High-Level Language in Computer
High-Level Language
The high-level language is the programming language such as BASIC, C, C++, COBOL, FORTRAN, Java, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Visual Basic, and Pascal, etc. These languages have strong abstraction, the style and the context which are more comfortable to learn. It never needs the addressing of hardware constraints when developing a program.
The program of high-level language must be interpreted before the execution. The high-level language deal with the variables, arrays, objects, complex arithmetic or Boolean expression, subroutines and functions, loops, threads, locks, etc. The high-level languages are closer to human languages and far from machine languages. It is similar to human language, and the machine is not able to understand this language.
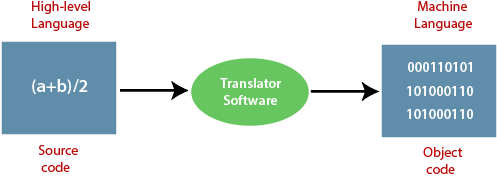
High-level languages are coders friendly, easy to code, debug, and maintain. These languages do not interact directly with the hardware. These languages are easy to implement. The software of translation plays an important role in the conversion of a high-level language to machine level language.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
Printf(“hello”);
getch();
return 0;
}
This is the example of C language, which is a middle-level language because it has the feature of both the low and high-level language. The human can understand this example easily, but the machine is not able to understand it without the translator. Every high-level language uses a different type of syntax.
Some languages are designed for writing desktop software programs, and other languages are used for web development.
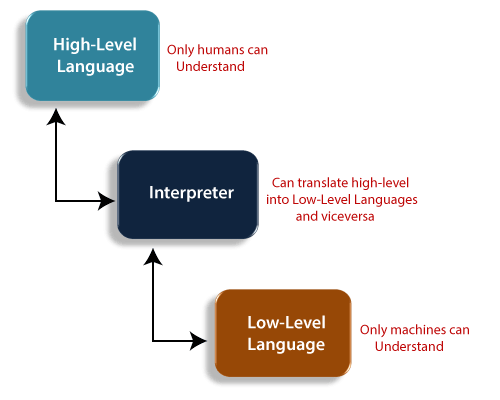
These all languages are considered as the high-level language because they must be processed with the help of a compiler or interpreter before the code execution. The source code is written in scripting languages like Perl and PHP can be run by the interpreter. These languages can convert the high-level code into binary code so that the machine can understand.
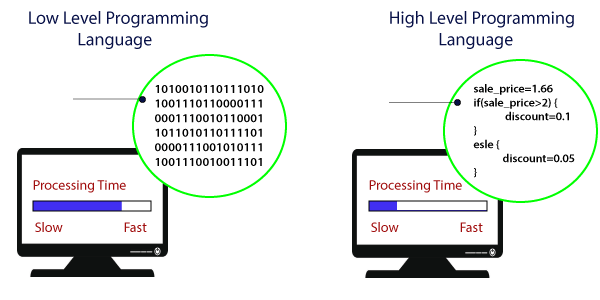
The advantage and disadvantage both exist in a high-level language. The slow processing time is the disadvantage of high-level language because the translator converts the program into binary language before the execution. The high-level language is close to the programmer and far away from the machine. We are explaining some high-level languages, which are given below:
1) FORTRAN
The name of this language indicates its meaning, which is "formula translation" because it was designed for the easy translation of math formulas into code. This language was published in 1957, and it is the first high-level programming language which is used for the scientific purpose.
The coders were able to write the programs 500% faster in high-level language as compared to low-level language. The efficiency was reduced by 20%, and this thing allowed the programmers to focus more on the problem-solving aspect of the problem.
2) COBOL
The full form of COBOL is "Common Business Oriented Language." It is developed in 1959 and used for the business and administrative purpose. When we save some data due to business purpose, and we compute that data after some time, then we require the COBOL language.
This language still used by the banks and other major companies which depends heavily on the accuracy and stability of their programs to keep their companies growing.
The COBOL language is divided into four parts:
- Identification Division.
- Environment Division.
- Data Division.
- Procedure Division.
3) BASIC
The BASIC language was the first language developed for the non-professional programmers. There is no need of any prerequisite to learn the BASIC language. The meaning of BASIC language is “Beginners all-purpose symbolic instruction code."
4) PASCAL
The PASCAL is the first programming language used for the teaching tool. It is a procedural programming language. This language supports structured programming and data structure.
5) SIMULA(OOPL)
The SIMULA was the first object-oriented programming language. It was developed in the 1960s. The first version of this language was developed as an extension of ALGOL, and the second version that is Simula67 was developed in 19.67. The main purpose of this language is to create computer simulations.
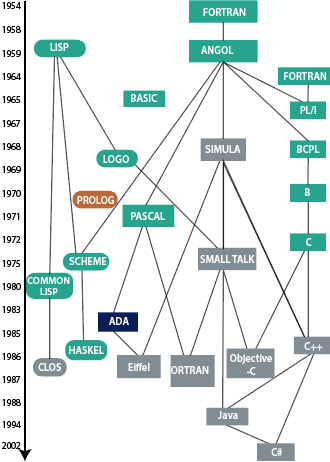
Fig. The Growth of various high-level languages.
The high-level languages are machine-independent. The programmers or coders do not require to know anything about the internal structure of the computer on which high-level language programs will be executed. Deal with high-level coders, enabling the programmers to write instructions using English word and familiar with the mathematical symbols and expressions.
Compiler
The compiler is the translator program software. This software can translate into its equivalent machine language program. The compiler compiles a set of machine language instructions for every program in a high-level language.

Linker
The linker is used for the large programs in which we can create some modules for the different task. When we call the module, the whole job is to link to that module and program is processed. We can use a linker for the huge software, storing all the lines of program code in a single source file.
Interpreter
The interpreter is the high-level language translator. It takes one statement of the high-level language program and translates it into machine level language instruction. Interpreter immediately executes the resulting machine language instruction. The compiler translates the entire source program into an object program, but the interpreter translates line by line.

Advantage of High-level language
- The high-level language is machine-independent.
- It is easier to learn and use.
- Few errors exist during the program development.
- The high-level language provides better documentation.
- It is easier to maintain.
The disadvantage of the high-level language
- The high-level language takes additional time to translate the source code to machine code.
- The programs of high-level language are comparatively slower than the programs of a low-level language.
- It cannot communicate directly with the hardware.
Limitations of the high-level language
- Less flexibility to control the computer's CPU, memory, and registers.
Fig. Learning high-level programming from the text.
Gaming software is the best example of learning high-level programming from the text. There are various game servers used in gaming Software. The high level of language always supports the portable code. The source code of high-level language is not designed to run on one type of machine — no need to acquire hardware knowledge for the creation of programs in the high-level language.