Data Link Layer Protocols
Data Link Layer Protocols
- Bluetooth Low Energy
- Z-Wave
- ZigBee Smart Energy
- LoRaWAN
- WirelessHART
- LTE-A
1. Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy or Bluetooth is a short-range communication protocol with the physical layer and medium access control layer. It is widely used in IoT enabled vehicles. Its low power consumption can reach ten times less than conventional Bluetooth, while its latency can reach 15 times. Your access control uses a medium access control (MAC) with low latency and fast transmission.
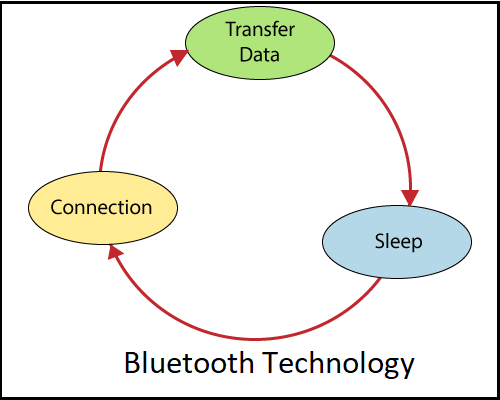
It follows master/slave architecture and offers two types of frames: advertising frames and data frames. The advertising framework is used for discovery and is sent by slaves in one or more dedicated advertising channels. Master nodes detect advertising channels to find slaves and connect them. After connection, the master informs the slave of its activation cycle and its planning sequence. Nodes are usually awake only when they communicate and fall asleep, otherwise to save energy
2. Z-Wave
Z-Wave is a low power MAC protocol. It is designed for home automation, especially for smart home and small business domains. It covers the range from 30 meters to 100 meters of a point-to-point connection. It is suitable for short messages in IoT applications, such as light control, power control, portable health control, and others.
It uses CSMA/CA for collision detection and ACK messages for secure transmission. It follows the Master/slave architecture. The Master controls the slaves, sends them commands, and manage the planning of the entire network.
Properties of Z-Wave protocol
Standard: Z-Wave Alliance ZAD12837 / ITU-T G.9959
Data transfer rate: 100kbps
Range: 30-100m
Frequency: 908.42GHz
3. ZigBee Smart Energy
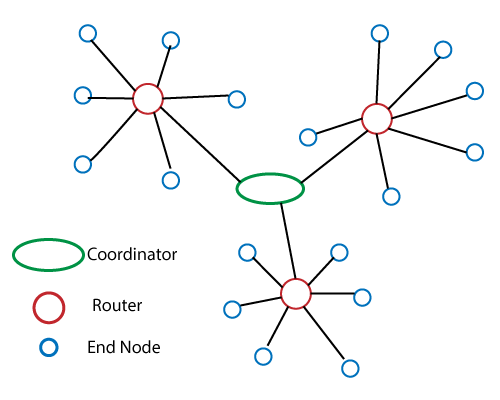
ZigBee Smart Energy is designed for a wide range of IoT applications. It includes smart homes, remote controls, and health systems. It supports a wide range of network topologies, including star, point-to-point, and cluster tree.
Properties of ZigBee protocol
Standard: ZigBee 3.0 based on IEEE802.15.4
Data transfer rate: 250kbps
Frequency: 2.4GHz
Range: 10-100m
4. LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network.
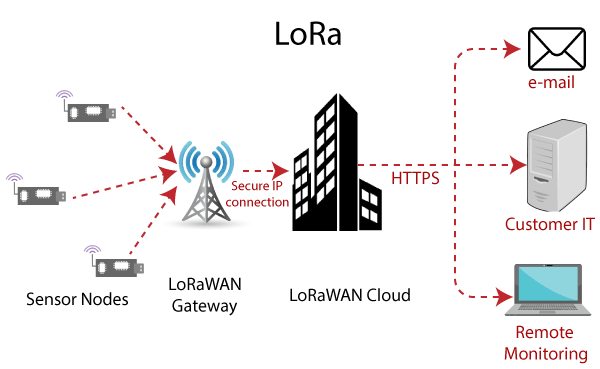
LoRaWAN is a new wireless technology designed for low-power WAN networks with low-cost communications, mobility, security, and bidirectional for IoT applications. It is an optimized low power protocol designed for scalable wireless networks with millions of devices. It supports redundant, location less, low cost, low power, and energy recovery operating technologies. It meets the future needs of the Internet of Things while providing mobility and ease of use.
Properties of LoRaWAN protocol
Standard: LoRaWAN
Range: 2-5km (urban environment), 15km (suburban environment)
Data Rates: 0.3-50 kbps.
Frequency: Various
5. WirelessHART
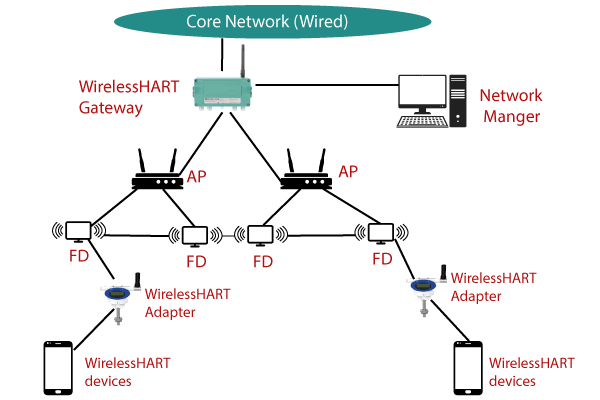
WirelessHART stands for Wireless Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol. It is a data link layer protocol that operates in the physical layer IEEE 802.15.4. It adopts Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) in its MAC. It is a secure and reliable MAC protocol. It uses advanced encryption to encrypt messages and calculate integrity for optimal reliability. WirelessHART Architecture shown in below.
6. LTE-A
Long-Term Evolution Advanced (LTE-A) is a set of standards designed for M2M (Machine to Machine) and IoT communication applications in cellular networks. LTE-A is a scalable, lower-cost protocol compared to other mobile protocols. LTE-A uses OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) as MAC access technology that divides the frequency into various bands each of which can be used separately.