Computer Memory
The computer memory is the storage space in the computer and related to the hardware integrated circuits. It can store the information for immediate use on the computer. The memory is a crucial element of the computer system. Memory and data storage can be measured in the megabyte, gigabyte, and terabyte. The computer cannot perform even a simple task without memory.
Mainly two types of memory exist in the computer system, which is given below:
1. Primary Memory / volatile memory.
2. Secondary Memory / non-volatile memory.
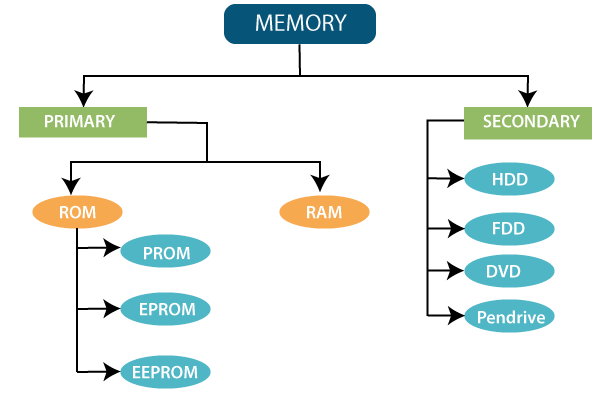
1. Primary memory/ Volatile memory
The volatile memory is the one which loses its content or data when the computer or hardware device shuts down suddenly. The primary memory is directly accessed by the central processing unit. Various types of memory exist in computer memory, such as cache memory, ROM, etc.
There are two types of primary memory which are given below:
RAM (random access memory)
ROM (read-only memory)
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Random-access memory is a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly. It consists of one or more memory modules that are used for temporary data storage. The RAM is generally located on the motherboard.
Random-access memory is the computing system, where the storage of data is actively using. The RAM (Random access memory) contains multiplexing and demultiplexing circuitry. The RAM is found in servers, PCs, tablets, smartphones, etc.
It is also divided into two parts:
SRAM (static random access memory)
DRAM (Dynamic random access memory)
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
The Static Random Access Memory is a semiconductor type Random access memory. It is faster and more expensive. The Static RAM is used for the CPU cache. It holds the data or information as long as the electric power is supplied.
It stores the bit of data or information on four transistors using two cross-coupled inverters. To access, transistors are used to manage the availability for the memory cell during reading and write operation.
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
The Dynamic Random Access Memory is used to store data or program code. It is a common type of memory used in personal computers, workstations, and servers.
The Dynamic RAM stores every bit of data into separate passive electronic component inside an integrated circuit board. The DRAM has one capacitor and one transistor per bit, but the Static Random Access Memory requires six transistors. Millions of capacitors and transistors can fit on a single memory chip in SRAM.
ROM (Read-only memory)
The data or information is pre-recorded in the Read-Only Memory. Once the data has been written onto the ROM chip, it cannot be removed. We can access that data at any time, and it is readable only. We are not able to write on ROM like RAM memory. The ROM is a non-volatile memory. There are four basic types of Read-only memory which are given below:
PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory)
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
Flash memory.
PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory)
The Programmable Read-Only Memory is the memory that can be modified once and read many times by the user according to the requirement. It is a memory chip, so once the data written onto the PROM, it remains there forever. To write the data onto PROM chip, we need a unique device which is known as PROM programmer or PROM burner.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
EPROM is a Programmable Read-Only Memory. This memory is erasable and re-usable according to the requirement. It is a non-volatile type of memory. The Dov Frohman develops the Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory in 1971 at Intel.
There is a transparent quartz crystal window at the top of this memory which allows the UV light to erase the data. The data or information on the EPROM memory can be deleted in a limited number of times.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
The EEPROM memory is integrated into microcontrollers for smart cards and remote keyless systems and other electronic devices to store a small amount of data or information. This memory has a limited life to erase and reprogramming of data or information. It is organized as the arrays of floating-gate transistors.
Flash memory
Flash memory is an Electrically Erasable Programming Read-Only Memory. It is non-volatile memory chips which are used to the storage and transfer the data or information between the personal computer and digital devices. The flash memory can be electronically programmed and erased.
2. Secondary memory/ Non-Volatile Memory
Secondary memory or non-volatile memory is the memory where programs and data or information is stored in the long term basis. There are two common storage devices: Hard disk and Optical disk. It is not connected directly to the processor. Secondary memory has a large capacity to store the data. It is slow in speed and cheap memory.
Hard disk
The hard disk is an electromechanical data storage device. It uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve digital information. The hard disk drive contains magnetic disk or platters rotating at high speed.
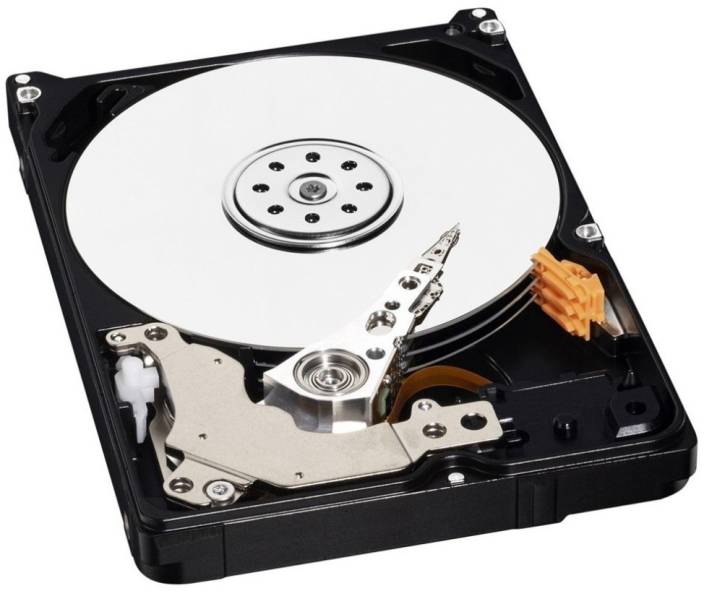

Figure: The Hard disk
It stores the data or information permanently. When the platters rotate the arm with the read/write head extends across the platters then, arm writes new data on the platters and read new information or data from them.
Structure of hard disk
The hard disk consists of several disks. There are three main parts of the hard drive which are given below:
Cylinder
The hard drive is divided into two tracks, and the tracks of all disks which have the same track value are known as a cylinder. The cylinder is the pile of tracks with the equal track value of the hard drive.
Head
The hard disk has two heads for reading or writing the data. One head is for the top, and the other head is used for the opposite side. The head value means the disk location and its side.
Sector
The track is composed of sectors on the hard disk. The number of tracks is the same on the hard drive. Sector is the minimal storage unit of the hard disk, and the size of one sector is always 512 bytes.
How can we store data in a hard disk?
The hard disk is the common storage which is used in the computer system. The stored data on the hard drive is in the form of 0s and 1s. The platter is the part of the hard disk that can store the data or information. The platters are the circular disk made of the non-magnetic material. The platters are further separated into the tracks and sectors.
Concept of trackers
The disk drive is the circular path on the surface of the disk on which the information or data is magnetically recorded. We can read the recorded information or data from the disk. The track is a physical division of data in the disk drive. The number of the track on the single surface in a drive is exactly equal to the number of cylinders in the drive. Cluster
The cluster is the group of sectors within the disk, and it is larger than the sector. The hard drive can easily find all the clusters on the disk because each cluster has its ID. Mainly the cluster is the group of servers.
Formatting of hard disk
The disk formatting is a process of preparing the hard disk drive to store the data. The formatting operation is created by one or more new file system in some cases. The process of generating the new file system is referred to as high-level formatting. Two levels of formatting hard disk drive are:
Low-level formatting
High-level formatting
Floppy disk
Floppy disk is also called the Floppy, diskette or simply disk and the storage type disk to store the data or information. It is thin and flexible magnetic storage medium which is sealed in the rectangular plastic enclosure lined with fabric that removes the dust particles.
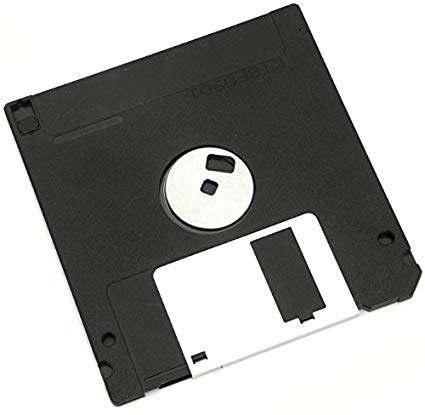

Figure: The Floppy disk
Compact disk (CD)
The compact disks are the small plastic disk which can store and retrieve the computer data or information. It replaces the floppy disk because the compact disk is faster and could hold more information or data.

Figure: The Compact disk
Pen drive
Pen drive is the storage device which is known as the secondary memory of the computer. It is inserted into the USB port of the computer system. The pen drive storage capacity range is from 8GB to 32GB and used to store graphics-heavy documents, photos, music files, and video clips.
The selected files can be transferred from the pen drive to any workstation. The pen drive is light weighted and micro characteristics which makes it possible to carry from one place to another. Today, mostly the pen drive has password encryption feature. The important information of family, medical records, photos can be backed up by these types of pen drives.

Figure: The Pen drive.
Zip disk
Zip disk is a small portable disk drive which is mainly used for backing up and archiving the files of the computer system. The zip drives come into two sizes, and the 100-megabyte size actually holds 100,431,872 bytes of data.
The zip drive can be bought in either the parallel or the small computer interface version. In the parallel version, the printer can be chained off the zip drive.

Figure: The Zip disk
Microdrive
IBM developed the microdrive in 1999. It is an extremely small hard disk that can fit in the compact card memory slot. The microdrive enables digital cameras which are design to use compact flash memory cards to gain larger storage capabilities.
The range of these drives is from 170MB to 8GB, and the compact flash memory replaces microdrives. When the microdrive released first, it was the smallest hard drive in the world.
These rotational media storage device designed to fit in the Compact flash type ll slots. Whether this drive is used to camera shooting or data storage is more than enough.

Figure: The Microdrive.
Memory stick
The memory stick is the storage media to the portable device. It’s a removable flash memory card format and developed by Sony in 1998. These memory sticks were available in the sizes up to 128MB. The original memory stick comes in the size and thickness of the chewing gum stick. It is available with and without the magic gate support.

Figure: The memory stick.
Smart cards
The smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit is a physical, electronic authorization device. It is used to control access to the resource. The smart card is the plastic credit card sized card with the embedded integrated circuit.
Some smart cards include the pattern of metal so that it can electrically connect with the internal chip. It can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. The smart cards are used as the transit passes and integrated ticketing by public transit operators. The smart cards provide strong security authentication for the single sign-in within the organization. The smartcard included a chip that can be either the microcontroller or embedded memory chip.

Figure: The smart card.
Online storage site
The online data storage refers to the storage of electronic data with the third-party service access by the internet. It is alternative to the traditional local storage such as disk, tape drives, etc. Online storage sites are portable, like optical media and flash drives.
Digital versatile disk (DVD)
The versatile digital disk is the optical disk storage medium similar to the compact disk. It can store the data with the enhanced data storage capacities as well as higher quality of videos and audio formats. The versatile digital disk is also known as the digital video disk.

Figure: The Digital versatile disk.
It has a large capacity, and its size starts with the 4.7GB. The polycarbonate plastic makes the layers in the versatile digital disk. It is categorized in various ways based on their applications. They are used for data reading only, and we cannot write the data on the DVD.