchain is simply a collection of records of time-stamped transactions that are managed by a group of servers. There is no central authority who controls the database. It can be updated by consensus between participants in the network, and a new transaction is recorded that can never be erased or tampered. But the big question is that how does a Blockchain work?
Let’s discuss the entire working process by dividing it into several individual steps.
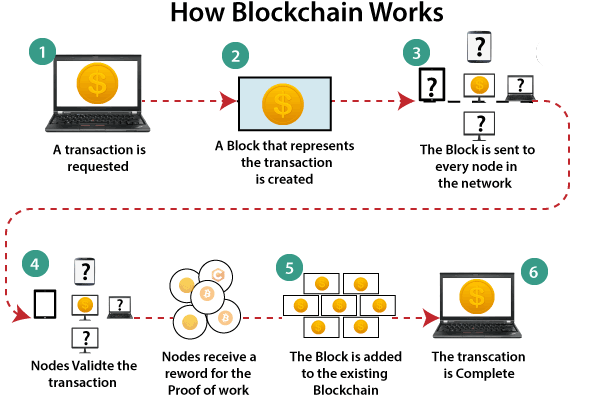
Firstly, when the sender party makes a call to transfer some money following steps occur:
Step 1: Let’s suppose two users in a Blockchain network, Alex and Brown, want to create a new transaction. Alex sends 50 BTC to Brown. They will request for the transaction to be mined.
Step 2: The transaction can take place if all the other participants in the network verify it as a genuine transaction. Thus, each user will receive the request to verify the transaction between Alex and Brown.
Step 3: The data of the transaction requires a hash value now to process the transaction. The hash function takes any data of input and converts it into a unique 64-bit string of output. Each client will check certain information about the transaction, such as does Alex have sufficient funds to make the transaction.
Step 4: Then, the transaction is forwarded to the participating nodes of the network. Once the verification is done, the transaction is ready to take place. Now, the transaction is added into the memory pool of Blockchain.
Step 5: Every block has a defined memory pool; hence several other verified transactions combine together to create a new block of the ledger. There can be a number of transactions in the block.
Step 6: The created block is then added to the existing Blockchain. Each new block will have a block header consisting of time-stamp, hash, previous hash, and transaction data summary. Every block has its unique hash value, which acts like its signature, or you can say fingerprint.
Step 7: The block is mined with the help of the hash function. After this, the transaction is completed, and money is sent to the second individual.
The above process repeats itself, and new blocks continue to get added into the Blockchain permanently after every 10 minutes. There is a unique concept of incentive and reward upon doing proof-of-work. The practical working of Blockchain will ask you to add $50 for each into the required software. The software will keep the money safe with itself and will check the winner. The system will reward this whole $100 to the winner.