How to drop a column in SQL?
How to drop a column in SQL
Introduction
- To delete a column from an already created table, one needs to use the ALTER command along with the DROP COLUMN clause.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE tablename DROP COLUMN ColumnName;
Where,
- Tablename is the name of an already existing table from which you have to delete a column.
- ColumnName is the name of the column which is to be deleted from an already existing table.
Example 1:
First, we will create a database with name “studentdb”. Then in that database we will create a table “student” and insert records into the table.
Now, we will delete a column ‘City’ from an existing table.
mysql> USE studentdb; Database changed mysql> SELECT *FROM student; +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+------+ | Stud_ID | Stud_Name | Course_ID | Course_Name | City | +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+------+ | 1 | Prajakta | 101 | DBMS | NULL | | 2 | Shweta | 102 | CN | NULL | | 3 | Nikita | 103 | OS | NULL | | 4 | Ankita | 104 | C | NULL | | 5 | Ashmita | 105 | JAVA | NULL | +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN City; Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.29 sec) Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> SELECT *FROM student; +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+ | Stud_ID | Stud_Name | Course_ID | Course_Name | +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+ | 1 | Prajakta | 101 | DBMS | | 2 | Shweta | 102 | CN | | 3 | Nikita | 103 | OS | | 4 | Ankita | 104 | C | | 5 | Ashmita | 105 | JAVA | +---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
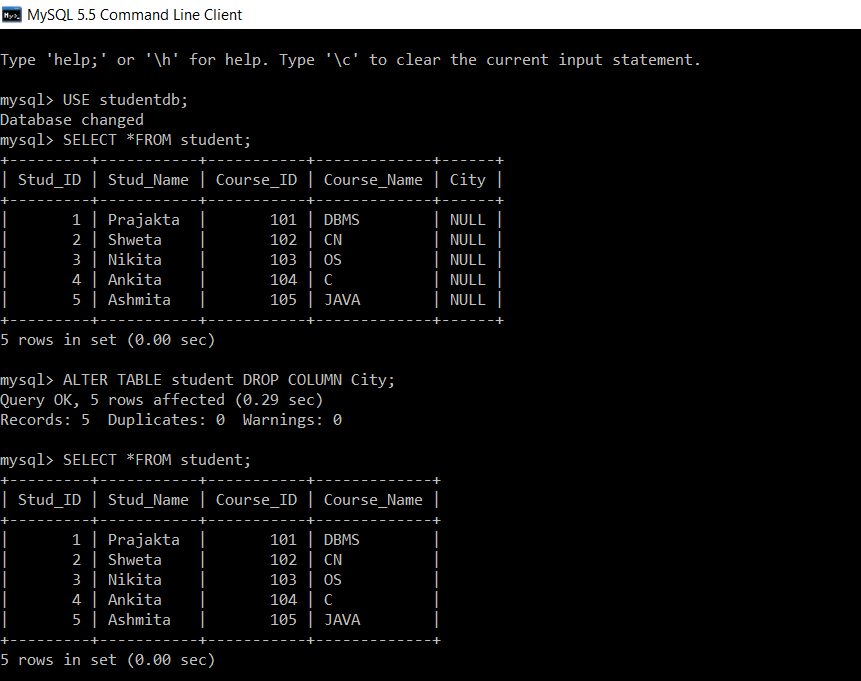
Column ‘City’ is removed from an existing student table.
Example 2:
We will delete a column ‘Stud_ID’ along with its primary key.
mysql> DESC student; +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Stud_ID | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | Stud_Name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | Course_ID | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | Course_Name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.02 sec) mysql> ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN Stud_ID; Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.28 sec) Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> DESC student; +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Stud_Name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | Course_ID | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | Course_Name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | +-------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
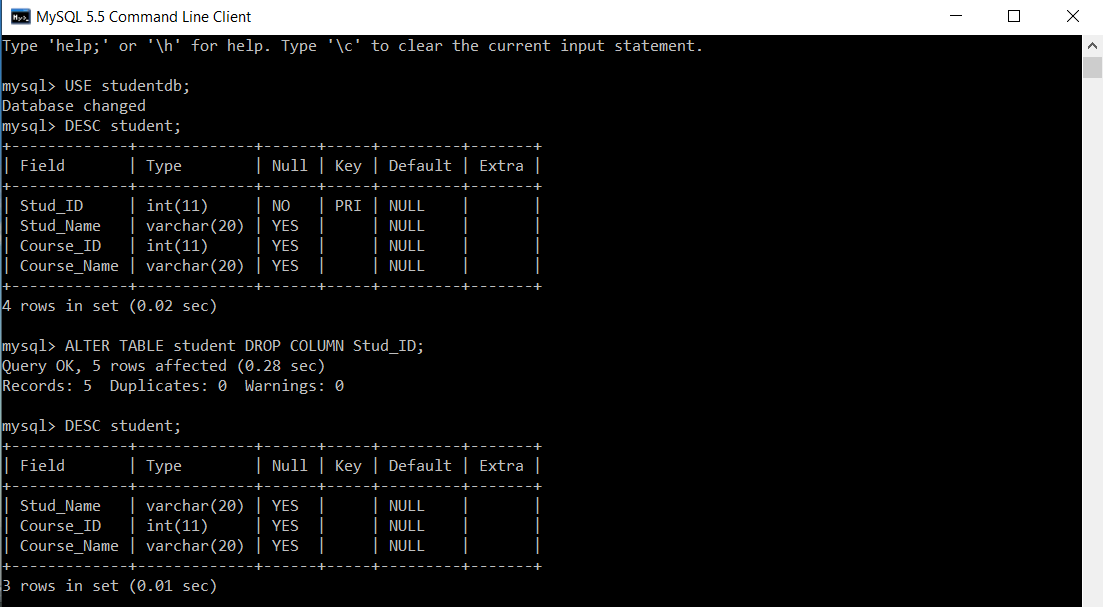
We have used DESC command in SQL to view the structure of student table. Before executing the ALTER command, there exists a primary key on ‘Stud_ID’. After executing the ALTER command along with the DROP column clause, ‘Stud_ID’ is removed from the table structure along with its primary key.