FTP: File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol
File transfer protocol is commonly called FTP. The most popular service of the Internet is to download the files. In other words, it is to transfer the files from one device to another device on the Internet. Every day thousands of files are transferred from one device to another device on the Internet using FTP. This protocol is also be used to upload the files on the Internet. FTP executes at the top of the TCP/IP stack.
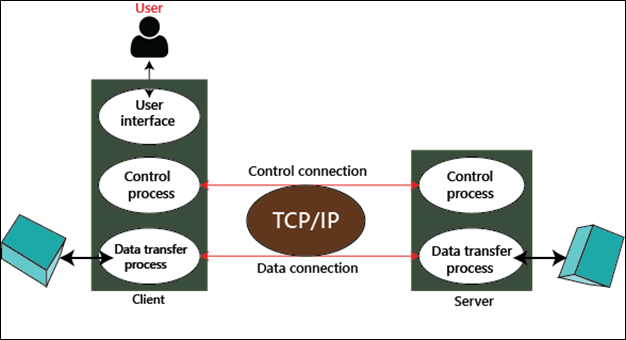
FTP is also a client-server protocol. Therefore, it establishes two TCP connections between the client and the server in which the first connection is used to control the conservation, and the second connection is used to transfer the files.
FTP Server
A computer that uses FTP to transfer the data is called an FTP server. Any user can access the data that is stored in the FTP server, while some data can be accessed by special users.
FTP is divided into two parts:
1. Anonymous Server
2. Non-Anonymous Server
Telnet
Telnet stands for the Terminal Network. Telnet is a text-based and application layer protocol that is used to access the remote devices via TCP/IP network. Telnet was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force in 1969. Telnet provides such services that are based on the command-line interface.
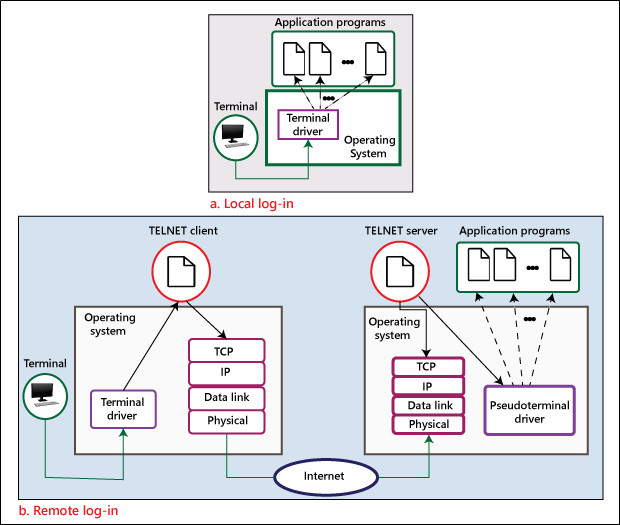
Telnet Concept
Telnet is an oldest internet facility. It allows you to use a remote computer sitting on any computer. It is also called a remote log-in method. Usually, a telnet program gives you a text-based window for another computer. If you have permission to access that system, you can work on it in the same way as you do on your computer. This facility is very useful for those people who want to do such work on other computers, which cannot be done through other facilities like FTP and HTTP.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
The HTTP is an application layer protocol. It is used to transfer the data over the websites. HTTP is a component of the Internet Protocol Suite. It defines the commands and utilities used to send the data to the web page.
Features of HTTP
There are three basic features of HTTP:
- Connectionless
- Media independent
- Stateless
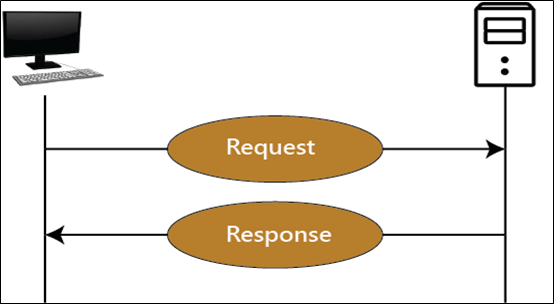
Connectionless: The HTTP client initiates the request to the HTTP server, and after a request is made, the client waits for the response. The server responses to the request of the client, and it sends a response to the client. After that, the client disconnects the connection.
Media independent: Any type of data can be sent via HTTP.
Stateless: HTTP is connectionless, and similarly, it is a stateless protocol because the client and server only know about each other during a current request.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
HTTPS is an application layer protocol through which secure communication can be done from any website over the Internet. It is a protocol that uses HTTP over connections encrypted by transport-layer security. It is mostly used to secure online shopping and banking websites.
HTTPS uses port 443 to transfer its data.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
SNMP was developed by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). It is used to manage the network. It is an internet standard protocol that monitors devices in IP networks, and it also collects and organizes the information of these devices. SNMP is supported by most network devices such as the hub, switch, router, bridge, server, modem, and printer, etc.
The concept of SNMP is based on the manager and agent. A manager is like a host that controls a group of agents, such as routers.
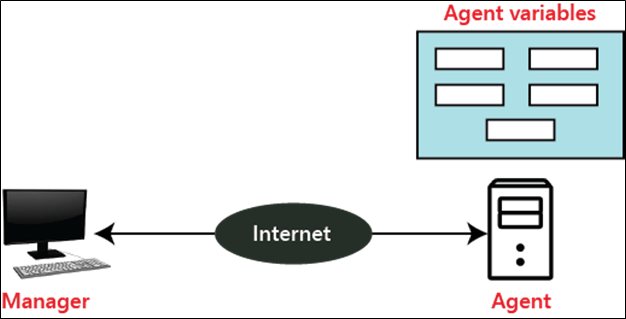
SNMP Manager: It is a computer system that monitors network traffic by the SNMP agent, and it queries these agents, takes answers, and controls them.
SNMP Agent: It is a software program that is located in a network element. It collects real-time information from the device and passes this information to the SNMP manager.
Management components
It has two components
- SMI
- MIB
SNMP Management: It defines the structure of packets that is shared between a manager and an agent.
SMI (Structure of Management Information): SMI is a network management component that defines the standard rules for the naming object and object type (including range and length) and also shows how to encode objects and values.
MIB (Management Information Base): MIB is the second component of the network management. It is virtual information storage where management information is stored.