Python BS4 Code
Python BS4 Code
The BS4 stands for BeautifulSoup version 4.x. The BeautifulSoup is a Python library which is used for pulling out data of the HTML & XML files using the Python program. The BeautifulSoup library was created basically for the purpose of web scraping.
What is the web scraping?
Web scraping is a technique through which we can extract the large amount of data from many websites at once. The web scraping plays a very important role when we want to import or scrap data from many other websites by writing a few lines of code. Following are some important points of the web scraping process:
- It extract the data from the websites in the unstructured format.
- By web scraping process, we can convert the extracted unstructured format data of website into structured format.
- One major important point of web scraping is that, it is legal only when we are extracting the data from the sites that allowed to used it legally.
Coming back to Python BS4 code, The BeautifulSoup library works with a parser which then provides a way to us for navigating, modifying and searching the parse tree in the web scrapping process.
As of Now, the latest version of BeautifulSoup or BS4 is 4.9.3 which we will be using in this part of tutorial. Now, let's move to the installation part of the BeautifulSoup library in our device. Only after that we will start working with the BeautifulSoup library in our Python program.
Installation of Python BeautifulSoup (BS4) library:
The BeautifulSoup library of Python is not an in-built library of it. We have to install this library before we start working on it. To install the BeautifulSoup, we can use the pip installer. We have to follow the below given steps to install the BeautifulSoup library in our device:
Step 1: Open the command prompt terminal in the system.
Step 2: Write the following command in terminal of command prompt:
pip install bs4
Step 3: Now, press the 'enter' key and command prompt will start installing latest version of BeautifulSoup in our device.
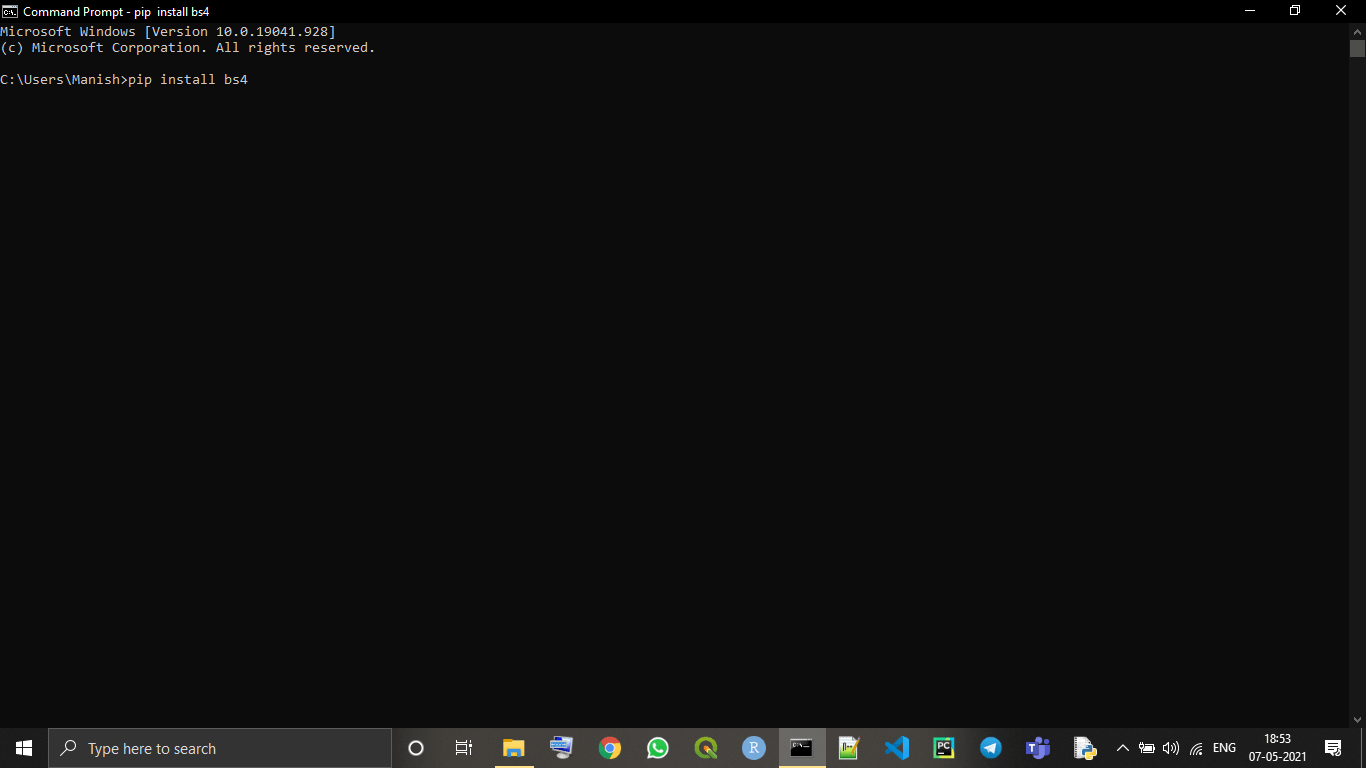
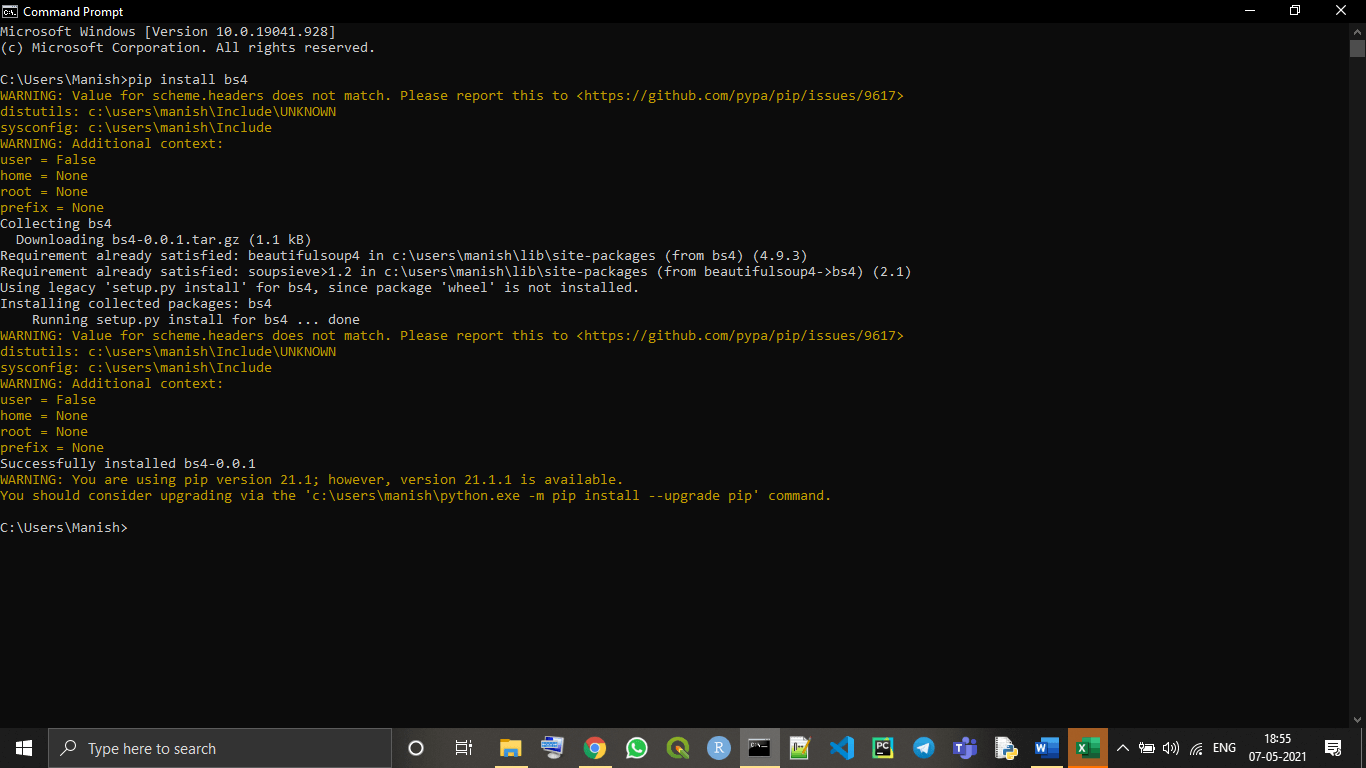
As we can see in the above image, the latest version of BeautifulSoup library is successfully installed in our system.
Installing a Parser:
The BeautifulSoup library supports third party Python external libraries and HTML parser. We have to install them according to our need while working with BeautifulSoup library. Following is the list of some HTML or XML parsers with their typical usages that BeautifulSoup library supports:
- Python's html.parser: The typical usage of Python's html.parser is 'BeautifulSoup(markup,"html.parser")'.
- lxml's XML parser: The typical usage of lxml's XML parser is 'BeautifulSoup(markup,"lxml-xml")'.
- lxml's HTML parser: The typical usage of lxml's HTML parser is 'BeautifulSoup(markup,"lxml")'.
- Html5lib: The typical usage of Html5lib parser is 'BeautifulSoup(markup,"html5lib")'.
Here we will use the Html5lib parser with our BeautifulSoup library and work on it.
Installing the html5lib library parser:
To install the html5lib library with the pip installer, we have to use the following command:
pip install html5lib
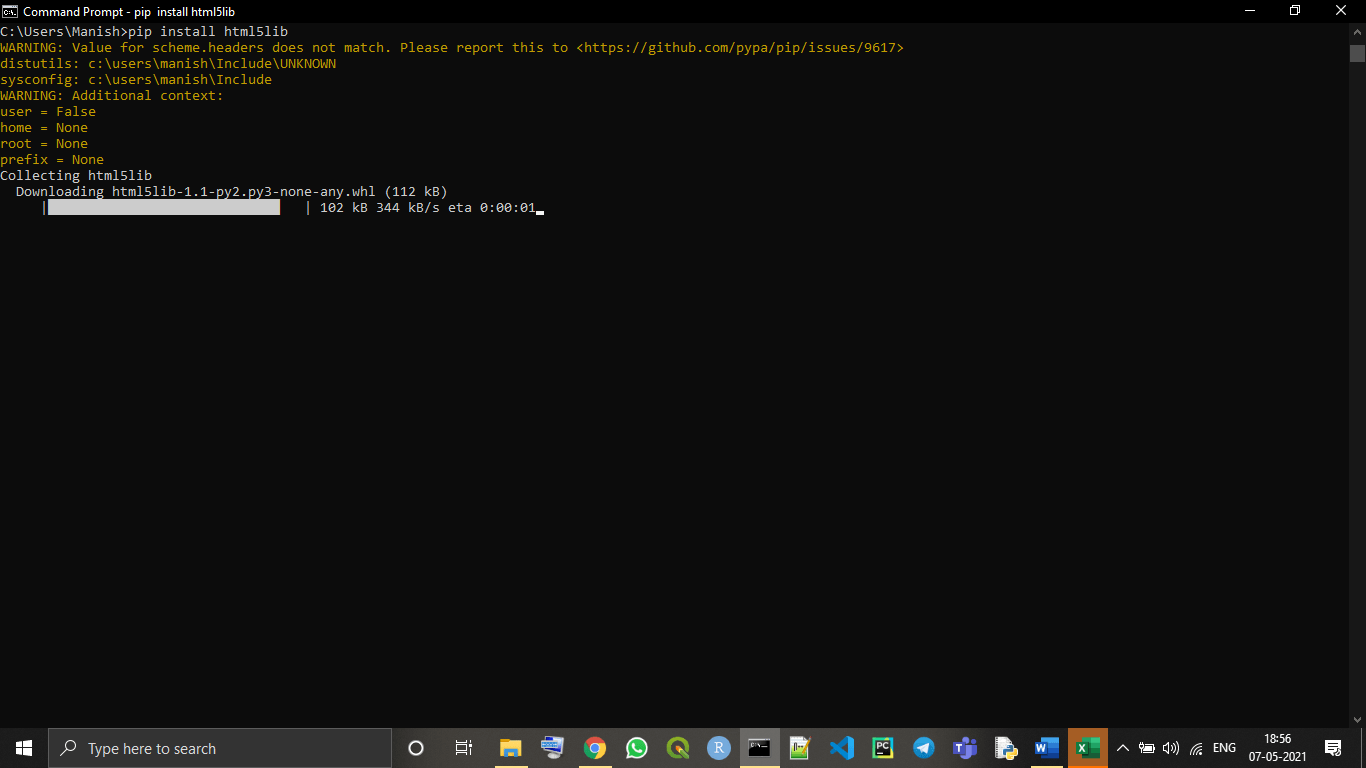
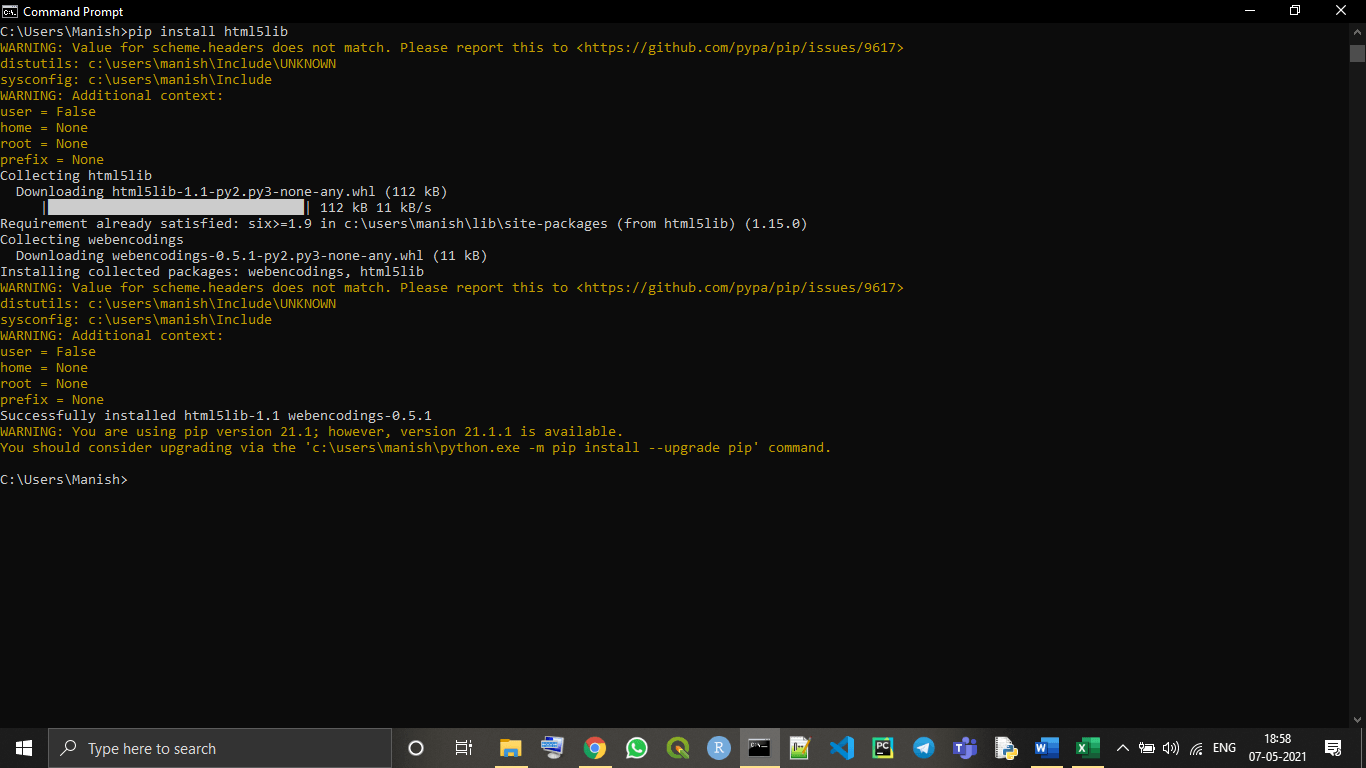
As we can see in the above image that we have successfully installed the html5lib library parser for BeautifulSoup library in our device.
We will use the BeautifulSoup library with the html5lib library parser to convert a complex HTML document given to us into a complex tree of Python objects with our Python program.
Prerequisites:
Before we start working with the BeautifulSoup library, we also have to install one more library (requests). This one external library is pre mandate before we start using the BS4 library. To install these two external libraries, we will again use the pip install in our command prompt terminal.
Installing the request library:
To install the request library with the pip installer, we have to use the following command:
pip install requests
As we can see above, we have already installed the pre-required external library in the machine. Now, we can start working with the BeautifulSoup library in our Python program.
Essential objects used in Python BeautifulSoup library
There are some essential objects in the complex Python tree of object that we will be using in this tutorial. Before we use those objects in our Python program, we must first learn about them in brief. Following is the list of some essential objects in Python BeautifulSoup library:
1. Tag Object:
A tag object present in the BeautifulSoup library corresponds to the tags present in the original HTML or XML document. Let's understand this through the following example program:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# defining a tag in the program
SoupTag = bs4.BeautifulSoup("<b ID = "bold">Not Extremely bold</b>)
# using the tag with tag object
tag = SoupTag.b
# printing the tag type in output of the program
print(type(tag))
Output:
<class "bs4.element.Tag">
That's how we can use a tag object from our BeautifulSoup library. The tag object contains lots of attributes and objects in it but the two most important featured objects of tags are name object & attributes.
2. Name object:
Every tag object we use in the BeautifulSoup library have a name of it which we call its name object. We can access the name object of a tag as .name. The name object is a very important feature of the tag object.
Syntax:
tag.name
3. Attributes Object:
Attributes are the features of the tag object. A tag object can have as many attributes as we want in it. In the tag object program, where we used the tag <b ID = "bold"> has an attribute named as 'ID' and we set the value of the ID attribute equals to bold. We can access the attributes of a tag object by using the tag object as a dictionary in our program.
Syntax:
tag[AttributeID]
We can also modify, add & remove attributes from a tag object in the BeautifulSoup library. We can perform these actions by treating the tag objects as the dictionary format in our Python program. We can understand this through the following example program:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # add an element in the tag object tag['GivenID'] = 'Boldest' # adding another attribute in the tag object tag['Second-Attribute'] = 27 tag # removing an attribute from the tag object del tag['GivenID']
Now, the first attribute of the tag object is deleted as we treated it like a dictionary in the above program.
4. Multi-valued Attributes objects:
As we know that, in HTML5, we have some attributes that can store multiple values inside its tag. Since, the BeautifulSoup library is able to import the code written in HTML, it also has the feature of Multi-valued Attributes in its tag objects. The classes (classes that consists of more than one css files) have the most common example of the multi-valued attributed tag objects.
Following are some other multi-valued attributes used in the tag objects of library:
- accesskey attribute
- rel attribute
- rev attribute
- Headers attribute and,
- accept-charset attribute.
We can understand the multi-valued attributes concepts in BeautifulSoup library through the following example Python program:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# define a multi attribute class
multi_attribute_class = { '*' : 'class'}
# defining multi-valued attributes in the class
Html_soup_object = BeautifulSoup('<p class="body strikeout"></p>', 'html', multi_valued_attributes = multi_attribute_class)
Html_soup_object.p['class']
[u'body', u'strikeout']
5. Navigable String objects:
We refer a string in the BeautifulSoup library as text within the text object. We write Navigable string objects as NavigableString while using it in the program. The BeautifulSoup library uses the NavigableString class for containing these bits form of the text present in the string.
We can understand the NavigableString class concepts in BeautifulSoup library through the following example Python program:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # defining a string in the tag object tag.string # defining features of it # u'Boldest' # type of the tag.string type(tag.string) # defining the NavigableString class in the tag object <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>
Note: As we know that strings are immutable in the Python. Therefore, we can modify or edit the string in the tag objects. But as the feature of string in Python, we can replace the string with another string. To replace the string present in tag object with another string, we have to use the following function in the program:
replace_with()
Let's understand this function through the following Python code:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# using the replace_with() to replace the string in tag object
tag.string.replace_with("String is No longer Boldest in the tag")
tag
If in some cases we want to use the NavigableString class outside the BeautifulSoup library, we have to use the Unicode() function in our Python program. The Unicode() function will help to turn NavigableString into a normal Python Unicode string in the program.
The BeautifulSoup Object:
When we talk about the BeautifulSoup object, it means we are talking about the completely parsed HTML or XML document as a whole. In many cases of completely parsed documents, we can also use the BeautifulSoup object as a tag object in our program. It means that the BeautifulSoup object supports most of the methods that we have described for navigating the tree and finding the tree. We can understand the BeautifulSoup Object concepts in a better way through an example Python program.
Example:
# importing the BeautifulSoup library in the program
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# using the BeautifulSoup object in a document
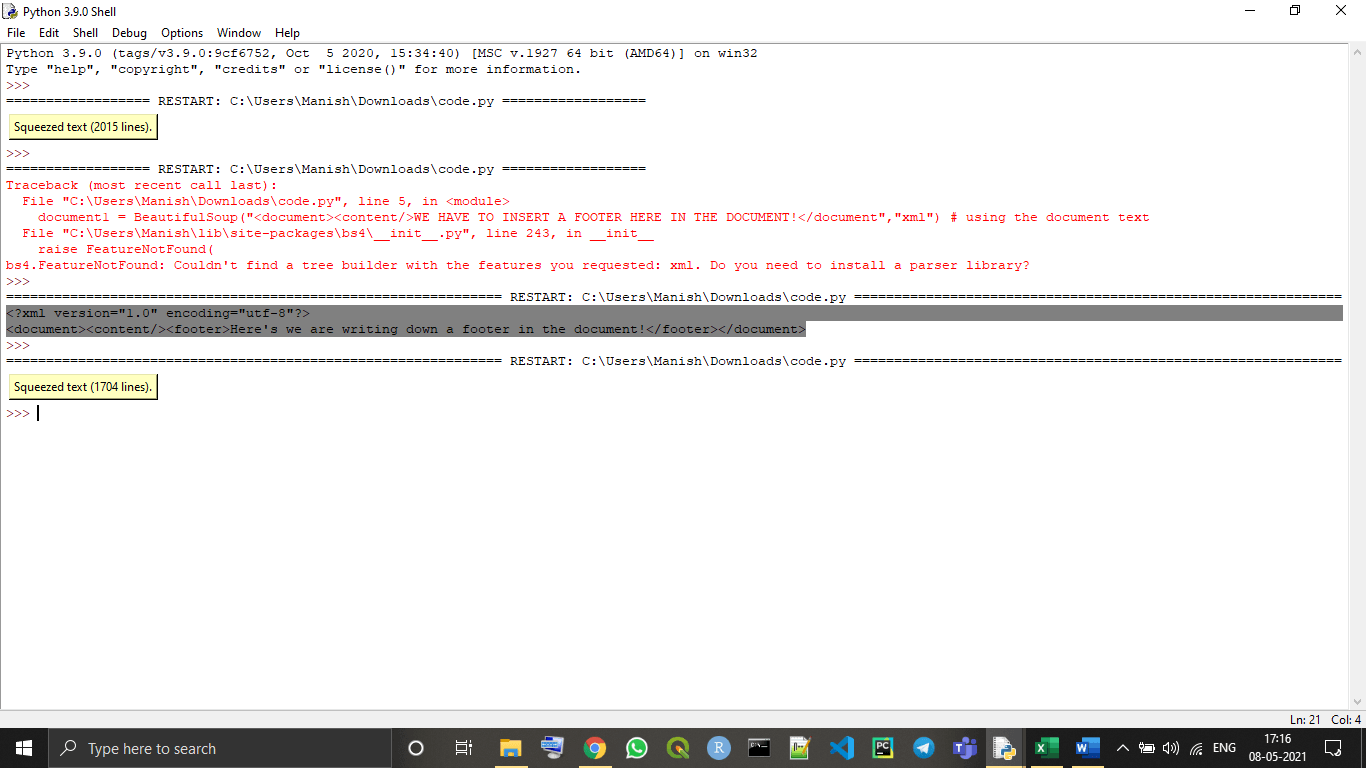
document1 = BeautifulSoup("<document><content/>WE HAVE TO INSERT A FOOTER HERE IN THE DOCUMENT!</document","xml") # using the document text
# defining a footer in the document
footer1=BeautifulSoup("<footer>Here's we are writing down a footer in the document!</footer>","xml")
# replacing the parsed document text with footer text
document1.find(text="WE HAVE TO INSERT A FOOTER HERE IN THE DOCUMENT!").replace_with(footer1)
# printing the BeautifulSoup object used parsed document
print(document1)
Output:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <document><content/><footer>Here's we are writing down a footer in the document!</footer></document>
Explanation –
In the above program, we have used a parsed document with the BeautifulSoup object.
Then we used the find() and after that replace_with() function on the parsed document to replacing the text present in the document.
As BeautifulSoup object is present in our function, we can easily use these methods and function in our program. As we can see in the output of the program, the parsed document have printed the text that we used in the replace_with() function i.e., text present in the footer we have defined.
Web Scrapping using the BeautifulSoup library:
As we have discussed in the starting, the BS4 or BeautifulSoup library is mainly designed for the purpose of Web Scrapping. Now, we have learned all the basics of the BeautifulSoup, let's move the web scrapping process.
Let's understand this through an example. By performing the web scrapping process practically with a program using the BeautifulSoup library, we can easily understand and learn all the concepts related to it. While doing the web scraping of a webpage, we will first extract the data from the webpage we are using and then we will inspect the whole web page. We can inspect the whole web page using the functions present in the BeautifulSoup library.
Example: Open a webpage. Let's open the webpage from our site i.e., TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE.COM and we will inspect the whole webpage and before extracting data from it we have to check that we are ensuring all the requirements related to it. Look at the following Python program:
# importing the request and BeautifulSoup libraries in the program from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import requests # defining the URL in the program (TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE) uRL = "https://www.tutorialandexample.com/" # Making a GET request from the URL to fetch the raw HTML content Html_Content_of_page = requests.get(uRL).text # Parsing the html content of the web page using BeautifulSoup Object BeautifulSoupObject = BeautifulSoup(Html_Content_of_page, "html5lib") # printing the parsed data of html in the output of program print(BeautifulSoupObject.prettify())
Output
Explanation –
In the above given program, as we can see that we have used the Python's in-built parser i.e., "html5lib" parser of Python. We have created a GET request from the requests library in the program to get the URL and create the parse tree object with the given URL. We are able to perform this action because of Html5lib parser and BeautifulSoup library.
The above given program will display all the html coding present in the TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE home page in the output of the program.
We can collect all the required data table with the help of BeautifulSoup object we have defined in the program. We can also get all required information from the TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE home page with the help of BeautifulSoup object we defined in the program.
So, let's print some of the interesting information from the home page in the output.
1. Printing the title of the web page:
We can print the title of the web page whom URL we are using in the program. We can do this by using the following line of code in our program:
print(BeautifulSoupObject.title)
Look at the following program:
# importing the request and BeautifulSoup libraries in the program from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import requests # defining the URL in the program (TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE) uRL = "https://www.tutorialandexample.com/" # Making a GET request from the URL to fetch the raw HTML content Html_Content_of_page = requests.get(uRL).text # Parsing the html content of the web page using BeautifulSoup Object BeautifulSoupObject = BeautifulSoup(Html_Content_of_page, "html5lib") # printing the title of the web page in the output of program print(BeautifulSoupObject.title)
Output of the program:
<title>Tutorial And Example - A Tutorial Website with Real Time Examples</title>
As we can see in the output, the title we printed in the output is included with the HTML tag. If we want to print the title of the web page, then we have to use the following line of code:
print(BeautifulSoupObject.title.text)
Look at the following program:
# importing the request and BeautifulSoup libraries in the program from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import requests # defining the URL in the program (TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE) uRL = "https://www.tutorialandexample.com/" # Making a GET request from the URL to fetch the raw HTML content Html_Content_of_page = requests.get(uRL).text # Parsing the html content of the web page using BeautifulSoup Object BeautifulSoupObject = BeautifulSoup(Html_Content_of_page, "html5lib") # printing the title of the web page without html tags in the output of program print(BeautifulSoupObject.title.text)
Output:
Tutorial And Example - A Tutorial Website with Real Time Examples
2. Printing links present in the web page:
We can also print the entire links present in the page along with the attributes of the link like title, href and its inner text. We can do this with the following Python code:
for link in BeautifulSoupObject.find_all("a"):
print("Inner Text is: {}".format(link.text))
print("Title is: {}".format(link.get("title")))
print("href is: {}".format(link.get("href")))
Example –
# importing the request and BeautifulSoup libraries in the program
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
# defining the URL in the program (TUTORIALANDEXAMPLE)
uRL = "https://www.tutorialandexample.com/"
# Making a GET request from the URL to fetch the raw HTML content
Html_Content_of_page = requests.get(uRL).text
# Parsing the html content of the web page using BeautifulSoup Object
BeautifulSoupObject = BeautifulSoup(Html_Content_of_page, "html5lib")
# printing the title of the web page without html tags in the output of program
print(BeautifulSoupObject.title.text)
# printing the links present in the page in the output of the program
for link in BeautifulSoupObject.find_all("a"):
print("The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: {}".format(link.text))
print("The Title of link present in the page is: {}".format(link.get("title"))) # printing the title attribute of the links present in the page
print("The Title of link present in the page is: {}".format(link.get("href"))) # printing the href attribute of the links in the page
Output:
In the output, all the links with the attributes are printed. Here we will be showing some of them in the below text: Tutorial And Example - A Tutorial Website with Real Time Examples The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Join YouTube Channel The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://bit.ly/346bUiN The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Home The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://tutorialandexample.com The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Trending The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: # The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Machine Learning The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/machine-learning-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Angular 8 The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/angular-8-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Artificial Intelligence (AI) The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/artificial-intelligence-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: ReactJS The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/reactjs-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Cloud Computing The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/cloud-computing-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Data Science The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/data-science-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Artificial Neural Network (ANN) The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/artificial-neural-network-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: Deep learning The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/deep-learning-tutorial/ The Inner Text of the link present in the page is: DevOps The Title of link present in the page is: None The Title of link present in the page is: https://www.tutorialandexample.com/devops-tutorial/
So here we understood and learned that that’s how we can do web scrapping of any website with the help of BeautifulSoup Library and we can use all the functions present in the BeautifulSoup Library while performing the web scrapping process. We can also print some important and interesting information of any website with the process of web scrapping using BeautifulSoup Library.