Queue Data Structure
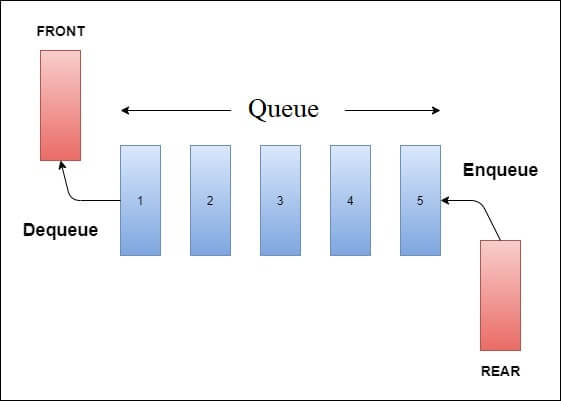
Queue in DS: The queue is a non-primitive and linear data structure. It works on the principle of FIFO (First In First Out). That is, the element that is added first, it is removed first, and the element that is added to the last, it is removed at the end.
We often use a queue in our real world, let's see an example of this: - a person who is come first in the railway ticket reservation line and goes firstly, and another person who is engaged in the last and that person goes out at the end.
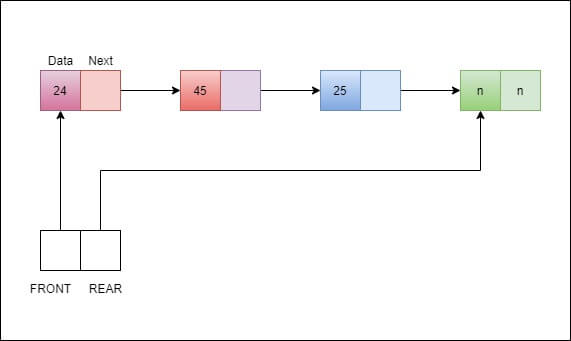
A queue has two ends, one is the front end, and the other is the rear end. The element is added to the rear end and removed from the front end.
The queue has the following conditions:
- If FRONT = 0, then the queue is empty.
- If REAR = size of the queue, then the queue is full.
- If FRONT = REAR, then there is at least one element in the queue.
- If you want to know the total number of elements in the queue, then you use this formula (REAR - FRONT) +1.
There are two primary operations in the queue.
- Enqueue
- Dequeue
When you insert an element in the queue, that process is called Enqueue, and when you remove an element from the queue, that process is called Dequeue.
Algorithm of Enqueue
This algorithm is used to add an element to the queue.
Initialize F = 0 and R = -1Check 0verflow If F = 0 and R = MAXSIZE or F = R + 1 then write overflow and exit if F = NULL set F = 0 and R = 0 else if R = MAXSIZE set R = 0 set R = R+1Queue[R] = itemExit
Algorithm of Dequeue
This algorithm is used to remove an element from the queue.
Check underflow if F < 0, write underflow and exit set item = Queue[F]if F = R then set F = R = NULL else if F = MAXSIZE then set F = 0 set F = F+1exit
Types of Queue
- Linear Queue
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
- Dequeue (Double Ended Queue)
Linear queue: The data elements in the linear queue are organized one by one in sequential order. It works on the principle of FIFO. The performance of the linear queue is inefficient as compared to the circular queue.
Circular queue: Circular queue is also called ring-buffer. The last node of the circular queue is connected to the first node. It works on the principle of FIFO. In the circular queue, the element is added from the rear end and removed from the front end.
Priority Queue: A priority queue is a linear data structure in which every node has some priority that is processed by the following rules.
- A higher priority element is processed before the lower priority element.
- If two elements are of the same priority, then those elements are processed according to the sequence in the queue.
- When deletion is performed, the element which has the highest priority removed first.
- When the addition is performed, the element which has the highest priority added first.
Dequeue: The full name of the dequeue is a double-ended queue. Dequeue is a linear data structure in which you can add and remove the elements from both the front and back ends.
There are two types of dequeue:
- Input-restricted Dequeue
- Output-restricted Dequeue
Input-restricted Dequeue
In this queue, elements can be removed from both ends of the queue, but can only be inserted from one end.
Output-restricted Dequeue
In this queue, elements can be inserted from both ends of the queue, but can only be removed from one end.
Applications of Queue
- It is used in CPU scheduling and disk scheduling. When the CPU is required at the same time for multiple abstract processes, then the different CPU scheduling algorithms are used by implementing the queue.
- It is used to transfer the data between two processes in the asynchronous manner. In this, the queue is used for synchronization. For example - IO buffers, pipes, file IO, etc.
- It is also used in print spooling.
- It is also used in the graph and BFS (Breadth-First Search). BFS is an algorithm in the data structure that traverses and searches the graph.
- It is also used to handle interruptions in real-time systems.
- The call center phone systems also use the queue structure. It is used to hold the customer calls in order until an executive is free.
Implementation of Queue
You can implement the queue via the array, stack, and linked list. An array is the easiest way to implement the queue.
To implement queue via an array.
- Create an array of the n size.
- Initialize the value of the FRONT and REAR to 0. This value means that the array is currently empty.
In this, the first element of the array is FRONT, and the last element of the array is REAR. When you add the elements in the array, the index of the REAR increases, but the FRONT remains the same. The implementation of queue operations is shown below: