Full form of IPO
What is the Full form of IPO
IPO: Initial Public Offering

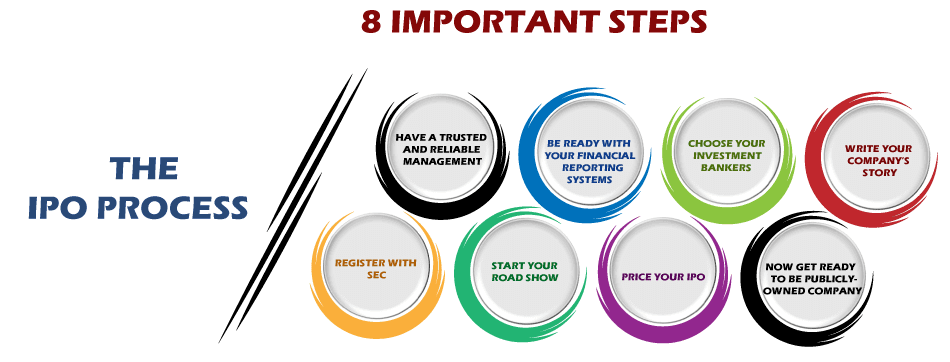
IPO stands for Initial Public Offering. It is a procedure through which a company can go public; in this, the company offers to sell its initial stock to the general public. The company can be either new or old irrespective of their age and can decide to be listed in the exchange and go public.
This can be understood easily with an example like, let's say, there is Company A, which is performing well and now desires to raise money for further growth and expansion. In such a case, if the company is fulfilling all the conditions and requirements as mentioned by the Securities and Exchange Board of India, the company can foregather money for further progress and advancement by furnishing the fresh shares to the general public, institutions, banks, and mutual funds.
The issuance of funds at a share price is usually decided or fixed by the investment banker and the company.
Thereby as soon as shares are furnished to the general public, the company will get them listed in the exchange and will go public, respectively. The entire process of listing the company by offering its shares is known as IPO or Initial Public Offering.
This unlocks the company's opportunity to use the capital for further advancement, expansion, progress, research, development on various marketing plans, or even to pay off the loan or debt.
Note: It is important to note here the respective company providing or offering its shares to the general public is not under any obligation to repay, refund, reimburse the invested capital or funds to public investors.
Moreover, the company that provides the shares is called an "issuer." The company is able to perform the procedure with the help of investment banks or other investors.
Soon after the IPO's completion, the company's shares are traded in the open and active market, and those shares can be sold further through secondary market trading by the investors.
Also, the owner of the company or enterprise is under no obligation to sell you anything until and unless the company has offered the sale of its stocks through IPO; it is only after this procedure that the general public can invest in it.
History of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs)

For many years the term IPO has been a catchword amongst investors and Wall Street.
The Dutch conducted the first modern IPO; they offered Dutch East India Company shares to the public.
Since then, there has been no looking back, and IPO has been continuously used by companies to gather or raise funds from the public investors through the dissemination of public share ownership.
2008 witnessed a financial crisis; as a result, the year recorded the least number of IPOs. The financial crisis was followed by a recession, and IPO's were halted, and for some years, there were hardly any new listings.
It is true that during the course of time, there has always been variation in the IPO trends, i.e., downtrend or uptrend.
Recently the buzz of the IPOs has shifted to the start-ups, having a private valuation of $1 billion or more.
Advantages of IPO
There are numerous benefits of an IPO. Some of the essential benefits have been listed below:
1) Listing of the shares
One of the greatest or massive benefits of an IPO is that the company can get their shares listed in the exchange. Even though the trading of the shares only begins by all the formalities or agreements that have been completed, including listing. Once everything is finished within the rules and regulations, the shares can then be traded like all other listed companies.
2) Raising Capital or gathering funds
Another considerable advantage or benefit of IPO is that it allows you to gather funds for further progress and the company's advancement. At times companies, enterprises try to collect funds through various investors, banks, or institutions. Still, they encounter various limitations so that they can adopt the route of Initial Public Offer or IPO in such a case.
However, it is very essential to lucidly mention in the offer document that how the funds or the money raised or collected will be utilized by the company.
3) Compliance in an IPO
In all the scenarios, it is very essential that there will be transparency. The obedience of rules, regulations, and guidelines as stated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India, RBI, exchanges, and various other organizations/ authorities.

Disadvantages of IPO
Apart from the benefits, Initial Public Offering also has several disadvantages:
- IPO makes it essential for companies to disclose their financial and business details and information.
- IPO often involves various charges, including legal costs, account costs, marketing costs, etc.
- IPO also requires a proper investment of time, effort, and attentiveness in management.
- The IPO process always involves the risk that the required funding will not be collected.
- The process of IPO often involves lack of control, mismanagement, and other problems due to new shareholders.
- IPO comes with risks of litigation, including derivative actions of shareholders and actions by private securities class.