PHP validation is used to check whether the field is filled or not in the proper way by the user.
There are two types of validation in PHP.
- Client Side Validation: Client side validation is performed on the client machine web browsers.
- Server Side Validation: Server side validation is performed after submitting the data by user to check the validation on the server machine.
Following are the some validation rules for field
| Field |
Validation Rules |
| Name |
Name should required letters and white-spaces |
| Website |
Website should required a valid URL. |
| Radio |
Radio must be selectable at least once. |
| Check Box |
Checkbox must be checkable at least once. |
| Email |
Email should required @ and. |
Let us take an example of Form validation with require.
Example
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.error {color: #FF0000;}
.divid{background-color:#9e9e9eb0;height: 290px;width: 170px;padding: 50px;margin:auto;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// All the defined variables set to empty values
$nameErr = $emailErr= $commentErr = $genderErr = $websiteErr = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameErr= "Name is required";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailErr = "Email is required";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$commentErr = "comment is required";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderErr = "Gender is required";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
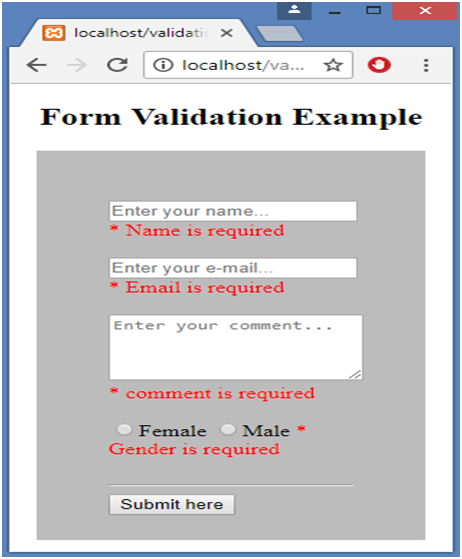
<h2 align="center">Form Validation Example</h2>
<div class="divid">
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Enter your name...">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $nameErr;?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="text" name="email" placeholder="Enter your e-mail...">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $emailErr;?></span>
<br><br>
<textarea name="comment" rows="4" cols="22" placeholder="Enter your comment ..."></textarea>
<span class="error">* <?php echo $commentErr;?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
<span class="error">* <?php echo $genderErr;?></span>
<br><br><hr>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit here">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
 Note:
Note:
The
“$_SERVER[“PHP_SELF”]” variable is a super global variable that is used to
returns the filename of the current executing script. It is always used by hackers.
The “
htmlspecialchars()” function is used to convert special characters to HTML entities( like
: < and > with
< and
>).
Example
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
Output
<form method="post" action= "test_form.php/"><script>alert('hacked')</script>">
PHP Captcha
PHP CAPTCHA stands for Competently Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. It is a type of challenge –response test that is used to determine whether user is human or not.
Example of Arithmetic CAPTCHA
<?php
error_reporting(1);
$arr=range(99,9);
$brr=range(99,9);
$randa=array_rand($arr);
$randb=array_rand($brr);
$a=$arr[$randa];
$b=$brr[$randb];
$r=$a+$b;
$cap=$a."+".$b;
if(isset($_POST['b1'])){
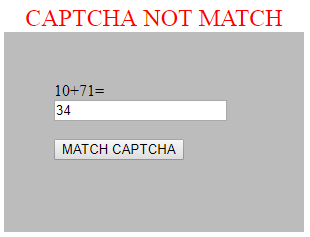
if($_POST['t2']==$_POST['t3']){
echo '<center>'.'<font color="blue" size="5">'."CAPTCHA MATCH THANKU".'</font>'.'</center>';
}
else{
echo '<center>'.'<font color="red" size="5">'."CAPTCHA NOT MATCH".'</font>'.'</center>';
}
}
?>
<html>
<style>
.divid{background-color:#9e9e9eb0;height: 100px;width: 200px;padding: 50px;margin:auto;}
</style>
<body>
<div class="divid">
<form method="post">
<?php
error_reporting(1);
echo $cap."=";
?>
<input type="hidden" name="t3" value="<?php echo $r;?>">
<input type="text" name="t2" autofocus><br><br>
<input type="submit" name="b1" value="MATCH CAPTCHA">
</form>
</div>
</html>
Output
 PHP Mail
PHP Mail
PHP mail() function is used to send the mail in PHP with various format like test message, html message and attachment message or file.
Syntax:
mail( to, subject, message, headers, parameters );
| Parameter |
Description |
| to |
The recipient's email address. |
| subject |
Subject of the email to be sent. This parameter cannot contain any newline characters(/n). |
| message |
It defines the message to be sent. Each line should be separated with a LF (\n). Lines should not exceed 70 characters |
| headers |
It is optional and specify additional headers, like From, Cc, and Bcc. The additional headers should be separated with a CRLF (\r\n) |
| parameters |
It is used to pass additional parameter. |
Sending Plain Text Emails
The easy way to send an email with PHP, only we have to pass three parameter in
mail() method.
Let us take an example
<html>
<head>
<title>Sending HTML email using PHP</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$to = 'rahul123@gmail';
$subject = 'Marriage Proposal';
$message = 'Hi Rahul Janu, will you marry me?';
$from = '[email protected]';
// Sending email
if(mail($to, $subject, $message,$from)){
echo 'Your mail has been sent successfully.';
} else{
echo 'Unable to send email. Please try again.';
}
?>
</body>
</html>
Output
Your mail has been sent successfully
PHP Mail with Attachment
We can also send mail with attachment only we have to include header information. Let us consider an example.
<?php
$to = "[email protected]";
$subject = "This is subject";
$message = "This is a text message.";
# Open a file
$file = fopen("/tmp/test.txt", "r" );//change your file location
if( $file == false )
{
echo "Error in opening file";
exit();
}
# Read the file into a variable
$size = filesize("/tmp/test.txt");
$content = fread( $file, $size);
# encode the data for safe transit
# and insert \r\n after every 76 chars.
$encoded_content = chunk_split( base64_encode($content))
# Get a random 32 bit number using time() as seed.
$num = md5( time() );
# Define the main headers.
$header = "From:[email protected]\r\n";
$header .= "MIME-Version: 1.0\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Type: multipart/mixed; ";
$header .= "boundary=$num\r\n";
$header .= "--$num\r\n";
# Define the message section
$header .= "Content-Type: text/plain\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Transfer-Encoding:8bit\r\n\n";
$header .= "$message\r\n";
$header .= "--$num\r\n";
# Define the attachment section
$header .= "Content-Type: multipart/mixed; ";
$header .= "name=\"test.txt\"\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Transfer-Encoding:base64\r\n";
$header .= "Content-Disposition:attachment; ";
$header .= "filename=\"test.txt\"\r\n\n";
$header .= "$encoded_content\r\n";
$header .= "--$num--";
# Send email now
$result = mail ( $to, $subject, "", $header );
if( $result == true ){
echo "Message sent successfully...";
}else{
echo "Sorry, unable to send mail...";
}
?>
 Note:
The “$_SERVER[“PHP_SELF”]” variable is a super global variable that is used to
returns the filename of the current executing script. It is always used by hackers.
The “htmlspecialchars()” function is used to convert special characters to HTML entities( like: < and > with < and >).
Example
Note:
The “$_SERVER[“PHP_SELF”]” variable is a super global variable that is used to
returns the filename of the current executing script. It is always used by hackers.
The “htmlspecialchars()” function is used to convert special characters to HTML entities( like: < and > with < and >).
Example
 PHP Mail
PHP mail() function is used to send the mail in PHP with various format like test message, html message and attachment message or file.
Syntax:
PHP Mail
PHP mail() function is used to send the mail in PHP with various format like test message, html message and attachment message or file.
Syntax: