CSS Selector: Sub String in Selenium IDE
CSS Selector: Sub String
CSS Selector Sub-string is used to match a partial string to locate a particular web element.
- There are three ways to match a substring using a CSS Selector.
- Match a prefix
- Match a suffix
- Match a substring
Now we will discuss each of them in details with an example,
MATCH A PREFIX:
- It will access a particular string using a ‘match a prefix’.
Syntax of Prefix:
css= [HTML tag]{[attribute^=prefix of the string]}.
[^]: It is a symbolic notation to match a string using a prefix.
A prefix of the string: matching operation performed based on a string.
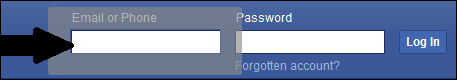
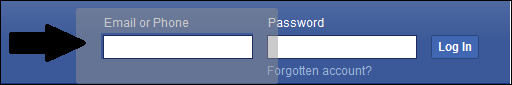
- For example, we will define the CSS Selector for the Email text box of a Facebook login page as css=input#email[name^='em']
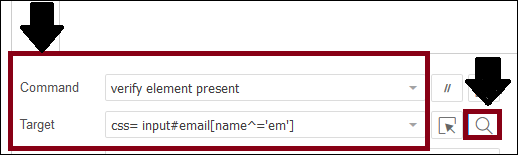
- Click on the Find button to verify whether the defined CSS Selector locates the desired element or not.
MATCH A SUFFIX:
- It will access a particular string using a ‘match a suffix’.
Syntax of Suffix:
css= [HTML tag]{[attribute$=suffix of the string]}
[$]: This is a symbolic notation to match a string using a suffix.
Suffix of the string: matching operation performed based on a string.
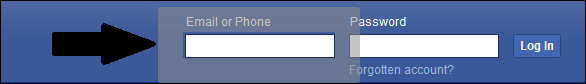
- For example, we will define the CSS Selector for the Email text box of the Facebook login page.
css=input#email[name*='ail']
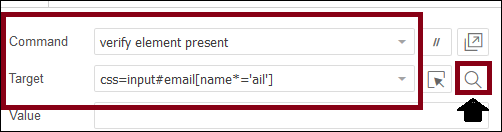
- Click on the Find button to verify whether the defined CSS Selector locates the desired element or not.
MATCH A SUBSTRING:
- It will access a particular string using a ‘match a substring’.
Syntax of substring:
css=<[attribute*=sub string]>
[*]:It is Symbolic notation to match a string using substring.
Substring: matching operation is performed based on a string
- For example, we will define the CSS Selector for the Email text box of the Facebook login page as css=input#email[name*='ail']
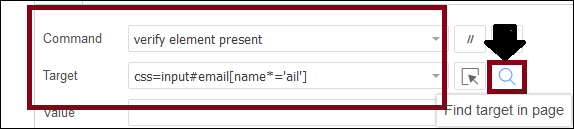
- Click on the Find button to verify whether the defined CSS Selector locates the desired element or not.