What is the ITIL Framework?
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL), also known as the ITIL framework. It is one of the most preferred and utilized
Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) frameworks.
- ITIL guides an organization and individuals to use Information Technology as a
- The objective is to enhance proficiency and achieve certain service levels.
- ITIL describes procedures, tasks, and checklists which aren't organization-specific.
- It determines a baseline from which it can plan, implement, and
What is the ITSM Lifecycle?
ITSM Lifecycle and the
ITIL Processes are well-established management method for
continual improvement. It was proposed by
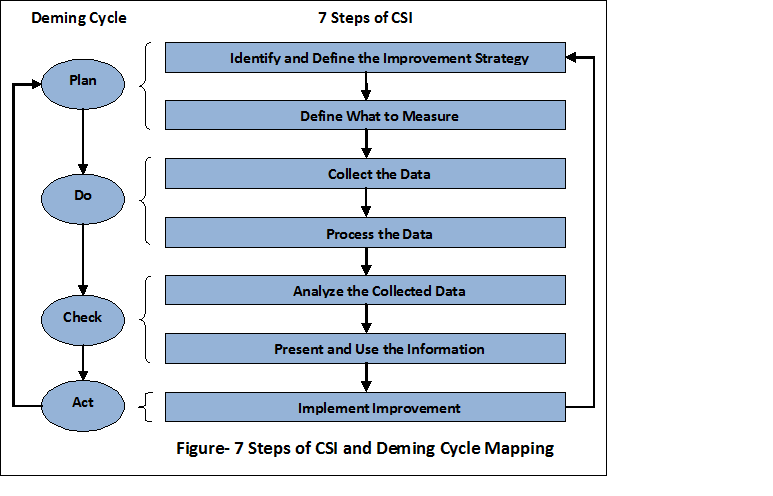
Dr. W. Edwards Deming. ITSM Lifecycle is also known as “
Deming Cycle” or
"Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)." The ITSM Lifecycle is organized in
five stages.
The service providers should evaluate their service on a regular basis and take corrective action if necessary.
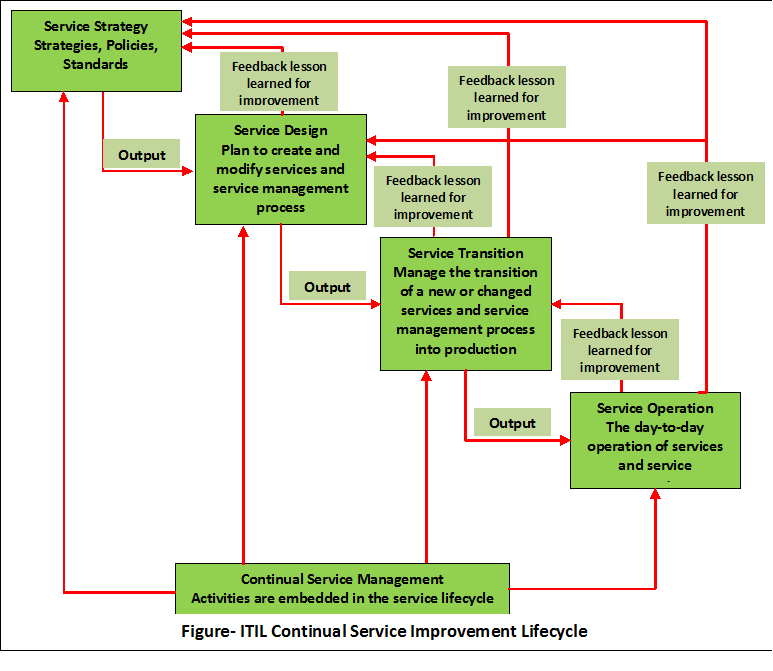
Lifecycle Stages and Processes:
The ITSM Lifecycle is organized in
five stages. These stages contain several ITIL processes.
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continual Service Improvement
ITIL Service Strategy
IT is
used to align the activities of the IT Department with the core business. In this stage, we decide on a strategy which is to serve to customers. The main processes of this stage are:
- Strategy Management
- Financial Management
- Demand Management
- Service Portfolio Management
- Business Relationship Management
ITIL Service Design
This stage demonstrates the services provided by the IT Department to support the business. In this stage, we
design and
alter services that are being
“offered to” or
“to be offered” to customers. The main processes of this stage are:
- Risk Management
- Design Coordination
- Supplier Management
- Capacity Management
- Availability Management
- Compliance Management
- Architecture Management
- Service Level Management
- Service Catalogue Management
- IT Service Continuity Management
- Information Security Management
ITIL Service Transition
In this stage,
services are handed-over from the development phase to the operations phase. The main processes of this stage are:
- Transition Planning and Support (Project Management)
- Service Asset and Configuration Management
- Release and Deployment Management
- Service Validation and Testing
- Knowledge Management
- Change Management
- Change Evaluation
ITIL Service Operation
This stage
ensures that services are delivered within the agreed service level. It maintains the continuity of business by resolving any kind of issues faced by users on day to day basis. The main processes of this stage are:
- Service Desk
- Request Fulfillment
- Event Management
- Access Management
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Technical Management
- Application Management
- IT Operations Management
- IT Operations Control
- Facilities Management
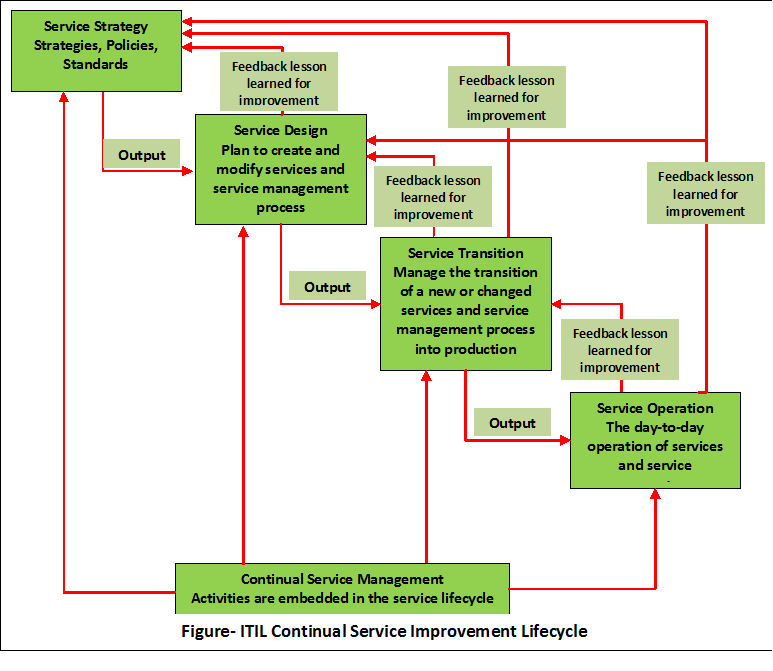
ITIL Continual Service Improvement
This stage
identifies and
implements improvements strategies to provide better service in the future. It is based on the
Deming Cycle. The main processes of this stage are:
- Service Review
- Process Evaluation
- Definition of CSI Initiatives
- Monitoring of CSI Initiatives
What is the ITIL Service Strategy Process?
A service strategy is the origin point of the ITSM Lifecycle. This model determines which types of services should be offered to which customers or markets. This is a
Market-Driven Lifecycle stage.
The service strategy also describes
4P's (
building blocks of service strategy) that are necessary for the successful execution of this module. The 4P’s are
Perspective, Position, Plan, and
Pattern.
If anyone of the 4P's is absent from the system, the activities of the service strategy stage cannot be completed successfully.
- Perspective: Describes the generalized plans and ideas (vision statement of an organization) that you have outlined for your organization’s future growth.
- Position: Describes how you are going to differentiate your organization from your competitors.
- Plan: Describes the actions that, you are going to take in order to achieve the established goals and objectives. It mainly focuses on the budgets, your portfolio of services, and improvement of past plans.
- Pattern: Describe the ongoing, repeatable actions that a service provider will have to perform in order to continue to meet its strategic objectives.
Goal
- To manage and grow profitably in the long-term.
- To make a decision on the strategy to serve customers.
- Think and act in a strategic manner.
What is the ITIL Service Design?
It
covers design principles and
methods for converting s
trategic business objectives into the portfolio of services and
services assets. It also defines how a planned service solution interacts with the larger business and technical environment.
Objectives
- Design new IT services, processes and other aspects of the ITSM.
- Change and improvement of existing services.
Goal
- Reduce total cost of ownership.
- Improve the quality and consistency of services.
- Develop more effective IT governance.
- Measure the effectiveness of system and
4P’s of Service Design
4Ps are the
building block of the service design stage. 4Ps are:
- People: An organization to acquire sufficient personnel with adequate knowledge level.
- Products: Essential technology that is required to deliver services.
- Partner: Hire that required skill/service for that part from partner or suppliers and deliver the whole service to its customers.
- Processes: Determine the expected outputs that are required to deliver the target output.
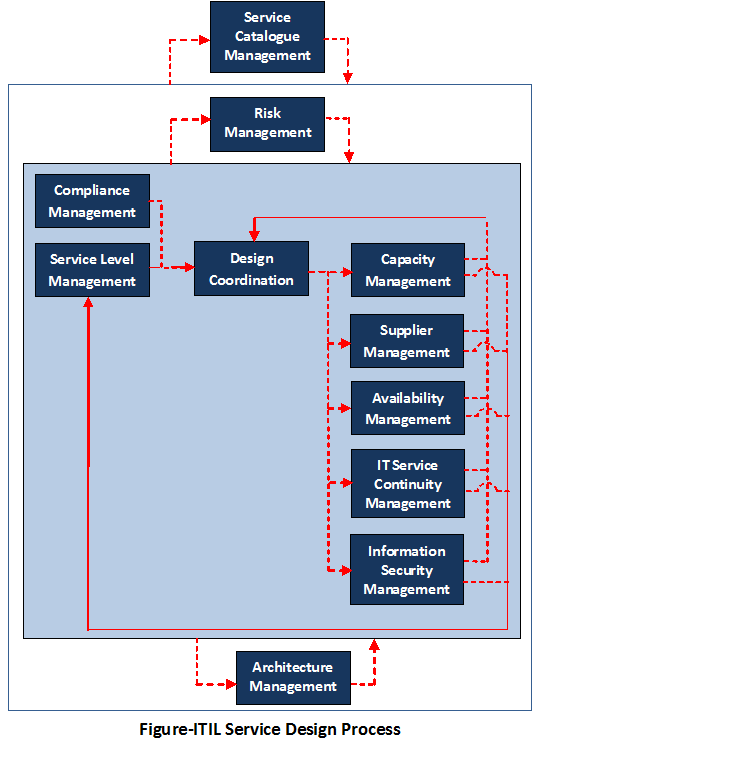 Service Design Process
Service Design Process
What is the ITIL Service Transition?
It typically covers the aspects of IT project management, rather than the business as usual. This stage
manages the transition of new or changed services from the service design phase to service operation phase.
Objective
- Develop and improve the capabilities used for deploying new or modified IT services into operation.
- It ensures that new and altered services meet customer requirements.
- Implement services with minimal effect on existing IT infrastructure services.
Goals
- Provide guidance for the developing and improving the capabilities for transitioning new and changed services into the live environment.
- Improve a Service Provider’s ability.
- Handles different changes, such as change of supplier, change service capabilities.
- Helps to create a blueprint for developing a modular approach to service installation.
Key Aspects
- Increasing productivity of business and customer.
- Reducing the deviation of actual plans and budget against the estimated value.
- Increasing the success rate of changes.
- Quick and efficient adaptability to new requirements.
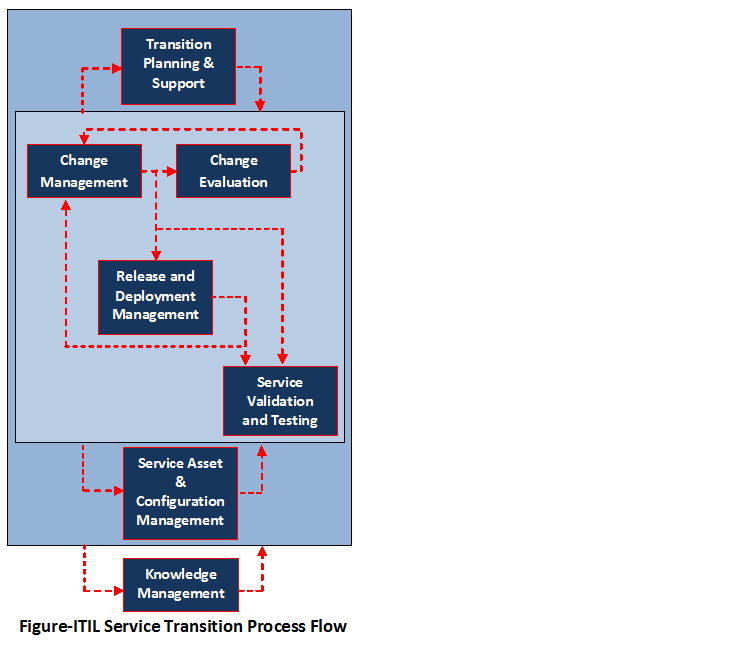
Service Transition Process
What is the ITIL Service Operation?
It is responsible for
monitoring services, resolving incidents, fulfilling the request and
carrying out operational tasks. This is the stage where all
design and
transition plans are executed and measured for actual efficiency. It
supports business operations and
takes control of any new or
changed services.
Objectives
- It reduces the impact of service outages on day-to-day business activities.
- It also ensures that IT services are provided to authorized personnel
- Select and accept the best practice to support organizations in delivering major benefits within SLA.
- It reduces incidents and problems.
- It supports users in using the actual service.
Key Benefits
- It allows an organization to take full advantage of service by reducing the duration and frequency of service outages.
- It supports the organization's security policy by ensuring that IT services will be accessed by authorized personnel only.
- It provides access to standard IT services; improve the productivity, quality of staffs and
- It reduces unplanned expenditure for both the business and IT through optimize the handling of services.
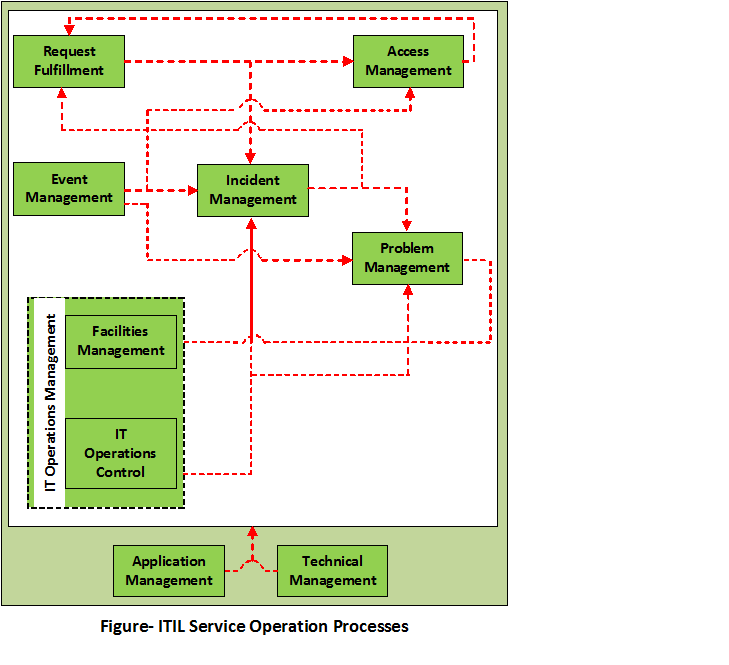
Service Operation Processes
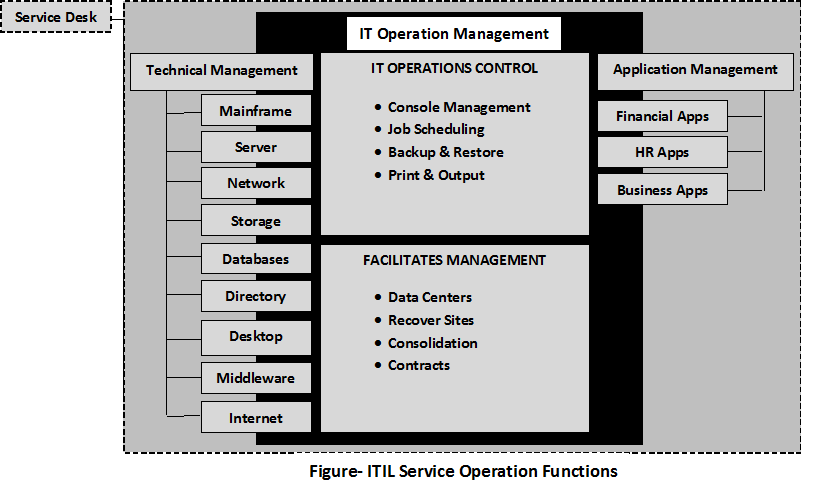
Service Operation Functions
There are
four functions and
two sub-functions.
- Service Desk
- Technical Management
- Application Management
- IT Operation Management
- IT Operations Control
- Facilitates Management
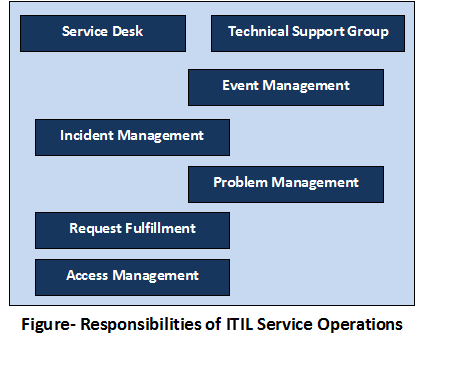
Responsibilities of Service Operations Functions on Processes
There are
two major functional groups:
Service Desk and
Technical Support Group (includes Technical, Application and IT Operation Management). The following figure describes the level of responsibilities.
 Service Operation Roles
Service Operation Roles
- IT Operations Manager
- IT Operator
- 1st Level Support
- 2nd Level Support
- 3rd Level Support
- Incident Manager
- Major Incident Team
- Service Request Fulfillment Group
- Problem Manager
- Access Manager
- Service Desk Manager
- Technical Analyst
- Applications Analyst
What is the Continual Service Improvement (CSI)?
It
improves service quality by learning from past successes and failures. CSI changes business requirements by identifying and implementing changes for improvements. It effectively
describes and
utilizes the concept of
Key Performance Indicator (KPI). KPI is a
metrics-driven process, for
reviewing, evaluating, and
benchmarking performance of services.
Objectives
- Review and analyze improvement opportunities in every lifecycle phase.
- Analyze and evaluate service level achievement results.
- Improve the cost-effectiveness of delivered IT services without impacting on customer satisfaction.
- Ensures quality management methods to support improvement activities.
This CSI acts as a guide and
provides continual feedback to every process groups (Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, and Service Operation) of
Service Management Life-Cycle.
 CSI Approaches
CSI Approaches
This process follows a
six-step approach for
reviewing, evaluation, planning and
implementing the improvement process. These are nothing but some pre-defined question, for which the CSI process tries to find answers. The questions are:
- What is the vision?
- Where are we?
- Where do we want to be?
- How do we get there?
- Did we get there?
- How do we keep up the momentum?
Improvement Process of CSI
There are
seven steps followed sequentially:
- Identify and define the improvement strategy
- Define what to measure
- Collect the data
- Process the data
- Analyze the collected data
- Present and use the information
- Implement Improvement
 Process of CSI
Process of CSI
- Service Review
- Process Evaluation
- Definition of CSI Initiative
- Monitoring of CSI Initiative

 Service Design Process
Service Design Process



 Service Operation Roles
Service Operation Roles
 CSI Approaches
This process follows a six-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning and implementing the improvement process. These are nothing but some pre-defined question, for which the CSI process tries to find answers. The questions are:
CSI Approaches
This process follows a six-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning and implementing the improvement process. These are nothing but some pre-defined question, for which the CSI process tries to find answers. The questions are:
 Process of CSI
Process of CSI