GPRS Full Form
GPRS
GPRS is the abbreviated form of General Packet Radio Service. GPRS is a service or facility for pack-oriented communication of the data or information. This service or the facility facilitates the communication for mobile on 2G or 3G mobile communication system.
- In other words, General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet-oriented mobile data service in the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) 2G and 3G cellular networks. GPRS was developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)as an advanced version of CDPD or the cellular packet switching technologies and i-mode. It is now supported by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).

- This facility or the service has its basis on the technique of modulation known as Gaussian Minimum Offset Coding (GMSK). In order to permit the GPRS in GSM or TDMA, two modules are necessary to be added-: GPRS Gateway Service Node (GGSN) and GPRS Service Node. (SGSN)
- GPRS is usually traded on the basis of holistic capacity or the quantity of data or information transmitted during the billing period; on the contrary, circuit-switched data is billed chiefly on the basis of per minute or sometimes in 1/3-minute increase. GPRS packet data limit can be calculated per MB of data, with or without rate limit.
What is the function or purpose of GPRS?
GPRS can be utilised for providing Internet protocol-based connections that help or assist in various business applications.
- GPRS is the best service, which means that bandwidth and latency depend on the number of other users using the service.
- At the same time, unlike circuit switching, circuit switching guarantees a specific quality of service (QoS) during a call or the connection.
- In the 2G system, GPRS facilitates the data transmission rate ranging from 56-114 kbps. 2G cellular technology in combination with GPRS is at times referred to as 2.5G, which is a technology between second-generation (2G) and third-generation (3G) cellular networks that can transmit data at medium speeds by using time division multiple access(TDMA) channels For example, unused in the GSM system. .GPRS is amalgamated in GSM Release 97 and later new versions.
History of GPRS
Let’s get to know the history behind the GPRS
- GPRS came into existence in the year 2000 as a service for packet-switched data. GPRS was integrated with the channel switched cell radio community GSM.
- GPRS expands its horizon, or the attain of the Fixed Internet through connecting cellular terminals all around the globe.
- The CELLPAC protocol was set up in 1991-1993 and became the number one cause for starting in 1993 configuration of regular or standardised GPRS through ETSI SMG.
- Specifically, the CELLPAC Voice & Data features were added in 1993
- ETSI Workshop determination that later came to be referred to as GPRS roots.
- The workshop entry is noted in 22 GPRS-associated US-Patents. Successor structures to GSM / GPRS consisting of W-CDMA (UMTS) and LTE, as applied through CELLPAC, rely on important GPRS operations for cellular Internet entryway or accessing the mobile internet.
- As in line with studies at the records of GPRS growth, the inventors of GPRS are Bernhard Walke and his scholar Peter Decker, the primary that made the system accessible to the mobile internet easily all around the world.
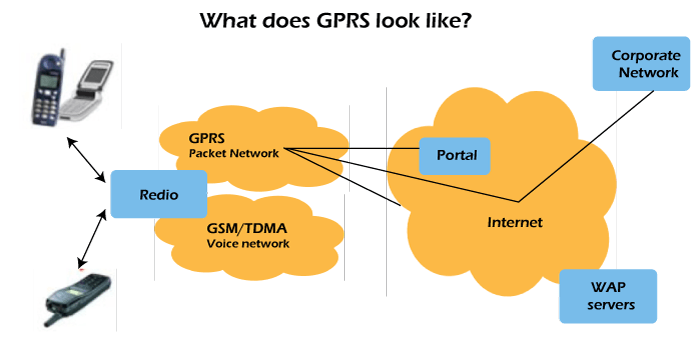
Technical Specifications
The GPRS core network enables 2G, 3G, and WCDMA cellular networks for the transmission of IP data packets to exterior networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integral part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
Services provided by GPRS
The provided GPRS service expands the data transmission capabilities in the GSM packet network, including the following services:
- SMS and broadcast
- Permanent Internet access
- Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS)
- Push-to-Talk (PoC)
- Instant Messaging and Online Status: Wireless Village
- Provides Internet applications for smart devices through the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP).
- Point to Point (P2P) services: networking through the Internet (IP).
- Group calls for multipoint connections; also facilitates point to multiple point service(P2M)
- When using SMS via GPRS, the SMS transmitting rate is approximately 30 SMS messages in a single minute. This is much rapid and swift in comparison to regular SMS via GSM, which has a transmission rate of approximately 6 to 10 SMS messages in a single minute.
Advantages of GPRS
There are various advantages of GPRS; some of these have been listed as follow;
- It offers better information switch velocity than constant telecommunication networks, i.e., it facilitates fast data transmission in comparison to the fixed networks.
- Its most effective velocity is 171.2 kbps, nearly three instances faster than constant-telecommunication velocity.
- It offers on spontaneous connection and instant information switch. It may be very economical and beneficial.
- It has modern and advanced packages. It offers net packages over cellular and additionally allows Web browsing, IM messages, E-trade, etc.
GPRS permits users in connecting to the Internet even when other service providers (including 3G or HSDPA) are not available.
What do I need for using GPRS?
- There are certain specific requirements in order to use GPRS.
- A network either of GSM or GPRS.
- An application that has a GPRS modem
- A sim card that has the service or facility of GPRS.
Features or Characteristics of GPRS
- This is a big step towards the third-generation network.
- It has the potential to provide the dynamic TDMA
- It brought about a massive transformation and eliminated the dial-up process that used to be complex and unmanageable.
Disadvantages of GPRS
- Apart from the advantages or benefits, there are certain disadvantages of the GPRS.
- The potential, capacity, or volume has limitations for its users.
- GPRS: User bandwidth is limited and slower than expected.
- In fact, it is difficult to answer GPRS calls when using a GPRS network.
- GPRS is determined to be 2.5G technology as it has is said to be more advance than the regular or old standard 2G digital technology, but it does not conform to the 3G technology claim.
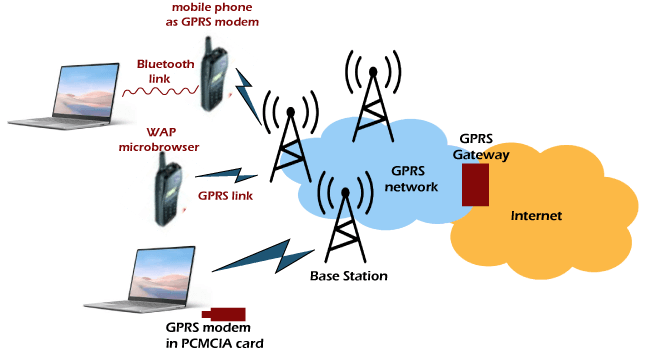
Protocols Backed by GPRS
GPRS backs some of the protocols; these are as follow;
- Internet Protocol (IP).In fact, embedded mobile browsers used IPv4 before IPv6 became mainstream.
- Cellular operators generally do not support Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), but if you use your mobile phone as a modem to connect to your computer, you can use PPP to route IP addresses. This allows you to dynamically assign IP addresses. (Use IPCP instead of DHCP) on the mobile equipage.
- Next in line is X.25 connection; these are commonly used in applications such as wireless payment terminals, although they have been eliminated from the standard. X.25 can still be backed over PPP or IP. but this essentially needs network routers to encapsulate or firmware/ software made into end-device or the terminal like UE - user device.
- When the user equipment (UE) uses TCP/IP, each phone can be assigned one or more IP addresses. Even during transmission, GPRS will save IP data packets and forward them to the mobile phone. TCP recovers lost packets (for example, a pause due to radio noise).
Hardware
Devices that support GRPS can be divided into majorly three classes;
Class A
- This class supports connecting of GPRS service and GSM service (voice, SMS) at the same time; these devices are now available.
Class B
- In this class, it supports connecting to GPRS service and GSM service, but one can use one facility at a time; both can't be used together. GPRS facility usually suspends and then resumes when the GSM service (voice call or SMS has ended). Most of the GPRS mobile belongs to Class B.
Class C
- In this class, hardware is connecting either using GPRS or GSM facility, and you must manually switch between services.
Coding Scheme and the Speed
- The uploading, downloading speeds that can be obtained in GPRS usually rely on a number of reasons. These reasons include;
- The number of BTS TDMA- times slots that have been allocated by the operator.
- The type of channel coding that has been used.
- The maximised capacity of the mobile is portrayed as GPRS multi-slot class.
Usage
- The maximised speed of the GPRS connection speed was proposed in 2003is similar to the 32-40 kbps of the modem and analog wired telephone network connection, relying on the mobile phone used.
- The delay or the latency is very high; Round Trip Time (RTT) is usually It is 600 to 700 milliseconds, often reaching 1 second. The priority of GPRS is usually lower than that of voice, so the connection quality varies greatly.
- Devices with improved RTT/latency are usually available (for example, with extended mode UL TBF function). In addition, selected network operators can update network functions, to significantly improve application-level performance. With these upgradations RTT time can be minimised, resulting in a substantial hike in the level of application through the different levels of speed.