Python program to display ASCII value of the character
Python program to display ASCII value of the character
The full form of ASCII is American Standard Code for Information Interchange. This example explains a program in Python to find the ASCII value of any input character. ASCII is a character encoding standard that specifies a numerical value for all characters and symbols used in computers.
We can convert the ASCII value of any character by using an inbuilt function ord(). This function converts the given character and returns an integer representing the Unicode code of the character. For example, ord(‘b’) returns the integer 98.
Example:
Input: b Output: 98 Input: E Output: 69
Source Code
The following source code returns the ASCII value of the given character:
#Program to print ASCII value of a character
char = input("Enter a character: ")
#Print the ASCII value of character
print("The ASCII value of '" + char + "' is", ord(char))
Output
CASE 1:
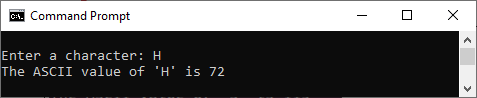
CASE 2:
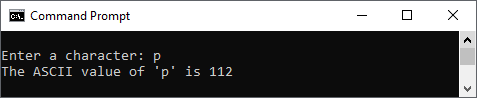
Explanation:
In this program, a user first asks to enter a character and store this character in a char variable. The ord() method will convert the characters and return their ASCII value. Finally, it prints the result on the screen using the print function.