CSS calc()
CSS calc(): The CSS calc() function is a CSS function of inbuilt type, which permits us to implement calculations. It is used for calculating the angle, integer frequency, number, time, percentage, and length. It also uses some arithmetic operators such as add (+), subtract (-), divide (/), and multiply (*).
It is an efficient concept of CSS because it permits us to incorporate the units, like pixels and percentages.
Syntax:
calc( Expression );
Property Values
This function in CSS holds any individual parameter expression. The outcome of such an expression can be recycled as any value. It can be a simple expression with the use of the arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /), and it is essential to define.
Key Points
- Some arithmetic operators like subtract (-) and add (+) must always be enclosed by the whitespace. Otherwise, the expression is treated as any invalid expression. For example, the expression calc(60%-4px) is invalid because this expression is interpreted as the percentage, pursued by any negative length. Let’s take another expression, calc(60%- 4px) is interpreted as any length and any subtraction operator.
- But the operators / and * do not require any whitespace, although it is suggested to insert them for consistency.
- The calc()function nesting is possible.
Example:
In the following example, we will use the function calc() to specify the height and the width of a div component. We will use the subtraction in the calc() function along with the similar units.
The expression’s result will be defined as the property value. Therefore, the height value is 275px, and the width value is 75%.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> CSS calc() function </title>
<style>
.exp
{
width: calc(150% - 75%);
height: calc(350px - 75px);
background-color: lime;
padding-top: 50px;
}
.exp1
{
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: bold;
color: green;
}
h1
{
color: green;
}
h2
{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<div class= "exp">
<div class= "exp1"> Welcome to this Page </div>
<h1> It is an illustration of CSS calc() function </h1>
<h2> width: calc(150% - 75%); </h2>
<h2> height: calc(350px - 75px); </h2>
</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>
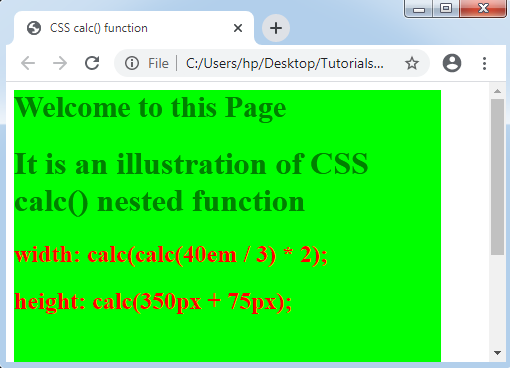
From the above example, it is possible to define the height and width values directly. But the expression within this example contains similar units. If the units are different, it will be difficult to write the values directly.
Output:
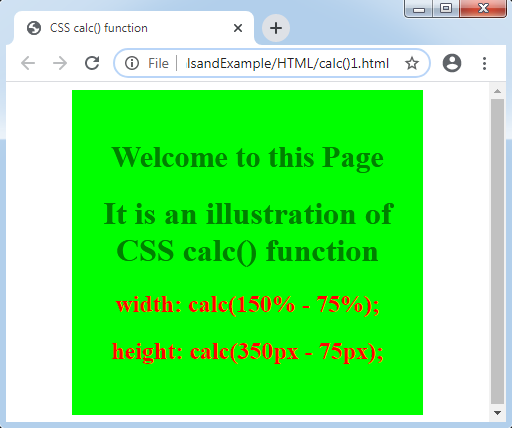
Let’s take another illustration where we will use some mixed units.
Example: using mix units
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> CSS calc() function </title>
<style>
.exp
{
width: calc(40% + 10em);
height: calc(350px + 75px);
background-color: lime;
padding-top: calc(10% - 10px);
padding-left: calc(10% + 10px);
}
.exp1
{
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: bold;
color: green;
}
h1
{
color: green;
}
h2
{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class= "exp">
<div class= "exp1"> Welcome to this Page </div>
<h1> It is an illustration of CSS calc() function </h1>
<h2> width: calc(40% + 10em); </h2>
<h2> height: calc(350px + 75px); </h2>
<h2> padding-top: calc(10% - 10px); </h2>
<h2> padding-left: calc(10% + 10px); </h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
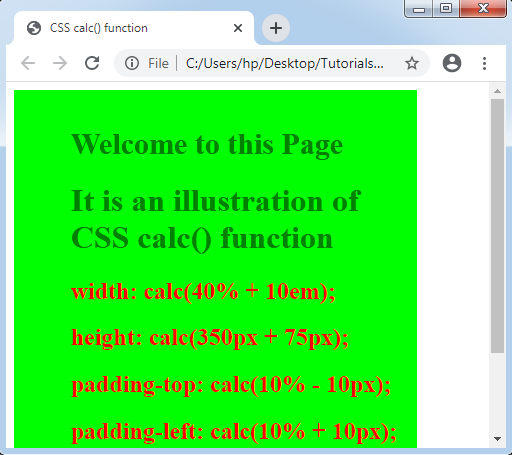
Let’s take another illustration where we will use some mixed units.
Example: calc() nested function
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> CSS calc() function </title>
<style>
.exp
{
width: calc(calc(40em / 3) * 2);
height: calc(350px + 75px);
background-color: lime;
}
.exp1
{
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: bold;
color: green;
}
h1
{
color: green;
}
h2
{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class= "exp">
<div class= "exp1"> Welcome to this Page </div>
<h1> It is an illustration of CSS calc() nested function </h1>
<h2> width: calc(calc(40em / 3) * 2); </h2>
<h2> height: calc(350px + 75px); </h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output: