Python Data Types
Python Data Types: The variable in Python is used to store values, and they can hold different values. Each variable in Python has its own data-type. Since Python is a dynamically typed language (The language in which we don't need to pre-define the data-type of the variables), Hence we don't need to define the data-type of the variables which we are declaring in our Python program.
Python interpreter implicitly binds the value which variable stores with its data type automatically.
p = 1
Here the variable p holds value 1, which is an integer data-type in Python. We did not define the data-type of the p variable while declaring it. The Python interpreter will automatically interpret the data-type of variable p as of integer type at the time we declared it and allocate memory to it inside Python.
The type() function
Python also enables us to check the data-type of the variables through which we can know which data-type value the variable is holding in the program. We need to use the type() function inside Python to check the data-type of the variable. When we run the type() function, it will return us the data-type of the variable we wrote inside the function.
Let's understand the working of type() function in Python with an example.
Example: Consider the following code written in Python:
#define variables with different data-type values x = 5 y = 2.3 z = 'Hello Python Developers' #check the data-type of these variables print(type(x)) print(type(y)) print(type(z))
Output:
<class 'int'> <class 'float'> <class 'str'>
Explanation:
In the above code, we have defined multiple variables that are storing values with different data-types. After that, we have used the type() function to find the data-type of the variables inside the program.
Hence, we can see that the Python interpreter has automatically defined the data-type of the variables according to the data-type of values they are storing and allocated memory to them.
Standard Data-types in Python
A variable inside Python can hold values of different data-types. For example, the name of a person is stored as string type, whereas the age of the person is stored as an integer data-type in Python.
Python provides us various standard data-types that we can see in many different programming languages. Data-type of the variables in Python defines the storage method of them in the memory. It is also to note that Python does not provide us any special type of data-type for variables such as long int etc.
Following are the names of the data-types that are defined inside Python:
1. Numbers
2. Sequence Type
3. Boolean
4. Set
5. Dictionary
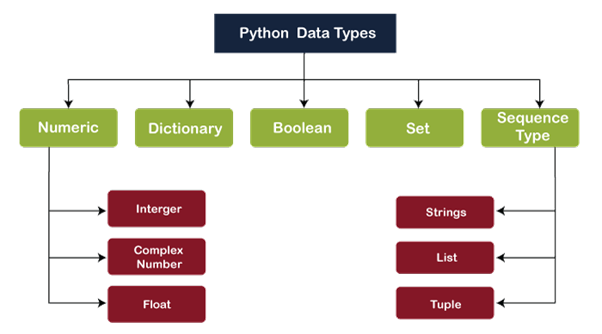
In this section of this Python tutorial, we will discuss in detail each data-type present in Python. We will also discuss how they are defined and how the Python interpreter will allocate memory to the variables with these data-types.
Before proceeding to the standard types of data-type in Python,
- We should note that we can change the variable's data-type by replacing the value it is holding with a different data-type value.
- And, the Python interpreter will dynamically allocate memory to it.
Numerical Data-type
The numerical data-type in Python represents the variables that are holding numbers. The int(integer), float and complex number data-types belong to numerical data-type in Python. In Python, number objects are created inside Python's memory when we assign number values to a variable.
- In Python, we have a type() function through which we can check the data-type of any variable. The type() function will give the class of the variable in output.
- Similarly, in Python, we also have an isinstance() function. The isinstance() function in Python is used to check to which particular class the object of variable belongs.
Example: Look at the following code:
#assign integer value to a variable
x = 3
#check data-type of variable 'x'
print("The type of x", type(x))
#define a variable with float number assigned
y = 26.24
#check data-type of variable 'y'
print("The type of y", type(y))
#Lets define a variable with complex number assigned to it
z = 7+5j
#check data type of variable 'z'
print("The type of z", type(z))
#check class of the object
print(" z is a complex number", isinstance(1+3j,complex))
Output:
The type of x <class 'int'> The type of y <class 'float'> The type of z <class 'complex'>
z is a complex number: True
Explanation:
In this code, we have defined three variables x, y and z with integer, float and complex number data-type, respectively. We have used the isinstance() function to check the object's class that variable 'z' is holding.
When we have put our complex number in the isinstance() function to check if it belongs to a complex class or not, Python gave us the data-type of all three variables. The isinstance() showed us that the condition stands true for z is a complex number.
Python supports the following three types of numeric data-type:
- Int (Integer)
- Float
- Complex Number
It is to be noted that Python does not support any special numeric data-type such as long int or double etc.
- Integer data-type: Variables with int data-type inside Python holds integer number objects. These integer number objects can be 10, 200, -30, -700 etc. In Python, there is no restriction for the length of an integer number. A variable with an integer data-type can hold a maximum value integer number. The value of integer number belongs to int.
Example:
#define variables and assign integer numbers to them.
i = 27
j = -72
k = 1010101010101010
#print variables i, j and k
print(i)
print(j)
print(k)
#Let’s check the data-type of variable i, j and k
print("The type of i",type(i))
print("The type of j",type(j))
print("The type of k",type(k))
Output:
27 -72 1010101010101010 The type of i <class 'int'> The type of j <class 'int'> The type of k <class 'int'>
We can see that despite the sign of numbers (negative or positive) or length of numbers, the data-type of the variable will be int only.
- Float data-type: In Python, the variables having float data-type represent that they are holding floating-point numbers objects such as 1.9, 2.34, 3.14 etc. The decimal limit of float data-type is up to 15 decimal points in Python. It means float data-type variables have accurate and precise object values up to 15 decimal points. Variables with both positive and negative numbers can have float data-type in Python.
Example:
#define variables and assign floating numbers to them.
i = 3.14
j = -2.34
k = 0.3010
#print variables i, j and k
print(i)
print(j)
print(k)
#Let’s check the data-type of variable i, j and k
print("The type of i",type(i))
print("The type of j",type(j))
print("The type of k",type(k))
Output:
3.14 -2.34 0.3010 The type of i <class 'float'> The type of j <class 'float'> The type of k <class 'float'>
- Complex number data-type: A complex number has two parts, i.e., real and imaginary, and has the structure same as a+ib. Here, 'a' represents the real part of the complex number, and 'ib' represents the real part of the complex number. The variables which hold complex numbers have complex data-type in Python. Example: 2+3i, 2.3+1.2i, 0.23i etc.
Example:
c = 2.3+0.23i print(c) #Check the data-type of variable 'c' print(type(c))
Output:
2.3+0.23i <class 'complex'>
Note: A variable which is storing number having only real part is also considered as complex data-type. Let's clear this through an example:
m = 0.23i
print(" m is a complex number", isinstance(o.23i,complex))
Output:
m is a complex number: True
2. Sequence Data-type:
In Python, the sequence data-type is an ordered or paired collection of similar or different data values. The sequence data-type allows us to store multiple object values in an efficient and organized manner.
- Variables with sequence data-type in Python are used to store values with characters, alphabets, words, lists etc.
- Like numeric data-type, sequence data-type also has three further data-types.
Following are the three types of sequence data-type present in Python:
- String
- List
- Tuple
Let's discuss each of these three data-types in detail.
String
A string in Python can be defined as a sequence of characters (including white spaces) represented inside the quotation marks. A variable storing a string object value is considered a string data-type. In Python, we can define string object value using single, double or triple quotation marks.
We can also define a multiline string using triple quotes at the beginning of the string and end our string in the next line by closing it with triple quotation marks.
Let's understand this string data-type through an example.
Example:
mkr = "A string object inside double quotation marks" print(mkr) str = '''This is a multiline string''' print(str)
Output:
A string object inside double quotation marks This is a multiline string
Explanation:
In the above code, we have defined a string mkr inside the double quotation mark. Then we defined multiline string str using five quotation marks and closed the string in the next line.
String Handling in Python:
- Handling a string inside Python is a straightforward task since Python provides us with many built-in functions.
- Python also provides us many operators for performing various operations on the string.
- In a string handling case, the '+' character (string addition operator) is used to concatenate(add) two string values. As in this operation, "Hi" + "Python Developers" will return "Hi Python Developers" as a single string to us.
- The '*' character (string multiple operators) is also known as the repetition operator for strings. As in this operator, "Hello"*2 will return 'HelloHello' in the output.
Example: look at the following code for string handling example:
mkr1 = 'Hello Python Developers' #defining string first with mkr1 name mkr2 = ' How are you all' #printing the string twice using multiple operator. print (mkr1*2) #printing the addition of str1 and str2 using concatenation operator print (mkr1 + mkr2)
Output:
Hello Python DevelopersHello Python Developers Hello Python Developers How are you all
Explanation:
In the above code, we have defined two strings, i.e., mkr1 and. Then we used the multiple operators to print string multiple times, and last, we added both strings using + operator.
List Data-type
Lists in Python are similar to arrays present in C, C++, or other programming languages. But unlike arrays, lists in Python can store object values of different data-types.
The items or objects stored in the list are enclosed by the square brackets [] and items are separated by comma (,).
Let’s understand the following example.
Example:
#Define a list list1 = [1, "Hello", "Python", 24] #Checking the type of list we have defined print(type(list1)) #Printing the list01 print (list1)
Output:
<class 'list'> [1, 'Hello', 'Python', 24]
List handling in Python
- Similar to string handling, we can also handle and operate our list straightforwardly.
- Python provides us many built-in functions, the same as for strings to perform operations in the list we have defined in our code.
- The operators for list data-type are the same as for string data-type, i.e., slice operator [:], concatenate operator (+) and multiple operators (*).
Let's look at an example of list handling in Python.
Example:
# Define a list with objects in it list01 = [1, "Hello", "Python", 2] #slice the defined list slicing operator print (list1[3:]) #Again List slicing print (list1[0:2]) # Add the list to itself using List Concatenation '+' operator print (list1 + list1) # Multiple the list using the List repetition '*' operator print (list1 * 3)
Output:
[2] [1, 'Hello'] [1, 'Hello', 'Python', 2, 1, 'Hello', 'Python', 2] [1, 'Hello', 'Python', 2, 1, 'Hello', 'Python', 2, 1, 'Hello', 'Python', 2]
We can insert or add object values or items inside the list that we have already created using various methods. We will discuss these various methods of adding values to list later sections of this tutorial.
Tuple
Tuple data-type in Python is used to hold multiple object values in a single variable. Tuple data-type is one of the built-in data-type in Python that is used for storing multiple object values inside a single variable. The other is dictionary, list and set.
- Items present inside tuple are ordered and unchangeable.
- Tuple data-type allows duplication, i.e., we can store the same value multiple times inside tuple variables.
- To Create a tuple data-type variable with a single value present in it, we need to use comma (,) after the value; otherwise, Python will consider this variable type as string data-type.
Let's see an example of a tuple to understand it detail.
#define a tuple with parentheses
sup = ("Hello", "Python", 1)
# Check the class type of sup
print (type(sup))
#Print the sup tuple we have defined
print (sup)
Output:
<class 'tuple'>
('Hello', 'Python', '1')
Explanation
In the above code, we have defined a tuple with name sup using parentheses and hold value inside it. Then, we checked the data-type of sup, and after checking the data-type of sup, we printed it.
Operations in Tuple
- As in lists or strings, performing operations on tuple is very straightforward in Python.
- Python provides us built-in functions and operators to perform various operations on the tuple.
- We can perform slicing, concatenation and repetition operation on a tuple in Python.
Look at the following code for understanding operations on tuple:
Example
sup = ("Hello", "Python", 1)
#Perform the slice operation on sup tuple
print (sup[1:])
print (sup[0:1])
#Perform the tuple concatenation operation using + operator on sup
print (sup + sup)
# Perform tuple repetition using * operator
print (sup * 3)
Output:
('Python', 1)
('Hello')
('Hello', 'Python', '1' 'Hello', 'Python', '1')
('Hello', 'Python', '1' 'Hello', 'Python', '1' 'Hello', 'Python', '1')
Explanation: In the above code, we have performed various operations i.e. slicing, concatenation and repetition on tuple sup. After that we printed the result.
Note: Tuple is read-only data structure: - In Python, tuples are immutable data-type which means we can't modify the size of the tuple after it has been defined.
- We even can't modify the values that are present inside a defined tuple.
- This property makes a tuple a very rigid variable in Python.
Let's see an example to understand the read-only property of the tuple data structure.
Example:
#define a tuple with mup name mup = (1, "Hello", "Python", "Developers", 2) # Checking class type of mup tuple we have defined print (type(tup)) #Let’s try to modify one of the object values presents in mup tuple and Python will throw an error while performing this modification operation t[2] = "hi"
Output:
<class 'tuple'> Traceback (most recent call last): File "code.py", line 6, in <module> t[2] = "hi"; TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
We can clearly see that tuple is a read-only data structure, and we can perform insertion or modification operations on tuple after defining it.
Dictionary Data-type:
The dictionary data-type in Python is a set of key-value pairs of items in an unordered manner. Dictionary in Python is very similar to the associative array where each key stores a unique value. Keys in a dictionary can only hold primitive data-types, whereas the object values are arbitrary objects in Python.
- In the dictionary, items are closed inside in the curly braces {}
- In the dictionary, items are separated from each other through a comma ().
Look at the following code for dictionary data-type.
Example:
dict = {1:'Jim', 2:'Carry', 3:'Jonas', 4:'Mike'}
# Printing dictionary dict that we have defined above
print (dict)
# Accesing value of dictionary using keys
print("1st name is "+dict[1])
print("2nd name is "+ dict[2])
print (dict.keys())
print (dict.values())
Output:
{1: 'Jim', 2: 'Carry', 3: 'Jonas', 4: 'Mike'}
1st name is Jim
2nd name is Carry
dict_keys([1, 2, 3, 4])
dict_values(['Jim', 'Carry', 'Jonas', 'Mike'])
Explanation:
In the above code, we have defined a dictionary data-type variable with dict name. Then we printed the dict dictionary. Then we printed the values of dictionary using its keys. After that, we asked for keys and values to print separately so that we can access any of them whenever we want.
Set data-type
Set data-type in Python is an unordered collection of data. The variables with set data-type stores values unorderly and doesn't have key values in them. Since the order of the values is undefined in the set, Python may return the changed sequence of the elements in the set while printing the set in output.
- Sets are iterable in nature.
- Sets are also mutable, i.e., we can modify elements of the set after creation.
- Set always has unique elements stored in them. It doesn't allow duplicity of elements.
- In Python, a set can contain various types of values with different data-types.
Defining a set in Python: In Python, we can define the set using the following two methods:
a). We can create a set variable in our Python program using Python's built-in set () function.
b). We can pass sequence of elements inside the curly braces {} and separate the values by comma {,}.
Example:
# Creating a set(set01) using built-in set() function in Python
Set01 = set()
# the set01 is an empty set
# creating a set(set02) by passing sequence elements in curly braces
set02 = {‘Jimmy’, 2, 3,’Python’}
# Check the class type of set01 and set02
print(type(set01))
print(type(set02))
# Printing the values present in set02
print(set02)
Output:
<class 'set'>
<class 'set'>
{3, 'Python', 'Jimmy', 2}
{'Python', 'James', 3, 2, 1}
{'Python', 'James', 2, 1}
Explanation: In the above code, we have defined two sets i.e. set01 and set02. The set01 is empty set whereas set02 is storing some elements.
Boolean data-type:
Like any other programming language in Python, boolean data-type has two built-in values, i.e., true and false. Boolean data-type is used for the condition statement codes to check if the statement is true or false.
- The class bool denotes the boolean data-type.
- True in boolean data-type can be represented by any non-zero value or 'T'.
- False in boolean data-type can be represented by zero value (0) or 'F'.
Example: Look at the following code for boolean type:
# A Python program to check the boolean data-type print(type(False)) print(type(True)) print(true)
Output:
<class 'bool'> <class 'bool'> NameError: name 'true' is not defined
We can see that the true or false value (with quotation marks) will be treated as Boolean type, and they are used for conditional statements. We will discuss Boolean type, and it's working in Python in detail later tutorial.