Deque in Data Structure
Deque
A deque referred as “Double-Ended Queue”, is a linear collection of data items same like queue data structure. deque has two ends, front end and rear end, deque is the unrestricted type of data structure, data item can be added into it either front or rear and also data item can be removed or deleted from it either front or rear. Thus, it doesn’t follow first in first out rule. So we can say deque is the hybrid linear structure who provides the functionality of queue and stack in a single data structure.

Sub types of Deque
- An input-restricted deque is the queue where deletion of data item can be done from both ends, but insertion can be done at one end only.
- An output-restricted deque is the queue where insertion can be done at both end, but deletion can be done from one end only.
Language Support:-
- In C++ provides implemention of deque as std::deque .
- In java provides deque interface in collections module.
- In python we can import deque from collections module.
Operations on Deque:-
- Deque() creates a new deque that is empty. It doesn’t take any parameters and it returns an empty deque.
- add_Front(data) adds a new data item in to the front of deque. We give data item as parameter and it returns nothing.
- delete_Front() removes the data item from the front of the deque, returns the data item and it will be modified.
- add_Rear(data) adds a new data item in to the end of deque, needs to take data as parameter and returns nothing.
- delete_Rear() removes the data item from the end of deque,
returns the data item and it will be modified.
- is_Empty() checks to see if the deque is empty and return boolean value.
- Size() returns the number of items in the deque and return an integer.
Implementation of Deque in C langauge
1. By Circular Array
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 10
void add_Front(int *, int, int *, int *);
void add_Rear(int *, int, int *, int *);
void del_Front(int *, int *, int *);
void del_Rear(int *, int *, int *);
void display(int *,int *, int *);
int main()
{
int deque[MAX];
int front, rear, data,n;
front = rear = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
deque[i] = 0;
}
add_Front(deque, 20, &front, &rear);
add_Rear(deque, 4, &front, &rear);
add_Front(deque, 7, &front, &rear);
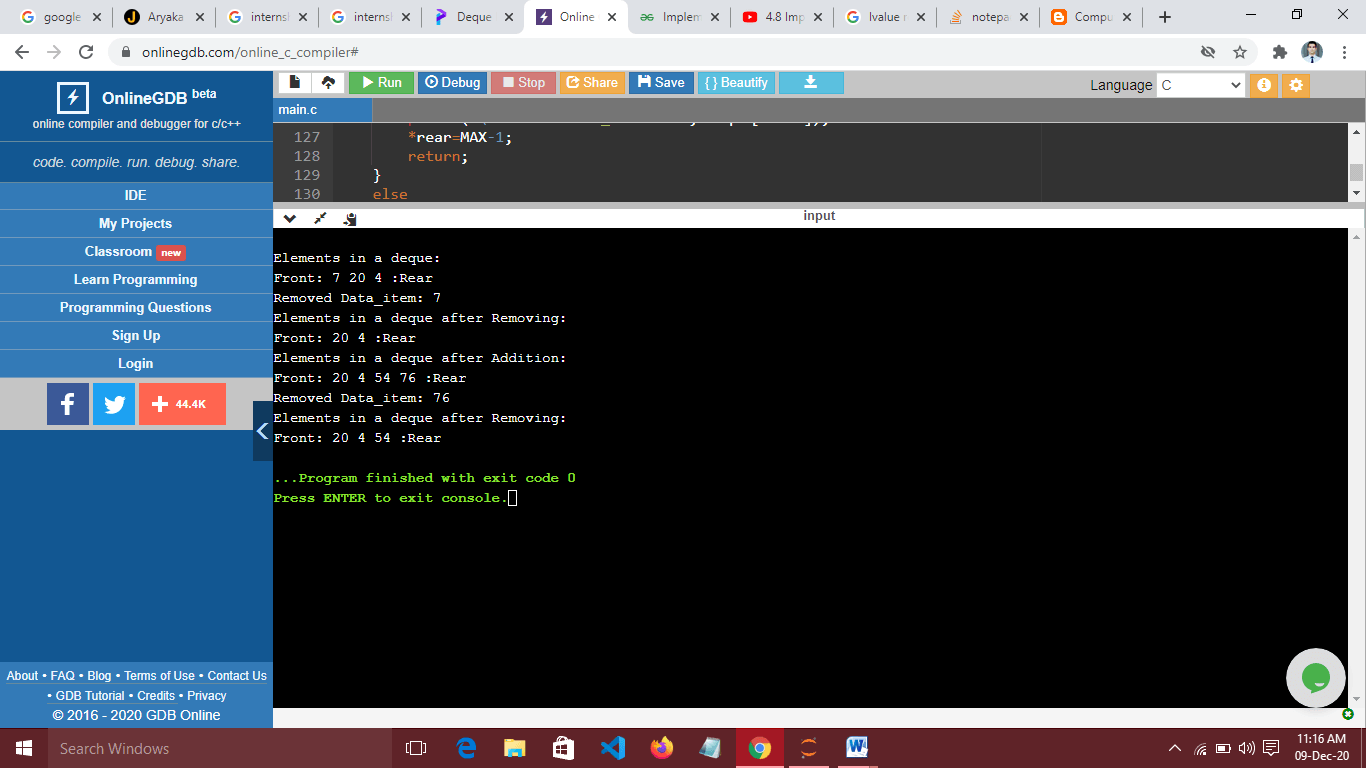
printf("\nElements in a deque: ");
display(deque, &front, &rear);
del_Front(deque, &front, &rear);
printf("\nElements in a deque after Removing: ");
display(deque, &front, &rear);
add_Rear(deque, 54, &front, &rear);
add_Rear(deque, 76, &front, &rear);
printf("\nElements in a deque after Addition: ");
display(deque, &front, &rear);
del_Rear(deque, &front, &rear);
printf("\nElements in a deque after Removing: ");
display(deque, &front, &rear);
}
void add_Front(int * deque, int data, int *front, int *rear)// For adding an element at the front of deque
{
if ((*front == 0 && *rear == MAX-1) || *front == (*rear)+1)// For checking deque is full or not
{
printf("\nDeque is full.\n");
return;
}
else if (*front == -1 && *rear==-1)
{
*front = *rear = 0;
deque[*front] = data;
return;
}
else if(*front==0)
{
*front=MAX-1;
deque[*front] = data;
return;
}
else
{
(*front)--;
deque[*front]=data;
return;
}
}
void add_Rear(int * deque, int data, int *front, int *rear)// For adding an element at the end of deque
{
if (*front == 0 && *rear == MAX-1 || *front== (*rear)+1 )
{
printf("\nDeque is full.\n");
return;
}
else if (*front == -1 && *rear==-1)
{
*front = *rear = 0;
deque[*rear] = data;
return;
}
else if(*rear==MAX-1)
{
*rear=0;
deque[*rear] = data;
return;
}
else
{
(*rear)++;
deque[*rear]=data;
return;
}
}
void del_Front(int *deque,int *front, int *rear)// For removing an element from the front of deque
{
if(*front == -1 && *rear==-1)
{
printf("\nDeque is Empty.\n");
return;
}
else if(*front==*rear)
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*front]);
*front=*rear=-1;
return;
}
else if(*front==MAX-1)
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*front]);
*front=0;
return;
}
else
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*front]);
(*front)++;
return;
}
}
void del_Rear(int * deque,int *front, int *rear)// For removing an element from the end of deque
{
if(*front == -1 && *rear==-1)// For checking deque is empty or not
{
printf("\nDeque is Empty.\n");
return;
}
else if(*front==*rear)
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*rear]);
*front=*rear=-1;
return;
}
else if(*rear==0)
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*rear]);
*rear=MAX-1;
return;
}
else
{
printf("\nRemoved Data_item: %d", deque[*rear]);
(*rear)--;
return;
}
}
void display(int *deque, int *front, int *rear)// For printing the elements of the deque
{
int i=*front;
printf("\nFront: ");
while(i!=*rear)
{
printf("%d ",deque[i]);
i=(i+1)%MAX;
}
printf("%d",deque[*rear]);
printf(" :Rear");
}
Output:-
2. By Doubly Linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node//
{
int info;
struct node *next;
struct node *back;
};
struct node *start = NULL;
struct node *uni = NULL;
void add_Front(int item) // For adding an element at the front of deque
{
struct node *p,*t,*k;
if(start == NULL)
{
p=start;
t=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node ));
start = t;
start->info=item;
start->next=p;
start->back=NULL;
}
else
{
k=start->back;
p=start;
t=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node ));
start=t;
start->info=item;
start->next=p;
start->back=NULL;
k=start;
}
}
void add_Rear(int item) // For adding an element at the end of deque
{
struct node *t,*p;
t=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node ));
if(start==NULL)
{
start=t;
start->info=item;
start->next=NULL;
start->back=NULL;
return;
}
else
{
struct node *p=start,*k;
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
}
k=p;
p->next=t;
p=p->next;
p->info=item;
p->next=NULL;
p->back=k;
uni=p;
}
}
void del_Front()// For removing an element from the front of deque
{
struct node *t,*p;
if(start==NULL)
{
printf("Deque is Empty\n");
}
else if(start->next==NULL)
{
printf("Removed Elements is %d\n",start->info);
start = NULL;
}
else
{
p =start;
t = start->next;
start = t;
start->back = NULL;
printf("Removed Elements is %d\n",p->info);
free(p);
}
}
void del_Rear()// For removing an element from the end of deque
{
struct node *t;
if(start==NULL)//For checking the deque is empty or not
{
printf("Deque is Empty\n");
}
else if(start->next==NULL)
{
printf("Removed Elements is %d\n",start->info);
start = NULL;
}
else
{
t=start;
while(t->next->next! = NULL)
{
t=t->next;
}
printf("Removed Elements is %d\n",t->next->info);
t->next=NULL;
return;
}
}
void traverse(struct node * t) // For printing the elements of the deque
{
if(t==NULL)
{
printf(" Deque is empty\n");
}
while(t->next!=NULL)
{
printf("%d<->",t->info);
t=t->next;
}
printf("%d\n",t->info);
}
void main()//Driver code
{
int n,data,i,item,pos;
while(1)
{
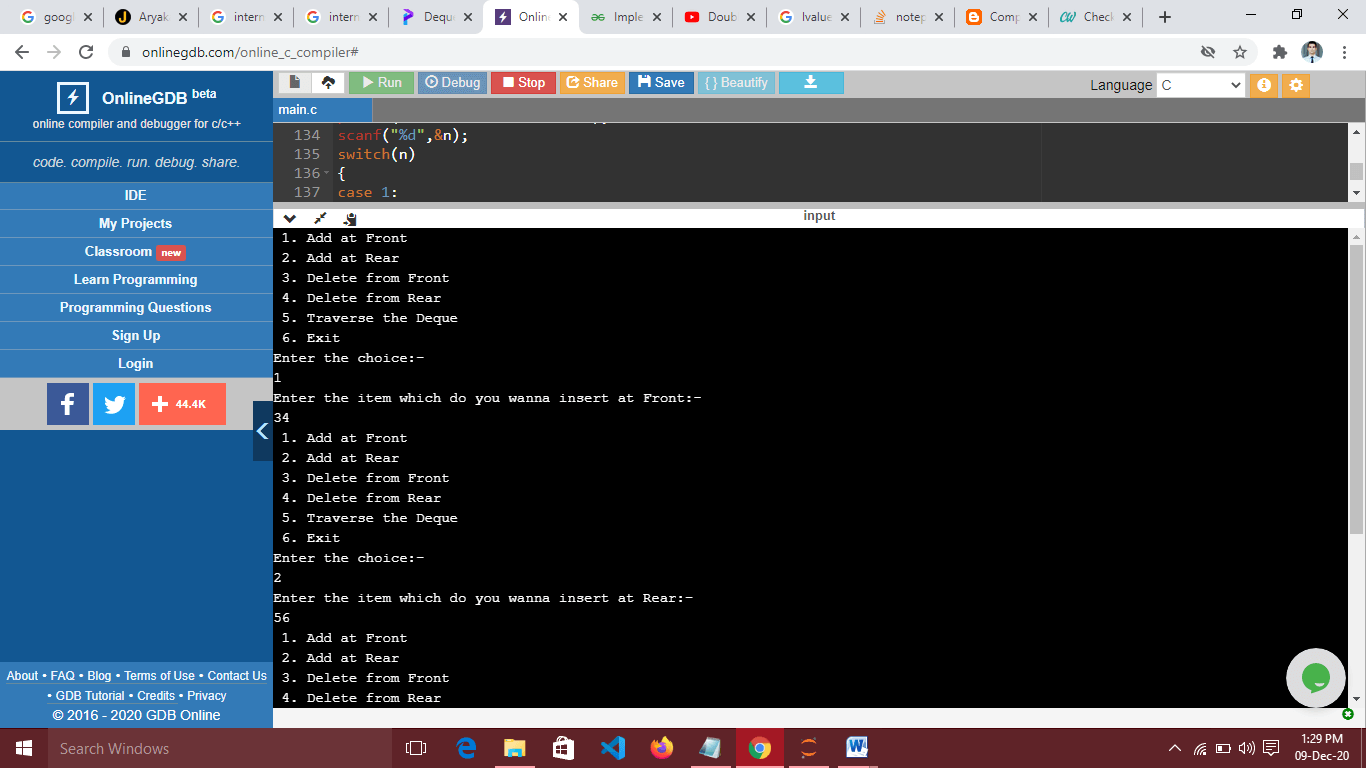
printf(" 1. Add at Front");
printf("\n 2. Add at Rear");
printf("\n 3. Delete from Front");
printf("\n 4. Delete from Rear");
printf("\n 5. Traverse the Deque");
printf("\n 6. Exit\n");
printf("Enter the choice:-\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
switch(n)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the item which do you wanna insert at Front:-\n");
scanf("%d",&item);
add_Front(item);
break;
case 2:
printf("Enter the item which do you wanna insert at Rear:-\n");
scanf("%d",&item);
add_Rear(item);
break;
case 3:
del_Front();
break;
case 4:
del_Rear();
break;
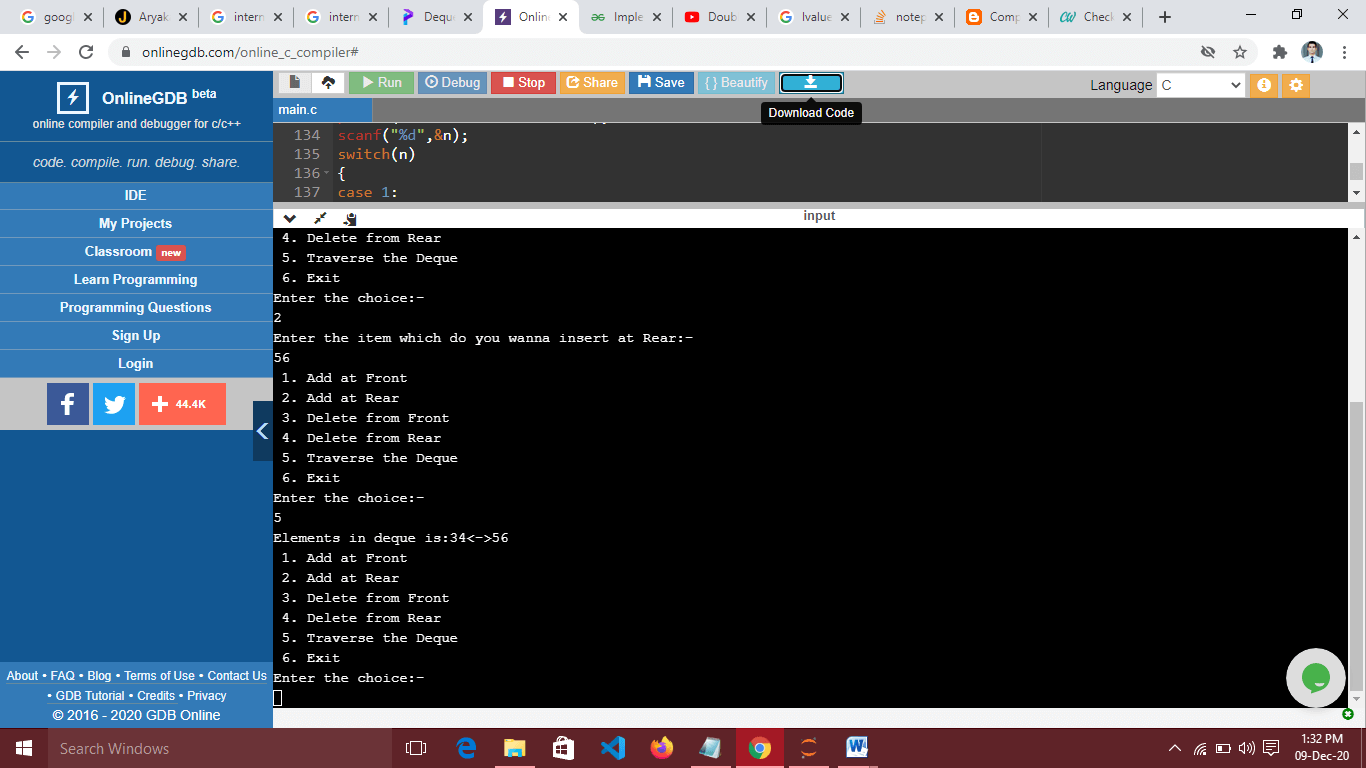
case 5:
printf("Elements in deque is:");
traverse(start);
break;
case 6:
exit(0);
}
}
}
Output:-
Deque implementation in python:-
We can use deque directly in python which will import deque from collections module. For practice purposes, we do possible implementation below of a deque using python list.
Class Deque(object): def_init_(self): Self.items=[] def is_Empty(self): Return self.items==[] def add_Front(self, data): self.itmes.insert(0,data) def add_Rear(self, data): self.items.append(data) def delete_Front(self): return self.items.pop(0) def delete_Rear(self): return self.items.pop() def size(self): return len(self.items)
In add_front we use the insert() method with position 0. So data item add 0th place of the list and if we want add data item in rear so we need to use append() method so data item can be added to the end of the list. Likely for removing data item from the queue we use pop() method with 0th position for remove data item from the front of list and simple use pop() method for remove data item from the end of the list.
Time Complexity of Deque Operations
The time complexity of deque operations like add_front(),add_Rear(),delete_front(),delete_Rear() is contant which is o(1) by Circular Array or Doubly Linked List.
In the above example, we have implemented various operations on deque assume as d and currently empty in the table given below:
| Deque Operation | Deque Contents | Retrun Value |
| d.is_Empty | [] | True |
| d.add_front(“cat”) | [“cat”] | |
| d.add_Rear(2) | [“cat”, 2] | |
| d.delete_Front() | [2] | “cat” |
| d.add_Rear(“dog”) | [2, ”dog”] | |
| d.add_Front(“tiger”) | [“tiger”, 2 ,”dog”] | |
| d.size() | [“tiger” ,2, ”dog”] | 3 |
| d.is_Empty() | [“tiger” ,2, ”dog”] | False |
| d.delete_Rear() | [“tiger”, 2] | “dog” |
| d.add_Front(10) | [10, ”tiger”, 2] | |
| d.delete_Front() | [ ”tiger”, 2] | 10 |
| d.size() | [“tiger”, 2] | 2 |
Applications of Deque
- In the internet browser’s history we use deque for recently visited URL’s as to the front of the queue.
- In computer application undo operation uses deque for storing application’s list.
- As deque supports both stack and queue operation, so it can be used as both.
Standard problem on Deque
An interesting problem that can be solved by deque data structure easily is palindrome problem. A Palindrome is a string if we read this string from both ends of it then it would be same like madam, radar etc. we will try to make solution so we can check the string whether it is a palindrome or not.
The solution of this problem we store the characters of string in deque from left to right like ordinary queue so front end will hold the first character of string and rear end will hold the last character of string after that we will remove the characters from front as well as rear end simultaneously and check them if they match to each other continuously then string is palindrome otherwise not.