Computer Network Architecture
Computer network architecture is a design in which all the computers are organized in a computer network. The architecture defines how computers must communicate with each other to obtain maximum benefits from a computer network, such as better response time, security, scalability, transfer data rate, connectivity, etc.
There are two most popular computer network architectures used.
- Peer to Peer Network
- Client-server Network
Peer to Peer Network
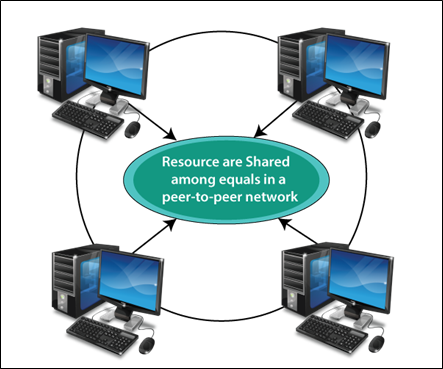
In a peer-to-peer network, each computer acts as its client and server, i.e., it can perform both requests and responses. A Peer-To-Peer network has no dedicated servers, but all computers act as a server for the data stored in them.
Peer to Peer network is a network to which all computers are used the same resources and rights as other computers. Its network designed primarily for the small local area.
The following Figure depicts a Peer-to-Peer Network, with each computer network acting as both client and server.
Advantages of Peer to Peer Network
- Less Costly: There are no dedicated servers, so the network is cost efficient.
- Simple Setup & Maintain: It is simple to set up and maintain.
- A network administrator is not required.
Disadvantages of Peer to Peer Network
- Security is another problem on this network because malware can easily be transmitted through the network.
- It usually doesn't work well with more than "10" users.
- We can’t access the shared data once the computer crashes or automatically turns off.
Client-server Network
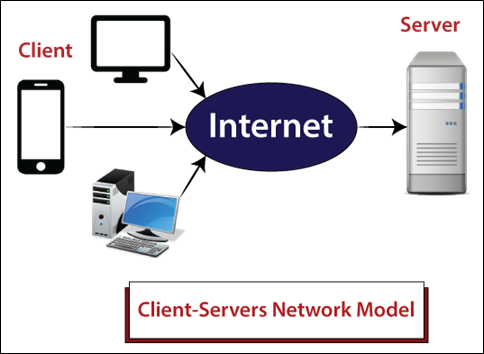
In a Client-Server Network, one central computer act as a hub that is known as a server, and all other computers are known as a client. A Client-Server network has a dedicated server providers. All shared data is stored in the server, which is shared with the client computer when the client computer makes a request. The server is responsible for managing all data, such as files, directories, printers, etc. All clients connect via a server.
The following Figure depicts a Client-Server Network.
Advantages of Client-Server Network
- Security in a client-server network is better because a server manages shared resources.
- The client-server network improves the overall performance of the system with the help of a dedicated server.
- Data backup is secure, as every computer does not need to manage the backup.
Disadvantages of Client-server Network
- The entire network is down in case of server failure.
- It difficult to set up and maintain.
- The client-server network is costly, as it requires a large memory server.
Difference Between Peer to Peer network and Client-Server network?
| Peer to Peer network | Client-Server network |
| It is used in small networks with less than "10" computers. | It usually used on both small and large networks. |
| In Peer-to-Peer Network, each computer is used to store its own data. | A centralized server is used to store data in a Client-Server network. |
| A Peer-To-Peer network is cheaper than a Client-Server network. | A Client-Server network is more expensive than a Peer to Peer network. |
| A Peer-To-Peer network is less stable and secure than Client-Server. | A client-server network is more stable and secure than Peer-To-Peer. |
| Peer to Peer doesn't need a server. | A powerful computer that acts as a server. |