ER Model: Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) with Examples
ER model stands for Entity-Relationship Model. It is a high-level data model diagram which defines the conceptual view of the database. It is a blueprint or design of a database that will be used to implement a database in the future. Entity-Relationship model is based on objects, called entities, and relationship among these entities. While formulating real-world scenario into the database model, the Entity-Relationship Model creates relationship set, entity set, general attributes, and constraints.
Features of ER Model
- This model is widely used to develop the initial design of the database.
- This model provides a collection of basic concepts which can be easily implemented in a database system.
- It describes data as a set of entities, attributes, and relationships.
- It provides the graphical or conceptual view of the database design.
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram?
An ERD or Entity-Relationship Diagram is the graphical representation of objects (entities) and relationship among those entities in the database. In other words, the ER diagram describes the logical structure of the database. It includes many special symbols, and its meanings make this model unique. For good database design, it is important to have an ER diagram.
A Simple Entity-Relationship Diagram
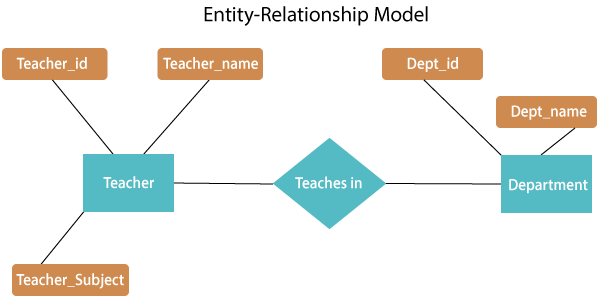
Entity-Relationship Diagram Symbols or Notations
Uses of Entity-Relationship Model:
- ER models can be used in designing the database.
- It provides useful concepts that allow a user to move from an informal description to precise description.
- This model or diagram was developed to facilitate database design by allowing the specification of the overall conceptual structure of a database.
- It is widely useful in mapping the meanings and interactions of real world enterprises onto a conceptual schema.
- These models can be used for the logical or conceptual design of database applications.
Advantages of ER Model
- Entity-Relationship Diagram or model is easy to create and understand.
- Entity-Relationship Model is very simple because if you know the relationship between attributes and entities, you can easily draw it.
- It is a tool for effective communication for database designer.
- It can be easily converted into a Relational Model by simply converting the ER Model into tables.
Limitations/Disadvantages of ER Diagram
Disadvantages of an Entity-Relationship Diagram include the following aspects:
- Entity-Relationship diagram is not suitable for those systems which contain semi-structured or unstructured data set.
- In the ER model, it is difficult to show data manipulation.
This model is especially popular for high-level design.