Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are +, -, *, /, % performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulo respectively.
Example:
- Select 100+222;
- Select salary+100
From teacher
Where teacher_id=1;
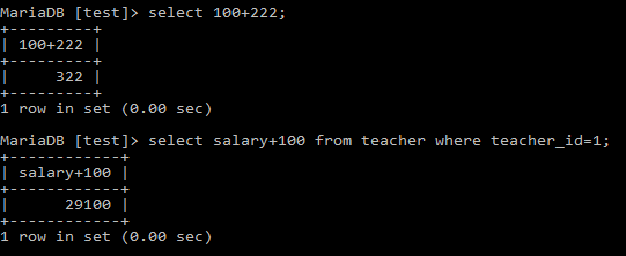
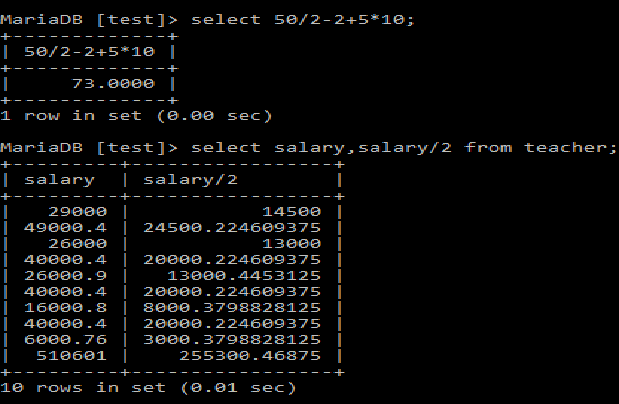
Following output screen shows different arithmetic operations. We can perform single operation at a time or multiple operations.
Comparison Operators
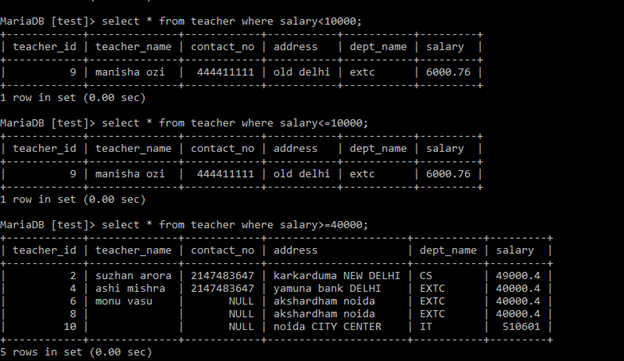
Comparison operators ‘<’, ‘<=’, ‘>’, >, =’, =’ performs less than, less than equal, greater than, greater than equal, equal respectively. Following output screen shows different comparison operators. Following output screen shows different queries with different comparison operations.
Logical Operators
AND, OR, NOT, LIKE, IN, BETWEEN, ALL, SOME, ANY, EXISTS are logical operators from which some operators ALL, ANY, EXISTS, SOME used in sub queries.
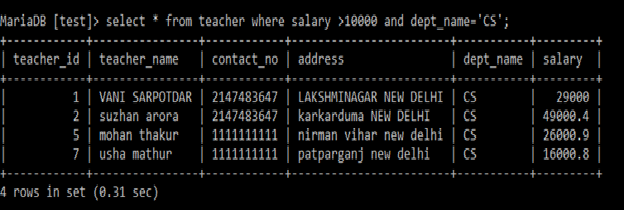
AND: It returns
TRUE, if all the conditions separated by A
ND are TRUE.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where salary>10000
and
dept_name=’CS’;
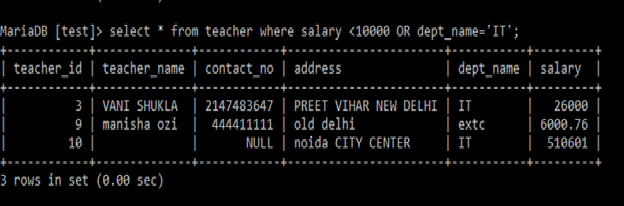
 OR:
OR: It returns
TRUE, if any of the conditions separated by
OR is TRUE.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where salary < 10000
OR
dept_name=’IT’;
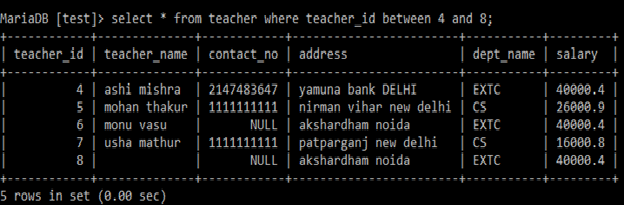
 BETWEEN:
BETWEEN: It returns true, if the operands are within the range of comparison.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id between 4 and 8;
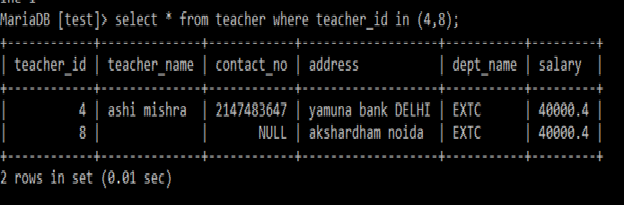
 IN:
IN: It returns true if the operand is equal to one of the list of expressions.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id in (4,8);
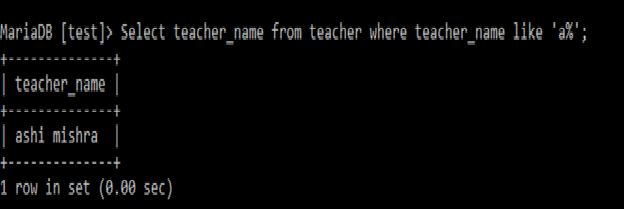
 LIKE:
LIKE: It returns true if the operand matches a pattern. ‘_’ underscore represents single character. ‘%’ percent represents one or more characters.
Example:
Q1. Find out teachers whose name start with ‘a’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like 'a%';
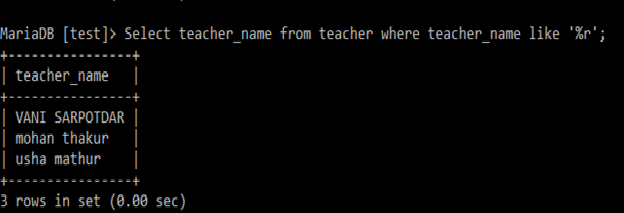
 Q2 Find out teachers whose name end with ‘r’?
Q2 Find out teachers whose name end with ‘r’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%r';
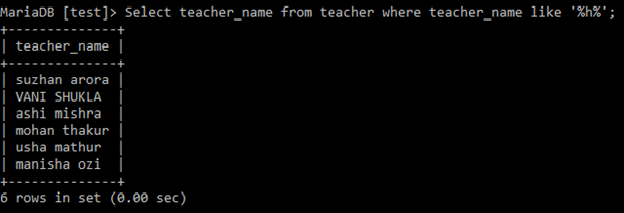
 Q3 Find out teachers whose name contains letter ‘h’?
Q3 Find out teachers whose name contains letter ‘h’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%h%';
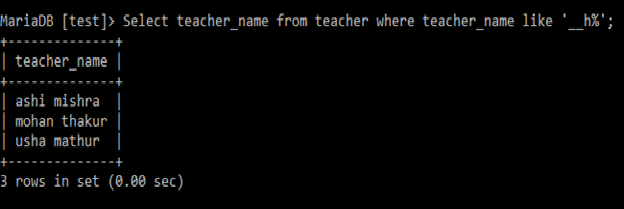
 Q4 Find out teacher whose name contains ‘h’ letter at third position?
Q4 Find out teacher whose name contains ‘h’ letter at third position?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '__h%';
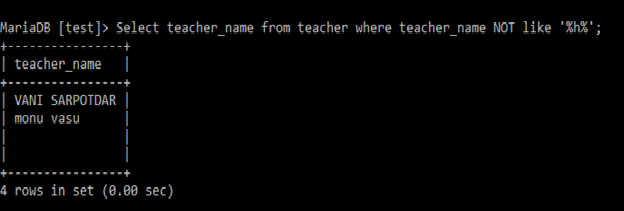
 If the condition is not true.
Example:
If the condition is not true.
Example:
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name NOT like '%h%';
Reference:
https://www.javatpoint.com/sql-operators
 Following output screen shows different arithmetic operations. We can perform single operation at a time or multiple operations.
Following output screen shows different arithmetic operations. We can perform single operation at a time or multiple operations.


 OR: It returns TRUE, if any of the conditions separated by OR is TRUE.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where salary < 10000
OR
dept_name=’IT’;
OR: It returns TRUE, if any of the conditions separated by OR is TRUE.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where salary < 10000
OR
dept_name=’IT’;
 BETWEEN: It returns true, if the operands are within the range of comparison.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id between 4 and 8;
BETWEEN: It returns true, if the operands are within the range of comparison.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id between 4 and 8;
 IN: It returns true if the operand is equal to one of the list of expressions.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id in (4,8);
IN: It returns true if the operand is equal to one of the list of expressions.
Example:
Select *
from teacher
where teacher_id in (4,8);
 LIKE: It returns true if the operand matches a pattern. ‘_’ underscore represents single character. ‘%’ percent represents one or more characters.
Example:
Q1. Find out teachers whose name start with ‘a’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like 'a%';
LIKE: It returns true if the operand matches a pattern. ‘_’ underscore represents single character. ‘%’ percent represents one or more characters.
Example:
Q1. Find out teachers whose name start with ‘a’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like 'a%';
 Q2 Find out teachers whose name end with ‘r’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%r';
Q2 Find out teachers whose name end with ‘r’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%r';
 Q3 Find out teachers whose name contains letter ‘h’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%h%';
Q3 Find out teachers whose name contains letter ‘h’?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '%h%';
 Q4 Find out teacher whose name contains ‘h’ letter at third position?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '__h%';
Q4 Find out teacher whose name contains ‘h’ letter at third position?
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name like '__h%';
 If the condition is not true.
Example:
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name NOT like '%h%';
If the condition is not true.
Example:
Select teacher_name
from teacher
where teacher_name NOT like '%h%';
 Reference:
https://www.javatpoint.com/sql-operators
Reference:
https://www.javatpoint.com/sql-operators