C++ Multimap
Definition:
In C++, a multimap is similar to a map with the additional concept, where multiple elements possess the same keys. It is also not necessary that the key values and mapped values must be unique. The scenario is different in the case of multimaps. In a multimap, keys are always found in sorted order. This ordered property makes it difficult for competitive programmers to implement multimaps.
Moreover, multi maps are associative containers that are formed by combining key-value and mapped value, which is usually sorted or is in a specific order. Elements in multimap may sometimes have equivalent keys.
A multimap has key values, which are generally used to sort and uniquely identify elements, and the mapped values store the definitions or function related to this key. Some differences in the key and mapped value may exist, which later is grouped forming pairs by combining both.
Syntax
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
Here,
Key: It identifies each element by key value. Keys can be different.
T: It identifies each element by mapped value. Mapped values may be different.
There are various functions associate with mulimaps. Some of them are as follows:
- begin() – It returns first element from the container while iteration.
- end() – It returns the last element from the container while iteration.
- size() – It returns the size or say number of elements present.
- max_size() – It returns maximum number of elements an iterator can hold.
- empty() – checks whether multimap is empty.
- pair<int,int> insert(keyvalue,multimapvalue) – It is used to insert new elements in the multimap.
There are still plenty of such functios present the C++ STL . We may now see some basic coding examples and algorithms working behind it.
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> Professors;
Professors[500] = "M. Chinnaswami";
Professors[200] = "Venugopal Iyyer";
Professors[350] = "Trichipalli Parampir";
Professors[600] = "Mutthuswami Iyer";
Professors[230] = "Rajshekhara Shriniwasana";
cout << "Professors[500]=" << Professors[5000] << endl << endl;
cout << "Size of the map: " << Professors.size() << endl;
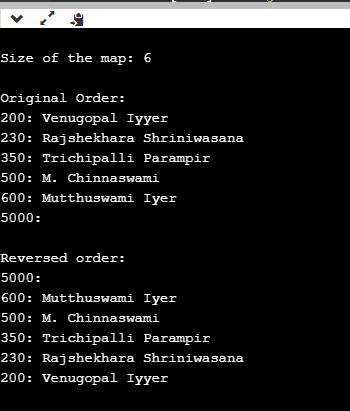
cout << endl << "Original Order:" << endl;
for( map<int,string>::iterator ii=Professors.begin(); ii!=Professors.end(); ++ii)
{
cout << (*ii).first << ": " << (*ii).second << endl;
}
cout << endl << "Reversed order:" << endl;
for(map<int,string>::reverse_iterator ii=Professors.rbegin(); ii!=Professors.rend(); ++ii)
{
cout << (*ii).first << ": " << (*ii).second << endl;
}
}
Output:
Explanation:
The above code explains how to map the key values associated with multimap. In the above code, we have taken arguments in the two forms i.e. integer and string to assign keys of Professors. We can visualize the output. Once the mapped values are sorted in ascending order and later in descending order, it gives us the idea that the mapped and key values can highly be useful for the data present in the form of arrays where we want to find the redundant values associated with them.
Note: The defined map provides a comparison operator in the map declaration to order the indexes. It provides a default comparison for the data type. In the example above, we can see that the key type is an integer with (=) operator and (<) operator can easily operate.
Let’s us now take a straight forward look to the other functions present through the data table below.
| Functions | Descriptions |
| constructor | It constructs multimap. |
| destructor | It destroys/removes multimap. |
| Iterators (cbegin, cend, rbegin, rend,crbegin, crend) | These functions manipulate the multimap using iterators from beginning to end and also in reversee order. |
| Capacity (empty, size and max_size) | These functios check size, maximum size and elements present or not. |
| Modifiers (erase, insert, clear, swap, emplace) | These functions are used to erase, insert, remove or clear, exchange or insert new elements by hint. |
| Observers (key_comp, value_comp) | Return copy of key comparison and value comparison. |
| Allocator (get_allocator) | Returns allocator used to construct the multimap. |
| Operations (count, upper_bound,lower_bound, find, equal_range) | Returns the element and the iterator with keys, counts, value of upper and lower bounds and matches elements with given key. |
Advantages of using Multimap
The advantages are listed below:
- It is comfortable to run through a multimap with iterators rather than using nested for-loop for the map and vector case.
- Once we had inserted a value into the multimap, we know that the iterator would remain valid until we remove it. This is a very strong property; we can't have it with the map of vectors.
- The value once inserted into a multimap remains valid until we remove it which is an added advantage over preferring a map of vectors.
- In multimap, to get elements of a key and map of vectors we simply use [] operator and can have a vector of elements.