Basic Networking Devices
Hubs
A hub is the most common networking device which is used to connect a lot of computers or networking devices. It works on the physical layer in the OSI model. It is used to increase the size of networks. There are multiple ports in the hub shown in below diagram.
When we send the data from one device to another device, then the hub doesn't check the destination. Hub sends that data to all connected devices, and then the receiver receives the data, and other devices discard the data. It is used to connect devices in the star topology. Shown in below Hub.
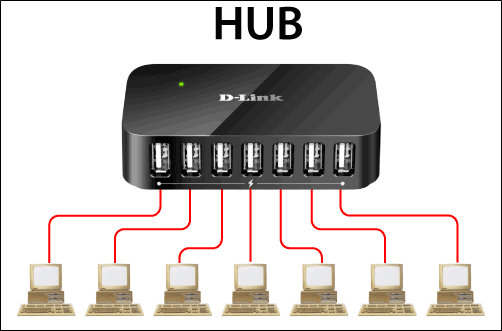
There are two types of the hub.
- Active Hub
- Passive Hub
Active Hub: In Active Hub, It regenerates the signal as well as increase the signal.It does require the power supply. These are also called as a Multiport Repeater.
Passive Hub: In Passive Hub, It does not regenerate the signal. Therefore, it does not require a power supply.
Advantages of Hub
- Hub improves performance, especially for distributed traffic and large file transfers.
- It enables PCI computers to perform at their best.
Disadvantages of Hub
- It is not suitable for large networks because they have limited port.
- Hub can't control the data traffic.
Switch
The switch is very similar to a hub. It is a device that has multiple ports. The switch accepts the ethernet connections from the network. The switch is more intelligent than a hub because the switch is used to store the physical addresses that are connected to it. The physical addresses are called MAC addresses in the table of the switch. Shown in below switch.
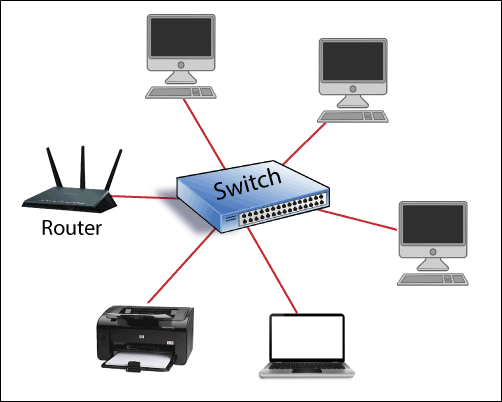
In the switch, the data packet is sent to the destination directly with the help of the MAC address.
Repeaters
A repeater is an electronic device which operates only in the physical layer.
It receives the data signal and regenerates the signal at higher power and sends it forward. The repeater then sends the refreshed signal. It can replicate and regenerate both digital and analog signals.
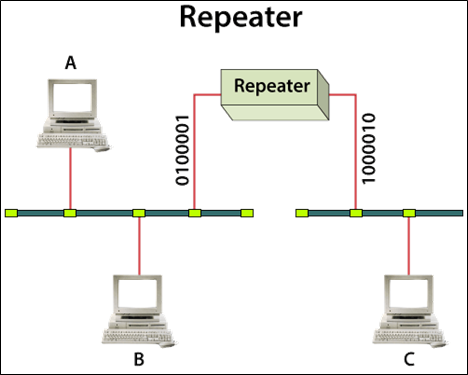
There are two types of Repeater
- Analog repeater
- Digital repeater
The analog repeater only amplifies the signal, whereas the digital repeater is reconstructed the signal and forward by removing errors from it.
NIC
NIC stands for Network Interface Card, which is a piece of computer hardware. It is used to connect the computer to a computer network. It allows users to connect either via wires or wirelessly. It is also called Network Interface Controller, Network adapter, LAN adapter, and Physical Network interface. The figure given below illustrates the diagram of NIC.

Bridges
The bridge is a computer networking device which works to connect the same type of protocol. It operates on the Physical layer and Data link layer of the OSI model. In the physical layer, it regenerates the signal which is received. In the data link layer, the bridge is to check the MAC addresses of "source and destination" in the frame. A bridge has the filtering capability. The bridge checks the destination address of a frame, and it decides from which outgoing PORT the frame should be sent it.
Advantages of the Bridge
- Reliability
- Manageability
- Scalability
Disadvantages of the Bridge
- A bridge can't filter out broadcast traffic.
- Only two networks can be connected with a bridge.
Router
The router is a networking device that connects two or more networks together. It transfers data packets between the computer networks. It decides the best way for a packet to transfer its destination. It works on the three-layer (physical, data-link, and network layers) of the OSI model. Generally, Router operates to connect various types of networks.