C++ Enumeration
C++ Enumeration
In C++, Enum is a special data type that contains some fixed sets of components that have various applications in the programming. Enum works fine with fixed constant sets where the sets me of various types.
Let us consider a week which has 7 days or all four directions. This kind of set is served very well using Enum in C++.
Enum in C++ is final implicit and constants are static. It can be thought of as classes that have well-defined or fixed sets of constants.
Consider these arguments to learn more about Enum:
- It can be traversed.
- It can have methods, fields, and constructors.
- It can be easier with switch statements.
- It enhances type safety.
- It cannot extend classes. Although, it may implement various interfaces by internally extending the enum class.
Generally, enum is a keyword used for enumeration in C++. It is used specifically with integral constants to enhance code readability and maintainability.
Consider the following syntax of enum:
enum enum_name {constant1, constant2, ……..};
Example:
enum animals{cow, horse, dog, cat};
enum card_deck{ace=4, kind=4, spade=4};
Let us look at some programming examples to understand better.
Example 1: Generic use
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
enum animals { Dog, Cat, Wilderbeast, Cow };
int main()
{
animals pet;
pet = Dog;
cout << "Pet: " << pet+1<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
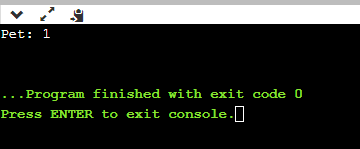
Explanation:
The above code is the simplest demonstration of working with enum in C++. We have assigned the enum keyword before the enum variable's name and have contained it in the various animal's names. The task is to return the position of the animal. To do this, we assigned the enum variable with another variable pet that holds the container's value. The container value with their respective position is then displayed on the console.
Note: There can be an N number of values in the containers. It is better to use lists or arrays in such cases, which allow random access. Although enum provides us the same features, it may increase the space complexity if the container's size is not defined on priority.
Example 2: Using Switch Statement
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
enum Direction { North, South };
Direction direction = North;
switch (direction)
{
case North:
cout << "Direction is North";
break;
case South:
cout << "Direction is South";
break;
default:
cout << "Direction can be either North or South";
}
return 0;
}
Output:
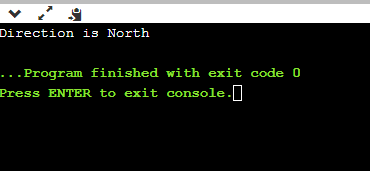
Explanation:
We have used the enum keyword with enumerated key names as directions with two values: North and South in the above code. We have also associated the enumerated keyword with the direction, which is assigned value as North initially. We have defined a switch case that takes direction as an argument and checks if the argument is North or South. If any of these two directions exist in the program, it will be printed, or else the default case will be displayed on the console through the switch statement.
Example 3: Traversing with the enum
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
enum home_groceris
{
Brush,
Paste,
Toothskie,
Watergun,
Floss,
Pan,
Spoon
};
int main()
{
int x;
// Traversing the home_groceris enum
for (x = Brush; x <= Spoon; x++)
cout << x << " ";
return 0;
}
Output:
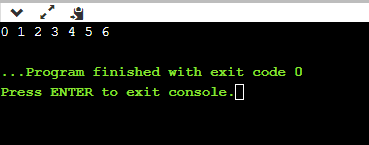
Explanation:
The above code is a demonstration of traversing using enum. We have defined an enumerated name as home_groceries and assigned certain items in the containers. In the driver code, we have defined a variable x that will iterate over the container's items from beginning to end. The output is shown in the picture is the respective count or, say, indexes of the items present in the enumerated container.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Enum
- Enum works well with string, but sometimes they don't work properly with numbers.
- Since enumeration is space-concerned, it possesses no capability to work with additional meta-data.
- While iterating through enumeration containers, enum is sufficient only in case the container is not too large. Random accessing is easy yet time-consuming.
- Enumerators can implement many interfaces, but it fails in extending classes.
- The advantage of using enumerators in C++ includes a lower maintenance requirement, improved program readability, and better-debugging capability.
- Another advantage is that enumerated constants are generated automatically by the compiler. Conversely, symbolic constants must be manually assigned values by the programmer