Laravel Route Parameters
Required Parameters:
We need to capture segments of the URI within our route.
We are going to see how to pass parameters through two or many views inside the closure function.
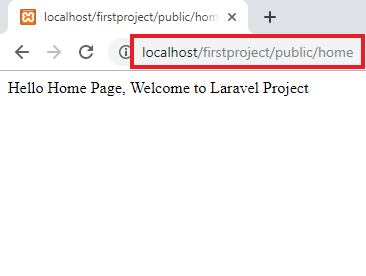
Route::get('/home', function () {
return "Hello Home Page,
Welcome to Laravel Project";
});
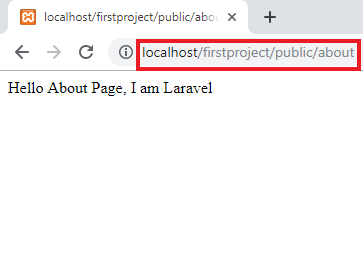
Route::get('/about', function () {
return "Hello About Page, I am
Laravel";
});
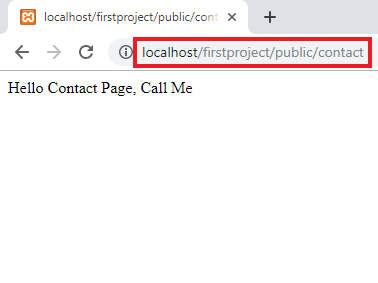
Route::get('/contact', function () {
return "Hello Contact Page, Call
Me";
});
Output:
We need to capture a user`s id from the URL.
We do so by defining route parameters.
Route::get(‘/user/{id}’,function($id)
{
Return ‘user ‘ , $id;
});
E.g.:
Route::get('/video/{id}', function($id) {
return "Here We Can Find
Video No. ". $id;
});
Output:
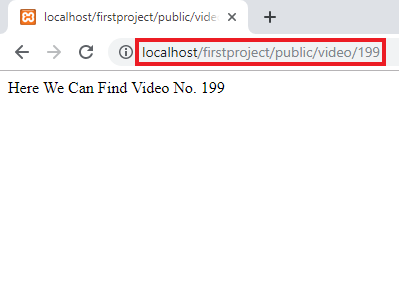
In the above example, we can see how to pass the variable to the closure function.
We define as many route parameters as required by our route:
Route::get(‘posts/{post}/comment}’,function( $postId, $commentId)
{
//
});
E.g.:
Route::get('/image/{id}/{name}', function($id, $name) {
return "Hii This Is Image No. ". $id . " " . $name;
});
Output:
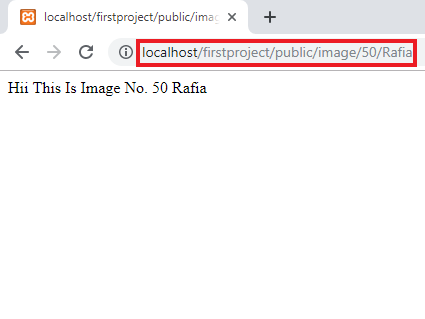
In the above example, the 50 is represented as an ( id ), the Rafia describes as a ( name ).
Route parameters are always enclosed within { } braces, and it should consist of any alphabetic characters. It may not contain a – character. Instead of using the – character, we use an underscore (_). Route parameters are placed into route callbacks/controllers based on their order – the names of the callback/controller arguments do not matter.
Optional Parameters
We need to specify route parameters occasionally, but we make the presence of route parameter route. We can place a (?) mark after the parameter name.
We make sure to give the route`s corresponding variable a default value.
Route::get(‘user/{name?},’function ($name = null)
{
Return $name;
});
Route::get(‘user/{name?},’ function ($name = ‘John’)
{
Return $name;
})
Regular Expression Constraints
We may constrain the format of our route parameters using the where method.
Route::get(‘user/{name}’,function ($name)
{
//
}) -> where(‘name’, ‘[A-Za-z]+’);
Route::get(‘user/{id}’, function ($id)
{
//
}) -> where(‘id’, ‘[0-9]+’);
Route::get(‘user/{id}/{name}’, ($id, $name)
{
//
}) -> where([‘id’ => ‘[0-9]+’, ‘name’ => ‘[a-z]’]);
The where method obtain the name of the parameters and a regular expression defining the parameter that should be constrained:
Global Constraints
We would like a route parameter to always be constrained by a given regular expression, we can use the pattern method. We can define these patterns in the boot method of ours RouteServiceMethod.
public function boot()
{
Route::pattern(‘id’, ‘[0-9]+’);
Parent::both();
}
Once the pattern has been defined, it will be automatically applied to all the outers using the parameter name:
Route::get(‘user/{id},’ function($id)
{
//
});
Encoded Forward Slashes
The Laravel routing component allows all the characters except /. We must explicitly allow / to be part of our placeholder using a where condition regular expression.
Route::get(‘search/{search}’, function ($search)
{
Return $search;
}) -> where(‘search’, ‘.*’);